Rotation 1 Question 1
1. A circular disc of radius $b$ has a hole of radius $a$ at its centre (see figure). If the mass per unit area of the disc varies as $\frac{\sigma _0}{r}$, then the radius of gyration of the
 disc about its axis passing through the centre is (2019 Main, 12 April I)
disc about its axis passing through the centre is (2019 Main, 12 April I)
(a) $\sqrt{\frac{a^{2}+b^{2}+a b}{2}}$
(b) $\frac{a+b}{2}$
(c) $\sqrt{\frac{a^{2}+b^{2}+a b}{3}}$
(d) $\frac{a+b}{3}$
Show Answer
Answer:
Correct Answer: 1. (c)
Solution:
- Key Idea Radius of gyration $K$ of any structure is given by
$$ I=M K^{2} \text { or } K=\sqrt{\frac{I}{M}} $$
To find $K$, we need to find both moment of inertia I and mass $M$ of the given structure.
Given, variation in mass per unit area (surface mass density),
$$ \sigma=\frac{\sigma _0}{r} $$
Calculation of Mass of Disc
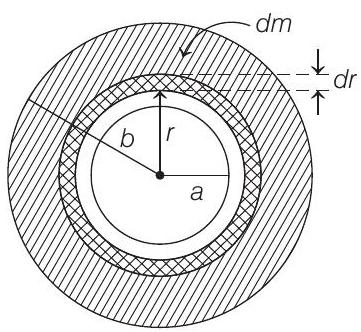
Let us divide whole disc in small area elements, one of them shown at $r$ distance from the centre of the disc with its width as $d r$.
Mass of this element is
$$ \begin{aligned} d m & =\sigma \cdot d A \\ \Rightarrow \quad d m & =\frac{\sigma _0}{r} \times 2 \pi r d r \quad \text { [from Eq. (i)] } \end{aligned} $$
Mass of the disc can be calculated by integrating it over the given limits of $r$,
$$ \begin{aligned} \quad \int _0^{M} d m & =\int _a^{b} \sigma _0 \times 2 \pi \times d r \\ M & =\sigma _0 2 \pi(b-a) \end{aligned} $$
Calculation of Moment of Inertia
$$ \begin{aligned} I=\int _0^{M} r^{2} d m & =\int _a^{b} r^{2} \cdot \frac{\sigma _0}{r} \times 2 \pi r d r=\sigma _0 2 \pi \int _a^{b} r^{2} d r=\sigma _0 2 \pi \frac{r}{3} _a^{b} \\ \Rightarrow \quad I & =\frac{1}{3} \sigma _0 2 \pi\left[b^{3}-a^{3}\right] \end{aligned} $$
Now, radius of gyration,
$$ \begin{aligned} K & =\sqrt{\frac{I}{M}}=\sqrt{\frac{\frac{2 \pi \sigma _0}{3}\left(b^{3}-a^{3}\right)}{2 \pi \sigma _0(b-a)}} \\ \Rightarrow \quad K & =\sqrt{\frac{1}{3} \frac{\left(b^{3}-a^{3}\right)}{b-a}} \end{aligned} $$
As we know, $b^{3}-a^{3}=(b-a)\left(b^{2}+a^{2}+a b\right)$
$$ \begin{array}{rlrl} & \therefore & K & =\sqrt{\frac{1}{3}\left(b^{2}+a^{2}+a b\right)} \\ \text { or } & K & =\sqrt{\frac{\left(a^{2}+b^{2}+a b\right)}{3}} \end{array} $$






