Differential Equations 1 Question 12
12. Let
(2015 Adv.)
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Show Answer
Answer:
Correct Answer: 12. (a, c)
Solution:
- Here,
On integrating both sides, we get
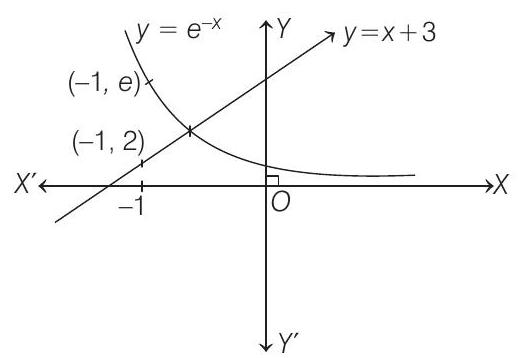
Clearly, the intersection point lies between






