current-electricity Question 28
Question: Q. 2. What is relaxation time ? Derive an expression for resistivity of a wire in terms of number density of free electrons and relaxation time.
A[SQP I 2017-18]
Show Answer
Solution:
Ans. Definition and Derivation.
[CBSE Marking Scheme, 2017]
Detailed answer :
(i) Relaxation time shows the effect of collisions among the electrons and ions or impurities on electrical conduction in a metal. It is the time taken for the drift velocity to decay
As drift velocity increases, relaxation time decreases since the electrons move the distance in which they frequently collide faster.
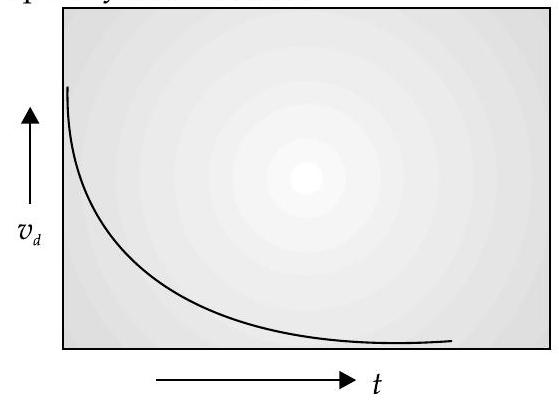
(ii) When a potential difference
The electric current through the conductor and drift speed are linked as
So,
At constant temperature :
Hence,
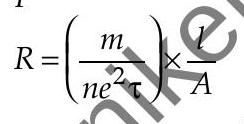
Comparing above expression with
where,






