Trigonometric - Trigonometric Functions (Lecture-01)
Trigonometrical ratios and Identities
1. An angle is positive, if it is measured in anti clockwise direction and is negative if it is measured in clock wise direction
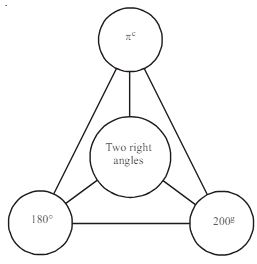
2. Angle in radian $=\dfrac{\text { length of the arc }}{\text { Radius of the circle }}$
$\text { i.e; } \theta=\dfrac{\ell}{\mathrm{r}}$
3.
| System of Measurement of Angles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Sexagesimal system $(\mathrm{D})$ | Centesimal system $(\mathrm{G})$ | Circular system $(\mathrm{C})$ |
| 1 right angle $=90^{\circ}(90$ degrees $)$ | 1 right angle $=100^{\circ}(100$ grades $)$ | 1 right angle $=\frac{\pi}{2}$ radians |
| $1^{\circ}=60^1(60$ minutes $)$ | $1^8=100^1(100$ minutes $)$ | $180^{\circ}=\pi$ |
| $1^1=60^{11}(60$ seconds $)$ | $1^1=100^{11}(100$ seconds $)$ |
Note: $\dfrac{\mathrm{D}}{90}=\dfrac{\mathrm{G}}{100}=\dfrac{2 \mathrm{C}}{\pi}$ OR (see the graph below)
4. Basic trigonometrical identities
(i) $\sin ^{2} \theta+\cos ^{2} \theta=1$
$\begin{aligned} & \Rightarrow \quad|\sin \theta| \leq 1 \text { and }|\cos \theta| \leq 1 \\ & \Rightarrow \quad-1 \leq \sin \theta \leq 1 \text { and }-1 \leq \cos \theta \leq 1 \end{aligned}$
(ii) $\sec ^{2} \theta-\tan ^{2} \theta=1$
$\begin{array}{ll} \Rightarrow & |\sec \theta| \geq 1 \\ \Rightarrow & \sec \theta \leq-1 \quad \text { or } \sec \theta \geq 1 \end{array}$
$\tan \theta$ may take any real value
(iii) $\operatorname{cosec}^{2} \theta-\cot ^{2} \theta=1$
$\Rightarrow|\operatorname{cosec} \theta| \geq 1$
$\Rightarrow \operatorname{cosec} \theta \leq-1 \quad$ or $\operatorname{cosec} \theta \geq 1$
$\cot \theta$ may take any real value.
5. Sign of Trigonometrical Ratio : To find the sign of a trigonometrical ratio, remember the sentence
| Add | Sugar | To | Coffee |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | S | T | C |
| 1stuadrant | 2nd quadrant | 3rd quadrant | 4th quadrant. |
Where A stands for all ratios are positive in 1 st quadrant
$\mathrm{S}$ stands for $\sin \&$ its reciprocal are positive in $2^{\text {nd }}$ quadrant
$T$ stands for tan & its reciprocal are positive in $3^{\text {rd }}$ quadrant
C stands for $\cos \&$ its reciprocal are positive in $4^{\text {rd }}$ quadrant
6. Domain & Range
| Function | Domain | Range |
|---|---|---|
| $\sin \theta$ | $R$ | $[-1,1]$ |
| $\cos \theta$ | $R$ | $[-1,1]$ |
| $\tan \theta$ | $R-\left\{(2 n+1) \dfrac{\pi}{2}, \mathrm{n} \in \mathrm{Z}\right\}$ | $\mathrm{R}$ |
| $\cot \theta$ | $\mathrm{R}-\{\mathrm{n} \pi, \mathrm{n} \in \mathrm{Z}\}$ | $\mathrm{R}$ |
| $\operatorname{cosec} \theta$ | $\mathrm{R}-\{\mathrm{n} \pi, \mathrm{n} \in \mathrm{Z}\}$ | $\mathrm{R}-(-1,1)$ |
| $\sec \theta$ | $\mathrm{R}-\left\{(2 \mathrm{n}+1) \dfrac{\pi}{2}, \mathrm{n} \in \mathrm{Z}\right\}$ | $\mathrm{R}-(-1,1)$ |
7. Trigonometric ratios in terms of each of the other
| $\sin \theta$ | $\cos \theta$ | $\tan \theta$ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| $\sin \theta$ | $\sin \theta$ | $\sqrt{1-\sin ^{2} \theta}$ | $\dfrac{\sin \theta}{\sqrt{1-\sin ^{2} \theta}}$ |
| $\cos \theta$ | $\sqrt{1-\sin ^{2} \theta}$ | $\cos \theta$ | $\dfrac{\sqrt{1-\cos ^{2} \theta}}{\cos \theta}$ |
| $\tan \theta$ | $\dfrac{\tan \theta}{\sqrt{1+\tan ^{2} \theta}}$ | $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1+\tan ^{2} \theta}}$ | $\tan \theta$ |
| $\operatorname{cosec} \theta$ | $\dfrac{1}{\operatorname{cosec} \theta}$ | $\dfrac{\sqrt{\operatorname{cosec}^{2} \theta-1}}{\operatorname{cosec}^{2}}$ | $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{\operatorname{cosec}^{2} \theta-1}}$ |
| $\sec \theta$ | $\dfrac{\sqrt{\sec ^{2} \theta-1}}{\sec \theta}$ | $\dfrac{1}{\sec \theta}$ | |
| $\cot \theta$ | $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1+\cot ^{2} \theta}}$ | $\dfrac{\cot \theta}{\sqrt{1+\cot ^{2} \theta}}$ | $\dfrac{1}{\cot ^{2} \theta-1}$ |
8. Sum and Difference formula.
(i) $\quad \sin (\mathrm{A} \pm \mathrm{B})=\sin \mathrm{A} \cos \mathrm{B} \pm \cos \mathrm{A} \sin \mathrm{B}$
(ii) $\quad \cos (\mathrm{A} \pm \mathrm{B})=\cos \mathrm{A} \cos \mathrm{B} \bar{\mp} \sin \mathrm{A} \sin \mathrm{B}$
(iii) $\tan (\mathrm{A} \pm \mathrm{B})=\dfrac{\tan \mathrm{A} \pm \tan \mathrm{B}}{1 \mp \tan \mathrm{A} \tan \mathrm{B}}$
(iv) $\tan \left(\dfrac{\pi}{4} \pm \mathrm{A}\right)=\dfrac{1 \pm \tan \mathrm{A}}{1 \mp \tan \mathrm{A}}$
(v) $\quad \cot (\mathrm{A} \pm \mathrm{B})=\dfrac{\cot \mathrm{A} \cot \mathrm{B} \mp 1}{\cot \mathrm{B} \pm \cot \mathrm{A}}$
(vi) $\sin (\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{B}) \sin (\mathrm{A}-\mathrm{B})=\sin ^{2} \mathrm{~A}-\sin ^{2} \mathrm{~B}=\cos ^{2} \mathrm{~B}-\cos ^{2} \mathrm{~A}$
(vii) $\quad \cos (\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{B}) \cos (\mathrm{A}-\mathrm{B})=\cos ^{2} \mathrm{~A}-\sin ^{2} \mathrm{~B}=\cos ^{2} \mathrm{~B}-\sin ^{2} \mathrm{~A}$
9. Multiple and half angles
(i) $\sin 2 \theta=\left\{\begin{array}{l}2 \sin \theta \cos \theta \\ \dfrac{2 \tan \theta}{1+\tan ^{2} \theta}\end{array}\right.$
Also, $\sqrt{1 \pm \sin 2 \theta}=|\cos \theta \pm \sin \theta|$
(ii) $\cos 2 \theta=\left\{\begin{array}{l}\cos ^{2} \theta-\sin ^{2} \theta \\ 2 \cos ^{2} \theta-1 \\ 1-2 \sin ^{2} \theta \\ \dfrac{1-\tan ^{2} \theta}{1+\tan ^{2} \theta}\end{array}\right.$
Also $1+\cos 2 \theta=2 \cos ^{2} \theta$
$1-\cos 2 \theta=2 \sin ^{2} \theta$
(iii) $\tan 2 \theta=\dfrac{2 \tan \theta}{1-\tan ^{2} \theta}$
Also $\dfrac{1-\cos 2 \theta}{\sin 2 \theta}=\tan \theta$
$\dfrac{1-\cos 2 \theta}{1+\cos 2 \theta}=\tan ^{2} \theta$
(iv) $\sin 3 \theta=\left\{\begin{array}{l}3 \sin \theta-4 \sin ^{3} \theta \\ 4 \sin \left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}-\theta\right) \sin \theta \sin \left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}+\theta\right)\end{array}\right.$
or $\sin ^{3} \theta=\dfrac{3 \sin \theta-\sin 3 \theta}{4}$
(v) $\quad \cos 3 \theta=\left\{\begin{array}{l}4 \cos ^{3} \theta-3 \cos \theta \\ 4 \cos \left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}-\theta\right) \cos \theta \cos \left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}+\theta\right)\end{array}\right.$
or $\cos ^{3} \theta=\dfrac{\cos 3 \theta+3 \cos \theta}{4}$
(vi) $\tan 3 \theta=\left\{\begin{array}{l}\dfrac{3 \tan \theta-\tan ^{3} \theta}{1-3 \tan ^{2} \theta} \\ \tan \left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}-\theta\right) \tan \theta \tan \left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}+\theta\right)\end{array}\right.$
10. Transformation formulae
(i) $\quad \sin \mathrm{C}+\sin \mathrm{D}=2 \sin \left(\dfrac{\mathrm{C}+\mathrm{D}}{2}\right) \cos \left(\dfrac{\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{D}}{2}\right)$
$\sin \mathrm{C}-\sin \mathrm{D}=2 \cos \left(\dfrac{\mathrm{C}+\mathrm{D}}{2}\right) \sin \left(\dfrac{\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{D}}{2}\right)$
$\cos \mathrm{C}+\cos \mathrm{D}=2 \cos \left(\dfrac{\mathrm{C}+\mathrm{D}}{2}\right) \cos \left(\dfrac{\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{D}}{2}\right)$
$\cos \mathrm{C}-\cos \mathrm{D}=-2 \sin \left(\dfrac{\mathrm{C}+\mathrm{D}}{2}\right) \sin \left(\dfrac{\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{D}}{2}\right)$
(ii) $\quad 2 \sin \mathrm{A} \cos \mathrm{B}=\sin (\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{B})+\sin (\mathrm{A}-\mathrm{B})$
$2 \cos A \sin B=\sin (A+B)-\sin (A-B)$
$2 \cos \mathrm{A} \cos \mathrm{B}=\cos (\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{B})+\cos (\mathrm{A}-\mathrm{B})$
$2 \sin A \sin B=\cos (A-B)-\cos (A+B)$
(ii) $\quad \tan \mathrm{A} _{ \pm} \tan \mathrm{B}=\dfrac{\sin (\mathrm{A} \pm \mathrm{B})}{\cos \mathrm{A} \cos \mathrm{B}}$
$\cot \mathrm{A} \pm \cot \mathrm{B}=\dfrac{\sin (\mathrm{B} \pm \mathrm{A})}{\sin \mathrm{A} \sin \mathrm{B}}$
(iv) $\quad \cot A-\tan A=2 \cot 2 \mathrm{~A}$
$\cot A+\tan A=2 \operatorname{cosec} 2 A=\dfrac{1}{\sin A \cos A}$
(v) $\quad 1 \pm \tan \mathrm{A} \tan \mathrm{B}=\dfrac{\cos (\mathrm{A} \mp \mathrm{B})}{\cos \mathrm{A} \cos \mathrm{B}}$
(vi) $\quad \cos \mathrm{A} \pm \sin \mathrm{A}=\sqrt{2} \sin \left(\dfrac{\pi}{4} \pm \mathrm{A}\right)=\sqrt{2} \cos \left(\dfrac{\pi}{4} \mp \mathrm{A}\right)$
11. Three angles
$\sin (A+B+C)=\cos A \cos B \cos C(\tan A+\tan B+\tan C-\tan A \tan B \tan C)$
$\cos (\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{B}+\mathrm{C})=\cos \mathrm{A} \cos \mathrm{B} \cos \mathrm{C}(1-\tan \mathrm{A} \tan \mathrm{B}-\tan B \tan \mathrm{C}-\tan C \tan \mathrm{A})$
$\tan (A+B+C)=\dfrac{\tan A+\tan B+\tan C-\tan A \tan B \tan C}{1-\tan A \tan B-\tan B \tan C-\tan C \tan A}$
12. Trigonometrical series
(i) $\quad \sin \mathrm{A}+\sin (\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{d})+\sin (\mathrm{A}+2 \mathrm{~d})+$ $+\sin (\mathrm{A}+(\mathrm{n}-1) \mathrm{d})=\dfrac{\sin \left(\mathrm{A}+\dfrac{(\mathrm{n}-1) \mathrm{d}}{2}\right) \sin \left(\dfrac{\mathrm{nd}}{2}\right)}{\sin \left(\dfrac{\mathrm{d}}{2}\right)}$
(ii) $\cos \mathrm{A}+\cos (\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{d})+\cos (\mathrm{A}+2 \mathrm{~d})+\ldots \ldots \ldots+\cos (\mathrm{A}+(\mathrm{n}-1) \mathrm{d})=\dfrac{\cos \left(\mathrm{A}+\dfrac{(\mathrm{n}-1) \mathrm{d}}{2}\right) \sin \left(\dfrac{\mathrm{nd}}{2}\right)}{\sin \left(\dfrac{\mathrm{d}}{2}\right)}$
(iii) $\cos \mathrm{A} \cdot \cos 2 \mathrm{~A} \cdot \cos 2^2 \mathrm{~A}$ ……………… $\cos 2^{\mathrm{n}-1} \mathrm{~A}=\dfrac{\sin \left(2^{\mathrm{n}} \mathrm{A}\right)}{2^{\mathrm{n}} \sin \mathrm{A}}$
(iv) $\quad(2 \cos \theta-1)(2 \cos 2 \theta-1)\left(2 \cos 2^{2} \theta-1\right) \ldots \ldots \ldots . .\left(2 \cos 2^{\mathrm{n}-1} \theta-1\right)=\dfrac{2 \cos 2^{\mathrm{n}} \theta+1}{2 \cos \theta+1} ; \mathrm{n} \in \mathrm{N}$
(v) $\tan \theta+2 \tan 2 \theta+2^{2} \tan 2^{2} \theta+2^{3} \tan 2^{3} \theta+\ldots \ldots \ldots . .+2^{\mathrm{n}} \tan 2^{\mathrm{n}} \theta+2^{\mathrm{n}+1} \cot 2^{\mathrm{n}+1} \theta=\cot \theta ; \forall \mathrm{n} \in \mathrm{N}$
(vi) $\sqrt{2+\sqrt{2+\sqrt{2+\ldots \ldots .+\sqrt{2+2 \cos 2^{\mathrm{n}} \theta}}}}=2 \cos \theta, \mathrm{n} \in \mathrm{N}$ where there are $\mathrm{n}$ square root signs on left hand side.
13. Greatest and least value of $\operatorname{asin} \theta \pm b \cos \theta$ is $\sqrt{a^{2}+b^{2}}$ and $-\sqrt{a^{2}+b^{2}}$ respectively
i.e. $-\sqrt{a^{2}+b^{2}} \leq \operatorname{asin} \theta \pm b \cos \theta \leq \sqrt{a^{2}+b^{2}}$
Also $\sin ^{2} \theta+\operatorname{cosec}^{2} \theta \geq 2$
$\cos ^{2} \theta+\sec ^{2} \theta \geq 2$
$\tan ^{2} \theta+\cot ^{2} \theta \geq 2$
14. Method of componendo and dividendo.
If $\dfrac{p}{q}=\dfrac{a}{b}$ then by componendo and dividendo we can write $\dfrac{p-q}{p+q}=\dfrac{a-b}{a+b}$ or $\dfrac{p+q}{p-q}=\dfrac{a+b}{a-b}$
Periodicity
All the six trigonometric functions are periodic $\sin \theta, \cos \theta, \operatorname{cosec} \theta, \sec \theta$ are periodic with period $2 \pi$ where $\tan \theta$ and $\cot \theta$ are period $\mathrm{c}$ with period $\pi$
Solved Examples
1. If $f(\theta)=\sin ^{4} \theta+\cos ^{4} \theta+1$, then the range of $f(\theta)$ is
(a) $\left[\dfrac{3}{2}, 2\right]$
(b) $\left[1, \dfrac{3}{2}\right]$
(c) $[1,2]$
(d) None of these
Show Answer
Solution:
$\begin{aligned} f(\theta) & =\left(\sin ^{2} \theta+\cos ^{2} \theta\right)^{2}-2 \sin ^{2} \theta \cos ^{2} \theta+1 \\ & =2-\dfrac{\sin ^{2} 2 \theta}{2} \end{aligned}$
$\therefore f(\theta) \min =2-\dfrac{1}{2}(1)=\dfrac{3}{2}$ and $f(\theta) \max =2-\dfrac{1}{2}(0)=2$
Answer: (a)
2. If $4 \mathrm{n} \alpha=\pi$, then the value of $\cot \alpha \cdot \cot 2 \alpha \cdot \cot 3 \alpha$ . $\cot (2 \mathrm{n}-1) \alpha$ is
(a) 1
(b) -1
(c) $\infty$
(d) None of these
Show Answer
Solution:
$\cot \alpha \cdot \cot (2 n-1) \alpha=\cot \alpha \cdot \cot (2 n \alpha-\alpha)=\cot \alpha \cdot \cot \left(\dfrac{\pi}{2}-\alpha\right)=\cot \alpha \cdot \tan \alpha=1$
Product of terms equidistant from the beginning and end is 1
The middle term is $\operatorname{cotn} \alpha=\cot \dfrac{\pi}{4}=1$
Given expression $=1.1 .1 \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots . . . . . . . . n$ times $=1$
Answer: (a)
3. If $\tan \dfrac{\alpha}{2}$ and $\tan \dfrac{\beta}{2}$ are roots of the equation $8 x^{2}-26 x+15=0$ then $\cos (\alpha+\beta)=$
(a) $-\dfrac{627}{725}$
(b) $\dfrac{627}{725}$
(c) 1
(d) None of these
Show Answer
Solution:
$\tan \left(\dfrac{\alpha}{2}+\dfrac{\beta}{2}\right)=\dfrac{\tan \dfrac{\alpha}{2}+\tan \dfrac{\beta}{2}}{1-\tan \dfrac{\alpha}{2} \tan \dfrac{\beta}{2}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{26}{8}}{1-\dfrac{15}{8}}=\dfrac{-26}{7}$
$\therefore \cos (\alpha+\beta)=\dfrac{1-\tan ^{2}\left(\dfrac{\alpha+\beta}{2}\right)}{1+\tan ^{2}\left(\dfrac{\alpha+\beta}{2}\right)}=\dfrac{1-\left(\dfrac{676}{49}\right)}{1+\left(\dfrac{676}{49}\right)}=\dfrac{-627}{725}$
Answer: (a)
4. If $\cos (x-y), \cos x, \cos (x+y)$ are in H.P, then $\left|\cos x \cdot \sec \dfrac{y}{2}\right|$ equals
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) $\sqrt{2}$
(d) None of these
Show Answer
Solution:
$\begin{aligned} & \cos x=\dfrac{2 \cos (x-y) \cos (x+y)}{\cos (x+y)+\cos (x-y)} \\ & \Rightarrow \quad \cos x=\dfrac{2\left(\cos ^{2} x-\sin ^{2} y\right)}{2 \cos x \cos y} \\ & 2 \cos ^{2} x \cos y=2 \cos ^{2} x-2 \sin ^{2} y \\ & 2 \sin ^{2} y=2 \cos ^{2} x(1-\cos y) \\ & 2\left(4 \sin ^{2} \dfrac{y}{2} \cos ^{2} \dfrac{y}{2}\right)=2 \cos ^{2} x \cdot\left(2 \sin ^{2} \dfrac{y}{2}\right) \\ & \Rightarrow \quad \dfrac{\cos ^{2} x}{\cos ^{2} \dfrac{y}{2}}=2 \Rightarrow \cos x \cdot \sec \dfrac{y}{2}= \pm \sqrt{2} \end{aligned}$
Answer: (c)
5. If $\tan \dfrac{\pi}{9}, x, \tan \dfrac{15 \pi}{18}$ are in A.P and $\tan \dfrac{\pi}{9}, y, \tan \dfrac{7 \pi}{18}$ are in A.P, then
(a) $2 x=y$
(b) $x=y$
(c) $x=2 y$
(d) None of these
Show Answer
Solution:
$2 \mathrm{x}=\tan 20^{\circ}+\tan 50^{\circ} \hspace {5 cm} 2 \mathrm{y}=\tan 20^{\circ}+\tan 70^{\circ}$
$2 \mathrm{x}=\dfrac{\sin 20^{\circ} \cdot \cos 50^{\circ}+\cos 20^{\circ} \cdot \sin 50^{\circ}}{\cos 20^{\circ} \cdot \cos 50^{\circ}}$ $\hspace {2.4 cm}$ $2 \mathrm{y}=\dfrac{\sin 20^{\circ} \cdot \cos 70^{\circ}+\cos 20^{\circ} \cdot \sin 70^{\circ}}{\cos 20^{\circ} \cdot \cos 70^{\circ}}$
$2 \mathrm{x}=\dfrac{\sin 70^{\circ}}{\cos 50^{\circ} \cdot \cos 20^{\circ}}$ $\hspace {5 cm}$ $2 \mathrm{y}=\dfrac{\sin 90^{\circ}}{\sin 20^{\circ} \cdot \cos 20^{\circ}}$
$2 \mathrm{x}=\dfrac{\cos 20^{\circ}}{\cos 50^{\circ} \cdot \cos 20^{\circ}}$
$\Rightarrow 2 \mathrm{x}=\dfrac{1}{\cos 50^{\circ}}=\dfrac{1}{\sin 40^{\circ}} \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots …..(1) \hspace {1.3 cm} 2 \mathrm{y}=\dfrac{2}{\sin 40^{\circ}}$ …………………..(2)
From (1) and (2)
$2 \mathrm{x}=\mathrm{y}$
Answer: (a)
6. The value of $\sin \dfrac{\pi}{n}+\sin \dfrac{3 \pi}{n}+\sin \dfrac{5 \pi}{n}+$. $\mathrm{n}$ terms is
(a) 1
(b) 0
(c) $\dfrac{\pi}{2}$
(d) None of these
Show Answer
Solution:
Given Series $=\dfrac{\sin \dfrac{n \pi}{2 n} \sin \left\{\dfrac{\dfrac{2 \cdot \pi}{n}+(n-1) \dfrac{.2 \pi}{n}}{2}\right\}}{\sin \dfrac{\pi}{2 n}}=\dfrac{\sin \dfrac{\pi}{n} \sin \left(\dfrac{\pi}{n}+\pi-\dfrac{\pi}{n}\right)}{\sin \dfrac{\pi}{2 n}}$
$=\dfrac{\sin \dfrac{\pi}{n} \cdot \sin \pi}{\sin \dfrac{\pi}{2 n}}=0$
Answer: (b)
7. $\sum\limits _{\mathrm{r}=1}^{\mathrm{n}-1} \cos ^{2} \dfrac{\mathrm{r} \pi}{\mathrm{n}}=$
(a) $\dfrac{\mathrm{n}}{2}$
(b) $\dfrac{\mathrm{n}}{2}-\dfrac{1}{2}$
(c) $\dfrac{\mathrm{n}}{2}-1$
(d) None of these
Show Answer
Solution:
$\sum\limits _{\mathrm{r}=1}^{\mathrm{n}-1} \cos ^{2} \dfrac{\mathrm{r} \pi}{\mathrm{n}}=\sum\limits _{\mathrm{r}=1}^{\mathrm{n}-1} \dfrac{1+\cos 2 \mathrm{r} \pi}{2}=\dfrac{1}{2} \sum\limits _{\mathrm{r}=1}^{\mathrm{n}-1} 1+\dfrac{1}{2} \sum\limits _{\mathrm{r}=1}^{\mathrm{n}-1} \dfrac{\cos 2 \mathrm{r} \pi}{\mathrm{n}}$
$=\dfrac{\mathrm{n}-1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\cos \dfrac{2 \pi}{\mathrm{n}}+\cos \dfrac{4 \pi}{\mathrm{n}}+\ldots \ldots \ldots+\cos 2 \dfrac{(\mathrm{n}-1) \pi}{\mathrm{n}}\right)$
$=\dfrac{n-1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{2} \cdot \dfrac{\sin \dfrac{2 \pi}{2 n} \cos \left\{\dfrac{\dfrac{2 \pi}{n}+\dfrac{2(n-1) \pi}{n}}{2}\right\}}{\sin \dfrac{\pi}{n}}$
$=\dfrac{\mathrm{n}-1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{2} \cdot \dfrac{\sin \dfrac{\pi}{\mathrm{n}} \cdot \cos \pi}{\sin \dfrac{\pi}{\mathrm{n}}}=\dfrac{\mathrm{n}-1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{\mathrm{n}}{2}-1$
Answer: (c)
Exercise
1. Let $\theta \in\left(0, \dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)$ and $\mathrm{t} _{1}=(\tan \theta)^{\tan \theta}, \mathrm{t} _{2}=(\tan \theta)^{\cot \theta}, \mathrm{t} _{3}=(\cot \theta)^{\tan \theta} \theta$ and $\mathrm{t} _{4}=(\cot \theta)^{\cot \theta}$, then
(a) $\mathrm{t} _{1}>\mathrm{t} _{2}>\mathrm{t} _{3}>\mathrm{t} _{4}$
(b) $\mathrm{t} _{4}>\mathrm{t} _{3}>\mathrm{t} _{1}>\mathrm{t} _{2}$
(c) $\mathrm{t} _{3}>\mathrm{t} _{1}>\mathrm{t} _{2}>\mathrm{t} _{4}$
(d) $t _{2}>t _{3}>t _{1}>t _{4}$
Show Answer
Answer: b2.* For a positive integer n, let $f _{\mathrm{n}}(\theta)=\left(\tan \dfrac{\theta}{2}\right)$
$(1+\sec \theta)(1+\sec 2 \theta)\left(1+\sec ^{2} \theta\right)$ $\left(1+\sec 2^{n} \theta\right)$, then
(a) $f _{2}\left(\dfrac{\pi}{16}\right)=1$
(b) $f _{3}\left(\dfrac{\pi}{32}\right)=1$
(c) $f _{4}\left(\dfrac{\pi}{64}\right)=1$
(d) $f _{5}\left(\dfrac{\pi}{128}\right)=1$
Show Answer
Answer: a, b, c3. Two rays are drawn through a point $\mathrm{A}$ at an angle $30^{\circ}$. A point $\mathrm{B}$ is taken on one of them at a distance ’ $\mathrm{a}$ ’ from the point $\mathrm{A}$. A perpendicular is drawn from the point $\mathrm{B}$ to the other ray, and another perpendicular is drawn from its foot to $\mathrm{AB}$ to meet $\mathrm{AB}$ at another point from where the similar process is repeated indefinitely. The length of the resulting infinite polygonal line is
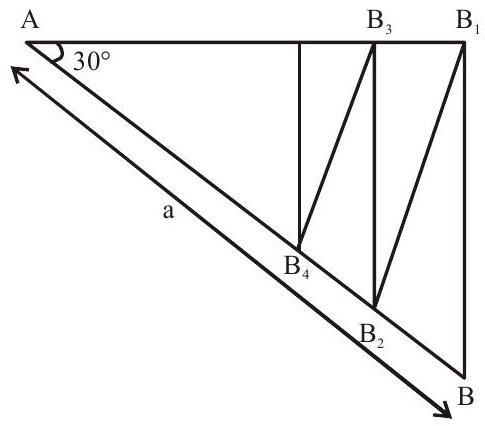
(a) $\mathrm{a}(2+\sqrt{3})$
(b) $\mathrm{a}(2-\sqrt{3})$
(c) a
(d) None of these
Show Answer
Answer: a4. If $\cos ^{6} \alpha+\sin ^{6} \alpha+\operatorname{ksin}^{2} 2 \alpha=1(0<\alpha<\pi / 2)$, then $k$ is
(a) $3 / 4$
(b) $1 / 4$
(c) $1 / 3$
(d) $1 / 8$
Show Answer
Answer: a5. In an acute angled triangle $A B C$, the least value of $\sec A+\sec B+\sec C$ is
(a) 6
(b) 8
(c) 3
(d) none of these
Show Answer
Answer: a6. The sum to infinite tems of the series $\cos \dfrac{\pi}{3}+\dfrac{1}{2} \cos \dfrac{2 \pi}{3}+\dfrac{1}{3} \cos \dfrac{3 \pi}{3}+\ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots .$. is
(a) 0
(b) 2
(c) 1
(d) 6
Show Answer
Answer: a7. If $\alpha=\dfrac{2 \pi}{7}$, then the value of $\tan \alpha \tan 2 \alpha+\tan 2 \alpha \tan 4 \alpha+\tan 4 \alpha \tan \alpha$ is
(a) 0
(b) -7
(c) $\dfrac{13}{4}$
(d) 2
Show Answer
Answer: b8. If $\sin (y+z-x), \sin (z+x-y) \sin (x+y-z)$ be is A.P., then $\tan x, \tan y, \tan z$ are in
(a) A.P.
(b) G.P
(c) H.P.
(d) None of these
Show Answer
Answer: a9.* $\dfrac{3+\cot 76^{\circ} \cot 16^{\circ}}{\cot 76^{\circ}+\cot 16^{\circ}}=$
(a) $\tan 16^{\circ}$
(b) $\cot 76^{\circ}$
(c) $\tan 46^{\circ}$
(d) $\cot 44^{\circ}$
Show Answer
Answer: c, d10. If $x \cos \alpha+y \sin \alpha=2 a, x \cos \beta+y \sin \beta=2 a$ and $2 \sin \dfrac{\alpha}{2} \sin \dfrac{\beta}{2}=1$, then
(a) $\cos \alpha+\cos \beta=\dfrac{2 a x}{x^{2}+y^{2}}$
(b) $\cos \alpha \cos \beta=\dfrac{2 \mathrm{a}^{2}-\mathrm{y}^{2}}{\mathrm{x}^{2}+\mathrm{y}^{2}}$
(c) $y^{2}=4 a(a-x)$
(d) $\cos \alpha+\cos \beta=2 \cos \alpha \cos \beta$
Show Answer
Answer: c11. Match the following:-
| Column I | Column II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | The maximum value of $\mathrm{y}=\cos (2 \mathrm{~A}+\theta)+\cos (2 \mathrm{~B}+\theta)$ where $\mathrm{A} \& \mathrm{~B}$ are constants is | (p) | $2 \sin (A+B)$ |
| (b) | The maximum value of $\mathrm{y}=\cos 2 \mathrm{~A}+\cos 2 \mathrm{~B}$ where $\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{B}$ is a constant $\& \mathrm{~A}, \mathrm{~B} \in\left(0, \dfrac{\pi}{2}\right)$ is | (q) | $2 \sec (A+B)$ |
| (c) | The minimum value of $\mathrm{y}=\sec 2 \mathrm{~A}+\sec 2 \mathrm{~B}$ where $\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{Bis}$ a constant \& $\mathrm{A}, \mathrm{B} \in\left(0, \dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)$ is | (r) | $2 \cos (A+B)$ |
| (d) | The minimum value of $y=\sqrt{\tan \theta+\cot \theta-2 \cos 2(A+B)}$ where $A, B$ are constants and $\theta \in\left(0, \dfrac{\pi}{2}\right)$ is | (s) | $2 \cos (A-B)$ |
Show Answer
Answer: $\mathrm{a} \rightarrow \mathrm{s} ; \mathrm{b} \rightarrow \mathrm{r} ; \mathrm{c} \rightarrow \mathrm{q} ; \mathrm{d} \rightarrow \mathrm{p}$12. Let $\mathrm{A} _{0} \mathrm{~A} _{1} \mathrm{~A} _{2} \mathrm{~A} _{3} \mathrm{~A} _{4} \mathrm{~A} _{5}$ be a regular hexagon inscribed in a circle of unit radius. Then the product of the lengths of the line segments $\mathrm{A} _{0} \mathrm{~A} _{1}, \mathrm{~A} _{0} \mathrm{~A} _{2}$ and $\mathrm{A} _{0} \mathrm{~A} _{4}$ is
(a) $\dfrac{3}{4}$
(b) $3 \sqrt{3}$
(c) 3
(d) $\dfrac{3 \sqrt{3}}{2}$
Show Answer
Answer: c13. If A, B, C, D are the smallest positive angles in ascending order of magnitude which have their sines equal to the positive quantity $\mathrm{k}$, then the value of
$4 \sin \dfrac{\mathrm{A}}{2}+3 \sin \dfrac{\mathrm{B}}{2}+2 \sin \dfrac{\mathrm{C}}{2}+\sin \dfrac{\mathrm{D}}{2}$ is
(a) $2 \sqrt{1-\mathrm{k}}$
(b) $2 \sqrt{1+\mathrm{k}}$
(c) $2 \sqrt{\mathrm{k}}$
(d) None of these
Show Answer
Answer: b14. Read the paragraph and answer the following questions .
If $\alpha, \beta, \gamma, \delta$ are the solutions of the equation $\tan \left(\theta+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)=3 \tan 3 \theta$, no two of which have equal tangents, then
(i) The value of $\tan \alpha+\tan \beta+\tan \gamma+\tan \delta$ is
(a) $1 / 3$
(b) $8 / 3$
(c) $-8 / 3$
(d) 0
(ii) The value of $\tan \alpha \tan \beta \tan \gamma \tan \delta$ is
(a) $-1 / 3$
(b) -2
(c) 0
(d) None of these
(iii) The value of $\dfrac{1}{\tan \alpha}+\dfrac{1}{\tan \beta}+\dfrac{1}{\tan \gamma}+\dfrac{1}{\tan \delta}$ is
(a) -8
(b) 8
(c) $2 / 3$
(d) $1 / 3$
Show Answer
Answer: (i) d (ii) a (iii) b15.* Which of the following is / are correct?
(a) $(\tan x)^{\log _{c}(\sin x)}>(\cot x)^{\log _{c}(\sin x)} \hspace {2 cm}, \forall x \in(0, \pi / 4)$
(b) $4^{\log _{c}(\operatorname{cosec} x)}<5^{\log _{c}(\operatorname{cosec} x)}$ $\hspace {3 cm}$ $,\forall \mathrm{x} \in(0, \pi / 2)$
(c) $\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^{\log _{c}(\cos x)}<\left(\dfrac{1}{3}\right)^{\log _{c}(\cos x)}$ $\hspace {2.4 cm}$,$\forall \mathrm{x} \in(0, \pi / 2)$
(d) $2^{\log _{e}(\tan x)}<2^{\log _{e}(\sin x)}$ $\hspace {3.5 cm}$,$\forall \mathrm{x} \in(0, \pi / 2)$










