Chapter 08 Heredity Exercise
EXERCISSES
1. A Mendelian experiment consisted of breeding tall pea plants bearing violet flowers with short pea plants bearing white flowers. The progeny all bore violet flowers, but almost half of them were short. This suggests that the genetic make-up of the tall parent can be depicted as
(a) TTWW
(b) TTww
(c) TtWW
(d) TtWw
Show Answer
Answer
(c) The genetic make-up of the tall parent can be depicted as TtWW
Since all the progeny bore violet flowers, it means that the tall plant having violet flowers has WW genotype for violet flower colour.
Since the progeny is both tall and short, the parent plant was not a pure tall plant. Its genotype must be Tt.
Therefore, the cross involved in the given question is
Therefore, half the progeny is tall, but all of them have violet flowers.
2. A study found that children with light-coloured eyes are likely to have parents with light-coloured eyes. On this basis, can we say anything about whether the light eye colour trait is dominant or recessive? Why or why not?
Show Answer
Answer
Let us assume that children with light-coloured eyes can either have LL or Ll or ll genotype. If the children have LL genotype, then their parents will also be of LL genotype.

LL
If the children with light-coloured eyes have
ll
Therefore, it cannot be concluded whether light eye colour is dominant or recessive.
3. Outline a project which aims to find the dominant coat colour in dogs.
Show Answer
Answer
Dogs have a variety of genes that govern coat colour. There are at least eleven identified gene series (A, B, C, D, E, F, G, M, P, S, T) that influence coat colour in dog.
A dog inherits one gene from each of its parents. The dominant gene gets expressed in the phenotype. For example, in the B series, a dog can be genetically black or brown.
Let us assume that one parent is homozygous black (BB), while the other parent is homozygous brown (bb)
bb BB
B B
In this case, all the offsprings will be heterozygous (Bb).
Since black (B) is dominant, all the offsprings will be black. However, they will have both B and
If such heterozygous pups are crossed, they will produce 25% homozygous black (BB),
B b
4. How is the equal genetic contribution of male and female parents ensured in the progeny?
Show Answer
Answer
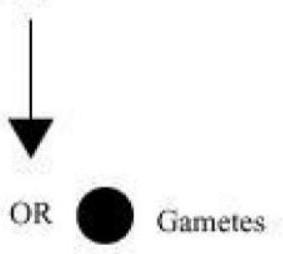
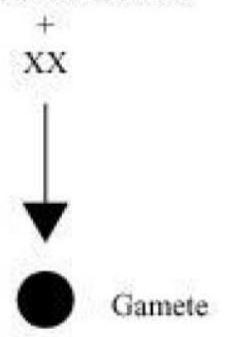
In human beings, every somatic cell of the body contains 23 pairs of chromosomes. Out of these 23 pairs, the first 22 pairs are known as autosomes and the remaining one pair is known as sex chromosomes represented as
Females have two X chromosomes and males have one X and one Y chromosome.
The gamete receives half of the chromosomes. Therefore, the male gametes have 22 autosomes and either
The female gamete, on the other hand, has 22 autosomes and X chromosome.
During reproduction, the male and female gametes fuse and thus the progeny receives 22 autosomes and one

Father 22 pairs of autosomes
XY

Mother
22 pairs of autosomes
Gamete

22 pairs of autosomes OR 22 pairs of autosomes
XY










