Chapter 07 Motion Exercise
Exercises

1. An athlete completes one round of a circular track of diameter
Show Answer
Answer
Diameter of circular track (D)
Radius of circular track
Time taken by the athlete for one round
Distance covered by athlete in one round
Speed of the athlete
Therefore, Distance covered in
Number of round in
Number of round in
After taking start from position
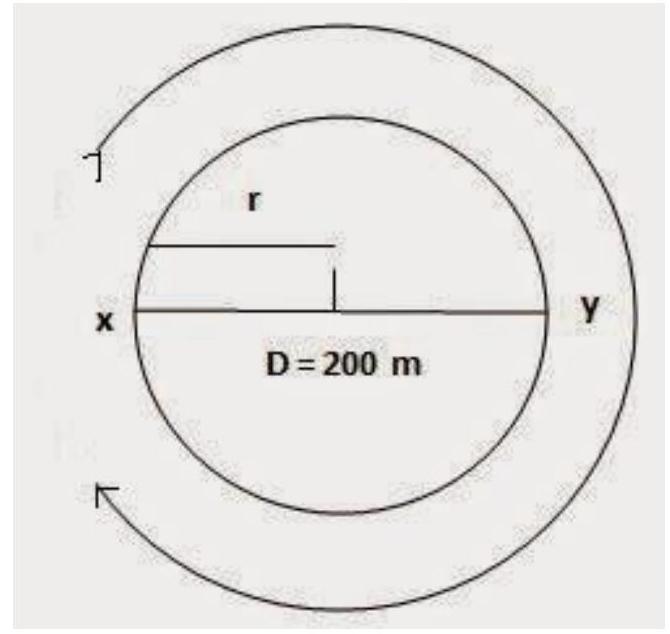
Hence, Displacement of the athlete with respect to initial position at
2. Joseph jogs from one end A to the other end B of a straight
Show Answer
Answer
Total Distance covered from
Total time taken
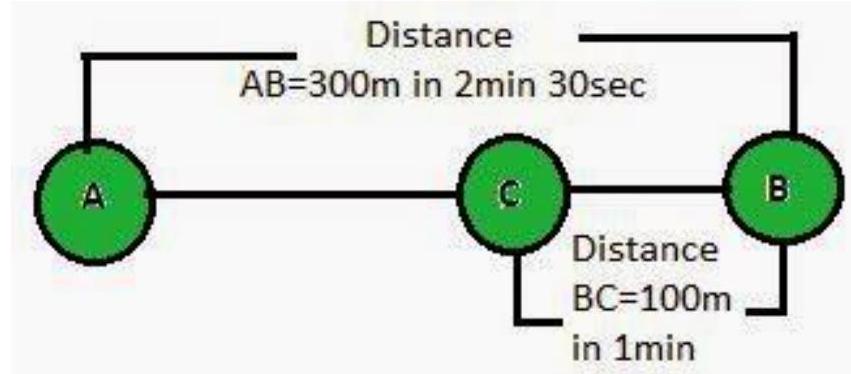
Therefore, Average Speed from AB = Total Distance / Total Time
Therefore, Velocity from AB =Displacement AB
Total Distance covered from
Total time taken from A to C = Time taken for AB + Time taken for BC
Therefore, Average Speed from AC = Total Distance /Total Time
Displacement (S) from
Time (t) taken for displacement from AC
Therefore, Velocity from AC = Displacement (s) / Time (t)
3. Abdul, while driving to school, computes the average speed for his trip to be
Show Answer
Answer
The distance Abdul commutes while driving from Home to School
4. A motorboat starting from rest on a lake accelerates in a straight line at a constant rate of
Show Answer
Answer
Given Initial velocity of motorboat,
Acceleration of motorboat,
Time under consideration,
We know that Distance,
Therefore, The distance travel by motorboat
5. A driver of a car travelling at
Show Answer
missing6. Fig 7.10 shows the distance-time graph of three objects A,B and
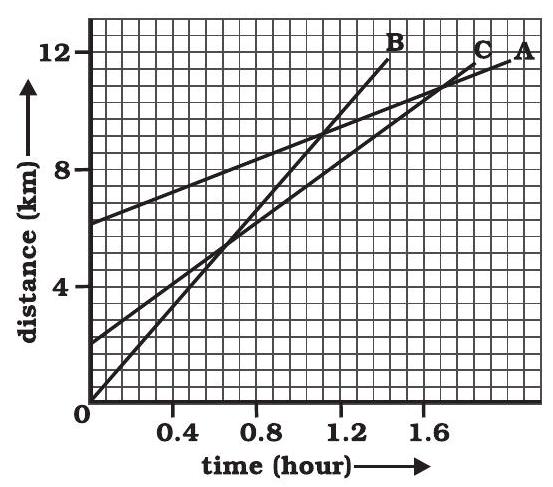
Fig. 7.10
(a) Which of the three is travelling the fastest?
(b) Are all three ever at the same point on the road?
(c) How far has C travelled when B passes A?
(d) How far has B travelled by the time it passes C?
Show Answer
Answer
(a) Object B
(b) No
(c)
(d)
(a) Speed
Slope of graph
Therefore, Speed = slope of the graph
Since slope of object B is greater than objects A and C, it is travelling the fastest.
(b) All three objects A, B and C never meet at a single point. Thus, they were never at the same point on road.
(c)
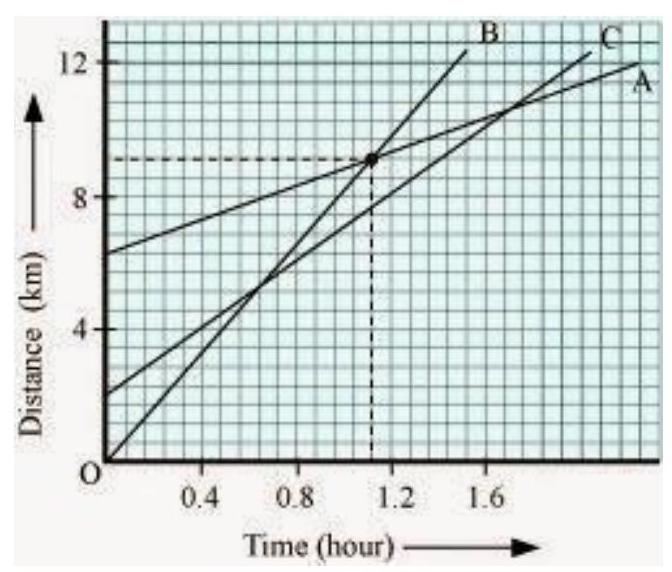
Since there are 7 unit areas of the graph between 0 and 4 on the Y axis, 1 graph unit equals
Since the initial point of an object C is 4 graph units away from the origin, Its initial distance from the origin is
When B passes A, the distance between the origin and C is
Therefore, total distance travelled by C in this time =
(d) The distance that object B has covered at the point where it passes C is equal to 9 graph units.
Therefore, total distance travelled by B when it crosses C =
7. A ball is gently dropped from a height of
Show Answer
Answer
Let us assume, the final velocity with which ball will strike the ground be ’
Distance or height of fall,
Downward acceleration,
As we know,
8. The speed-time graph for a car is shown is Fig. 7.11.
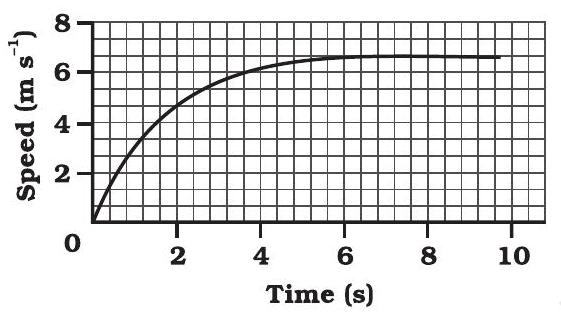
Fig. 7.11
(a) Find how far does the car travel in the first 4 seconds. Shade the area on the graph that represents the distance travelled by the car during the period.
(b) Which part of the graph represents uniform motion of the car?
Show Answer
Answer
(a)
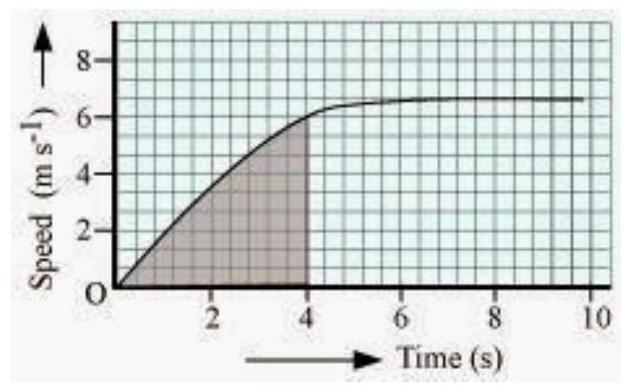
The shaded area which is equal to
(b)
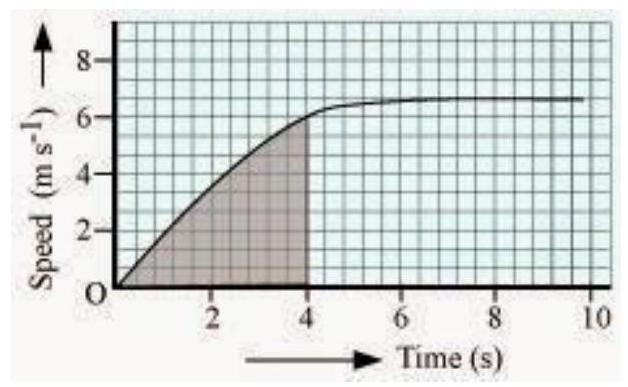
The part of the graph in red colour between time
9. State which of the following situations are possible and give an example for each of these:
(a) an object with a constant acceleration but with zero velocity
(b) an object moving with an acceleration but with uniform speed.
(c) an object moving in a certain direction with an acceleration in the perpendicular direction.
Show Answer
Answer
(a) It is possible; an object thrown up into the air has a constant acceleration due to gravity acting on it. However, when it reaches its maximum height, its velocity is zero.
(b) It is possible; acceleration implies an increase or decrease in speed, and uniform speed implies that the speed does not change over time
Circular motion is an example of an object moving with acceleration but with uniform speed.
An object moving in a circular path with uniform speed is still under acceleration because the velocity changes due to continuous changes in the direction of motion.
(c) It is possible; for an object accelerating in a circular trajectory, the acceleration is perpendicular to the direction followed by the object.
10. An artificial satellite is moving in a circular orbit of radius
Show Answer
Answer
Radius of the circular orbit,
Time taken to revolve around the earth,
Speed of a circular moving object,










