Chapter 06 Lines And Angles Exercise-02
EXERCISE 6.2
1. In Fig. 6.23, if $\mathrm{AB}||\mathrm{CD}, \mathrm{CD}|| \mathrm{EF}$ and $y: z=3: 7$, find $x$.
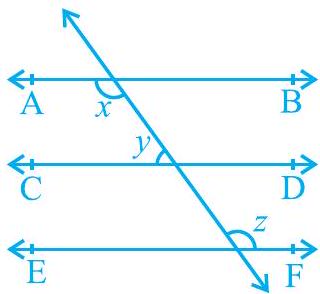
Fig. 6.23
Show Answer
Solution
It is given that $A B | C D$ and $C D | E F$
$\therefore A B | C D|| E F$ (Lines parallel to the same line are parallel to each other) It can be observed that $x=z$
(Alternate interior angles) … (1)
It is given that $y: z=3: 7$
Let the common ratio between $y$ and $z$ be $a$. $\therefore$
$y=3 a$ and $z=7 a$
Also, $x+y=180^{\circ}$ (Co-interior angles on the same side of the transversal) $z$
$+y=180^{\circ}$ [Using equation (1)]
$7 a+3 a=180^{\circ}$
$10 a=180^{\circ} a=$
$18^{\circ} \therefore x=7 a=7 \times 18^{\circ}=$
2. In Fig. 6.24, if $\mathrm{AB} || \mathrm{CD}, \mathrm{EF} \perp \mathrm{CD}$ and $\angle \mathrm{GED}=126^{\circ}$, find $\angle \mathrm{AGE}, \angle \mathrm{GEF}$ and $\angle \mathrm{FGE}$.
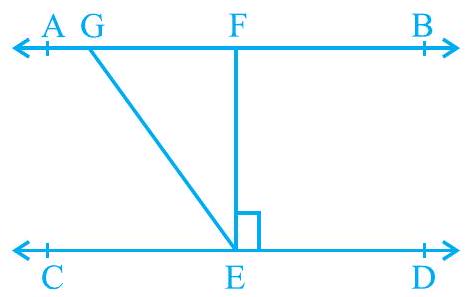
Fig. 6.24
Show Answer
Solution
It is given that, $A B | C D$
EF CD
$\therefore GED=126^{\circ}$
$\therefore \therefore$ GEF $+\therefore F E D=1260$
$\therefore \quad GEF+90^{\circ}=126^{\circ}$
$\therefore \therefore \quad GEF=36^{\circ}$
$\therefore \quad$ AGE and GED are alternate interior angles.
$\therefore \quad \therefore \quad$ AGE $=$ GED $=126^{\circ}$
Howềver, $AGÉ+FGE=180^{\circ}$ (Linear pair)
$\therefore \quad 1260^{\circ}+FGE=180^{\circ}$
$\therefore \quad \therefore \quad FGE=180^{\circ}-126^{\circ}=54^{\circ}$
$AGE=126^{\circ}, \therefore GEF=36^{\circ}, \therefore FGE=54^{\circ}$
3. In Fig. 6.25, if $\mathrm{PQ} || \mathrm{ST}, \angle \mathrm{PQR}=110^{\circ}$ and $\angle \mathrm{RST}=130^{\circ}$, find $\angle \mathrm{QRS}$.
[Hint : Draw a line parallel to ST through point R.]
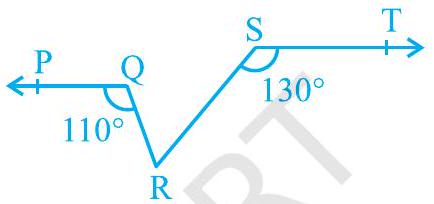
Fig. 6.25
Show Answer
Solution
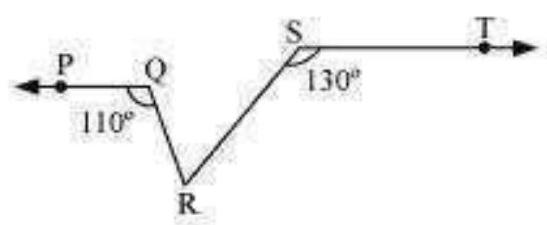
Let us draw a line XY parallel to ST and passing through point $R$. $\therefore PQR+QRX=180^{\circ}$ (Co-interior angles on the same side of transversal QR)
$\therefore 110^{\circ}+Q R X=180^{\circ}$
$\therefore QRX=70^{\circ}$
Also,
$\therefore RST+\therefore$ SRY $=180^{\circ}$ (Co-interior angles on the same side of transversal SR) $0+S R Y=180^{\circ} 130$
$\therefore SRY=50^{\circ}$
$XY$ is a straight line. RQ and RS stand on it.
$\therefore \therefore QRX+\therefore QRS+\therefore SRY=180^{\circ} \circ+QRS+50^{\circ}=180^{\circ} 70$
$QRS=180^{\circ}-120^{\circ}=60^{\circ}$
$\therefore$
4. In Fig. 6.26, if $\mathrm{AB} || \mathrm{CD}, \angle \mathrm{APQ}=50^{\circ}$ and $\angle \mathrm{PRD}=127^{\circ}$, find $x$ and $y$.
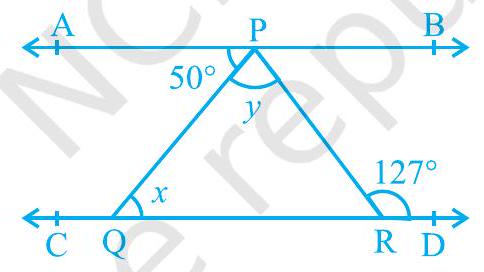
Fig. 6.26
Show Answer
Solution
$\therefore APR=\therefore PRD$ (Alternate interior angles) In the given figure, if $AB | CD, APQ=50^{\circ}$ and $\therefore$ $P R D=1270$, find $x$ and $y$.
$50^{\circ}+y=127^{\circ} y=$
$127^{\circ}-50^{\circ} y=$
770
Also, $A P Q=P Q R$ (Alternate interior angles)
$50^{\circ}=x \quad x=50^{\circ}$ and $y=770$
5. In Fig. 6.27, PQ and RS are two mirrors placed parallel to each other. An incident ray $\mathrm{AB}$ strikes the mirror $\mathrm{PQ}$ at $\mathrm{B}$, the reflected ray moves along the path $\mathrm{BC}$ and strikes the mirror $\mathrm{RS}$ at $\mathrm{C}$ and again reflects back along $\mathrm{CD}$. Prove that $\mathrm{AB} || \mathrm{CD}$.
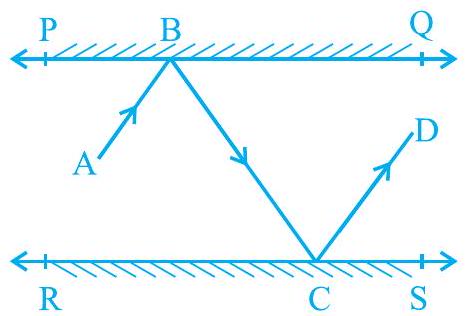
Fig. 6.27
Show Answer
Solution
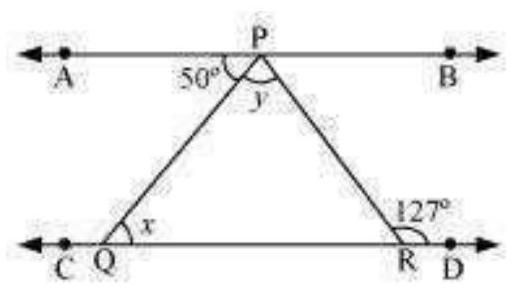
Let us draw $BM \therefore PQ$ and $CN \therefore RS$.
As PQ || RS,
Therefore, BM || CN
Thus, $BM$ and $CN$ are two parallel lines and a transversal line $BC$ cuts them at $B$ and
C respectively.
$\therefore A=3$ (Alternate interior angles) 2
However, $1=2$ and $3=* 4$ (By"laws of reflection)
$\therefore 1=2 \doteq 3=4$
Also, $\dot{1}+2 \stackrel{\dot{\circ}}{=} 3+\dot{4}$
$\therefore ABC=\ddot{DCB}$
However, these are alternate interior angles. :
$A B|| C D$










