Rotation 2 Question 12
12. A mass $m$ is moving with a constant velocity along a line parallel to the $X$-axis, away from the origin. Its angular momentum with respect to the origin
(1997C, 1M)
(a) is zero
(b) remains constant
(c) goes on increasing
(d) goes on decreasing
Show Answer
Answer:
Correct Answer: 12. (b)
Solution:
- $|\mathbf{v}|=v=$ constant and $|\mathbf{r}|=r$ (say)
Angular momentum of the particle about origin $O$ will be given by
$$ \begin{array}{ll} & \mathbf{L}=\mathbf{r} \times \mathbf{p}=m(\mathbf{r} \times \mathbf{v}) \\ \text { or } \quad & |\mathbf{L}|=L=m r v \sin \theta=m v(r \sin \theta)=m v h \end{array} $$
Now, $m, v$ and $h$ all are constants.
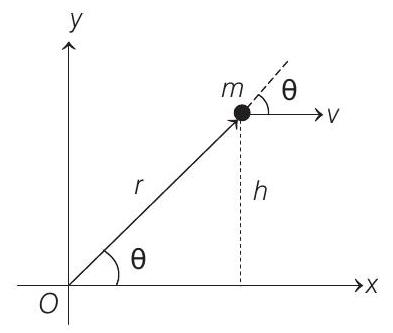
Therefore, angular momentum of particle about origin will remain constant. The direction of $\mathbf{r} \times \mathbf{v}$ also remains the same (negative $z$ ).
NOTE Angular momentum of a particle moving with constant velocity about any point is always constant. e.g. Angular momentum of the particle shown in figure about origin $O$ will be
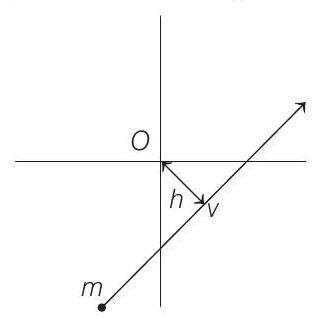
$L=m v h=$ constant






