Heat and Thermodynamics 5 Question 54
55. One mole of a monoatomic ideal $p$ gas is taken through the cycle shown in figure $(1993,4+4+2 M)$ $A \rightarrow B$ : adiabatic expansion
$B \rightarrow C$ : cooling at constant volume
$C \rightarrow D$ : adiabatic compression
$D \rightarrow A$ : heating at constant volume.
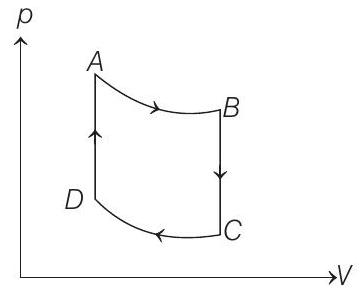
The pressure and temperature at $A, B$, etc., are denoted by $p _A, T _A, p _B, T _B$ etc., respectively. Given that, $T _A=1000 K, p _B=(2 / 3) p _A$ and $p _C=(1 / 3) p _A$, calculate the following quantities
(a) The work done by the gas in the process $A \rightarrow B$.
(b) The heat lost by the gas in the process $B \rightarrow C$.
(c) The temperature $T _D$. (Given : $\left.(2 / 3)^{2 / 5}=0.85\right)$
Show Answer
Answer:
Correct Answer: 55. (a) $1869.75 J$ (b) $5297.6 J$ (c) $500 K$
Solution:
- Given, $T _A=1000 K, p _B=\frac{2}{3} p _A, p _C=\frac{1}{3} p _A$
Number of moles, $n=1, \gamma=\frac{C _p}{C _V}=\frac{5}{3}$ (monoatomic) (a) $A \rightarrow B$ is an adiabatic process, therefore
$$ p _A^{1-\gamma} T _A^{\gamma}=p _B^{1-\gamma} T _B^{\gamma} $$
$\therefore \quad T _B=T _A\left(\frac{p _A}{p _B}\right)^{\frac{1-\gamma}{\gamma}}$
$=(1000)\left(\frac{3}{2}\right)^{\frac{1-5 / 3}{5 / 3}}=(1000)\left(\frac{3}{2}\right)^{-2 / 5}$
$=(1000)\left(\frac{2}{3}\right)^{2 / 5}$
$T _B=(1000)(0.85)$
$\therefore \quad T _B=850 K$
Now, work done in the process $A \rightarrow B$ will be
$$ \begin{aligned} & W _{A B}=\frac{R}{1-\gamma}\left(T _B-T _A\right) \\ = & \frac{8.31}{1-5 / 3}(850-1000) \text { or } W _{A B}=1869.75 J \end{aligned} $$
(b) $B \rightarrow C$ is an isochoric process $(V=$ constant $)$
$$ \begin{aligned} \therefore \quad \frac{T _B}{T _C} & =\frac{p _B}{p _C} \\ \therefore \quad T _C & =\left(\frac{p _C}{p _B}\right) T _B \\ & =\left(\frac{(1 / 3) p _A}{(2 / 3) p _A}\right) 850 K \\ T _C & =425 K \end{aligned} $$
Therefore, $Q _{B C}=n C _V \Delta T=(1)\left(\frac{3}{2} R\right)\left(T _C-T _B\right)$
$$ \begin{aligned} & =\left(\frac{3}{2}\right)(8.31)(425-850) \\ Q _{B C} & =-5297.6 J \end{aligned} $$
Therefore, heat lost in the process $B C$ is $5297.6 J$.
(c) $C \rightarrow D$ and $A \rightarrow B$ are adiabatic processes. Therefore,
$$ \begin{aligned} p _C^{1-\gamma} T _C^{\gamma}=p _D^{1-\gamma} T _D^{\gamma} & \Rightarrow \frac{p _C}{p _D}=\left(\frac{T _D}{T _C}\right)^{\frac{\gamma}{1-\gamma}} \\ p _A^{1-\gamma} T _A^{\gamma} & =p _B^{1-\gamma} T _B^{\gamma} \\ \Rightarrow \quad \frac{p _A}{p _B} & =\left(\frac{T _B}{T _A}\right)^{\frac{\gamma}{1-\gamma}} \end{aligned} $$
Multiplying Eqs. (i) and (ii), we get
$$ \frac{p _C p _A}{p _D p _B}=\left(\frac{T _D T _B}{T _C T _A}\right)^{\frac{\gamma}{1-\gamma}} $$
Processes $B \rightarrow C$ and $D \rightarrow A$ are isochoric. $(V=$ constant $)$
Therefore, $\frac{p _C}{p _B}=\frac{T _C}{T _B}$ and $\frac{p _A}{p _D}=\frac{T _A}{T _D}$
Multiplying these two equations, we get
$$ \frac{p _C p _A}{p _D p _B}=\frac{T _C T _A}{T _B T _D} $$
From Eqs. (iii) and (iv), we have
$$ \begin{array}{rlrl} & & \left(\frac{T _D T _B}{T _C T _A}\right)^{\frac{\gamma}{1-\gamma}} & =\left(\frac{T _C T _A}{T _B T _D}\right) \\ \text { or } & \left(\frac{T _C T _A}{T _D T _B}\right)^{\frac{1-\gamma}{\gamma}} & =\left(\frac{T _C T _A}{T _B T _D}\right) \\ \Rightarrow & \frac{T _C T _A}{T _D T _B} & =1 \\ \text { or } & T _D=\frac{T _C T _A}{T _B} & =\frac{(425)(1000)}{850} \\ \text { or } & T _D & =500 K \end{array} $$






