Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current 2 Question 10
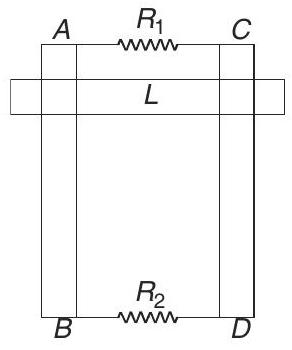
11. Two parallel vertical metallic rails
There is a uniform horizontal magnetic field of
Show Answer
Answer:
Correct Answer: 11.
Solution:
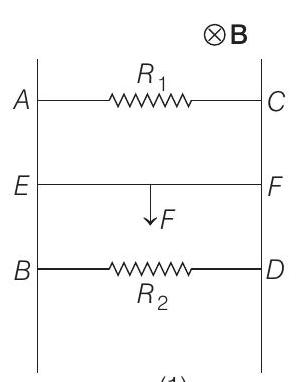
- Let the magnetic field be perpendicular to the plane of rails and inwards
Power dissipated in
Therefore
Similarly,
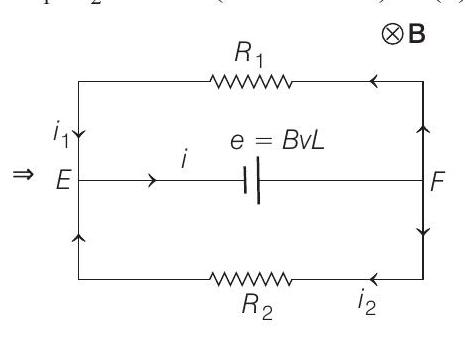
Now, the total current in bar
(from
(1)
(2)
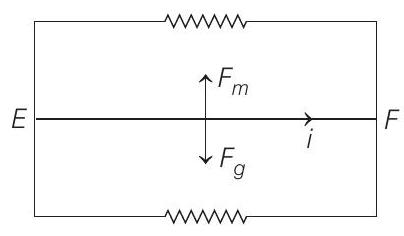
Under equilibrium condition, magnetic force
i.e.
From Eq. (vi)
or
Multiplying Eq. (v) by
Hence, terminal velocity of bar is
Power in






