Current Electricity 2 Question 5
5. In the circuit shown, the potential difference between $A$ and $B$ is
(2019 Main, 11 Jan II)

(a) $3 V$
(b) $1 V$
(c) $6 V$
(d) $2 V$
Show Answer
Solution:
- In the given circuit, let’s assume currents in the arms are $i _1, i _2$ and $i _3$, respectively.
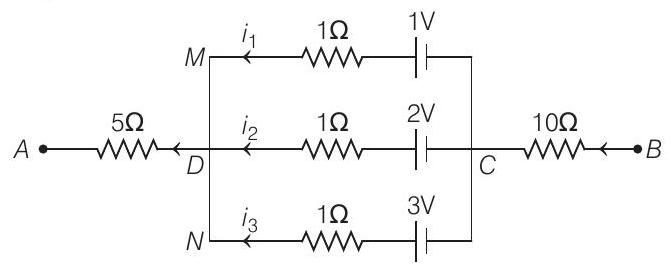
Now, $\quad i _1=\frac{V _1}{R _1}=\frac{1}{1}=1 A$
Similarly, $\quad i _2=\frac{2}{1}=2 A$
and $\quad i _3=\frac{3}{1}=3 A$
Total current in the $\operatorname{arm} D A$ is
$$ i=i _1+i _2+i _3=6 A $$
As all three resistors between $D$ and $C$ are in parallel.
$\therefore$ Equivalent resistance between terminals $D$ and $C$ is
$$ \begin{aligned} & \frac{1}{R _{D C}} & =\frac{1}{1}+\frac{1}{1}+\frac{1}{1} \\ \therefore \quad & R _{D C} & =\frac{1}{3} \Omega \end{aligned} $$
So, potential difference across $D$ and $C$ is
$$ \begin{array}{lll} & & V _{D C}=i R _{D C}=6 \times \frac{1}{3} \\ \Rightarrow & & V _{D C}=2 V \\ \text { Now, } & V _{A D} \text { and } V _{C B}=0 \end{array} $$
(In case of open circuits, $I=0$ )
So, $\quad V _{A B}=V _{A D}+V _{D C}+V _{C B}=V _{D C}$
So, $\quad V _{A B}=2 V$






