Straight Line and Pair of Straight Lines 5 Question 1
1.
Let
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Show Answer
Answer:
Correct Answer: 1. (b)
Solution:
- Let
Therefore,
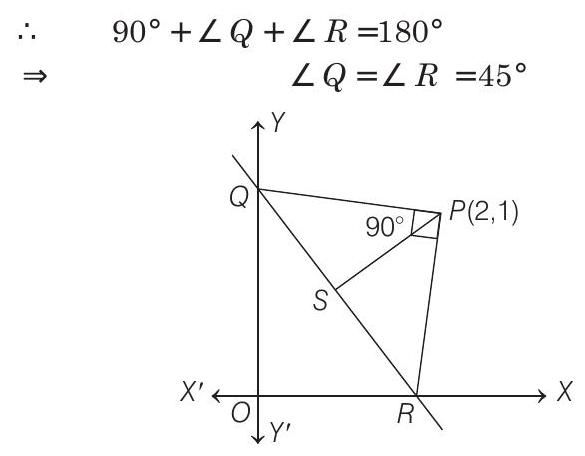
Now, slope of
[given]
But
Let
Therefore, joint equation of






