3D Geometry 3 Question 53
####53. Let
(2018 Adv.)
(a) The line of intersection of
(b) The line
(c) The acute angle between
(d) If
Show Answer
Answer:
Correct Answer: 53. (c, d)
Solution:
- We have,
| and | |
| Here, | |
| and |
(a) Direction ratio of the line of intersection of
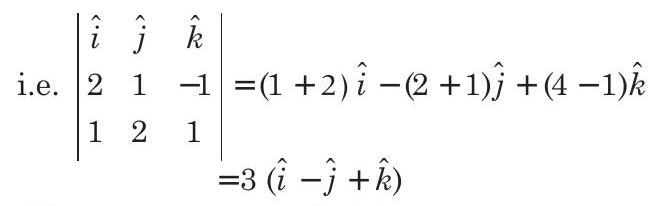
Hence, statement
(b) We have,
This line is parallel to the line of intersection of
Hence, statement (b) is false.
(c) Let acute angle between
We know that,
Hence, statement (c) is true.
(d) Equation of plane passing through the point
Now, distance of the point
Hence, statement (d) is true.






