3D Geometry 3 Question 20
####20. The plane containing the line
(2019 Main, 11 Jan I)
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Show Answer
Answer:
(c)
Solution:
- Let the direction vector of the line
Since, the required plane contains this line and its projection along the plane
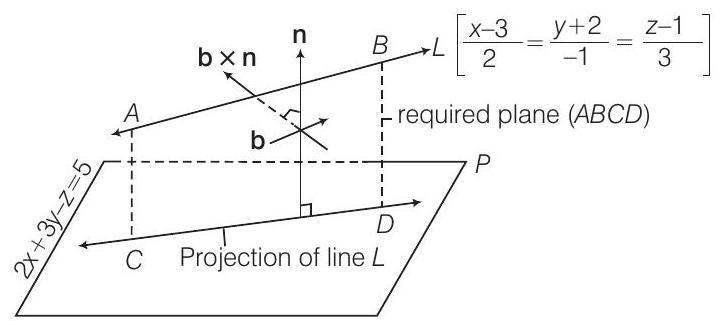
Normal vector of the plane
Now, the required plane contains
Since, the plane contains the line
Now, the equation of required plane is
Note that






