Mathematics 11
- Chapter 1 Sets
- Chapter 2 Relations And Functions
- Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
- Chapter 4 Complex numbers and quadratic equations
- Chapter 5 Linear Inequalities
- Chapter 6 Permutations And Combinations
- Chapter 7 Binomial Theorem
- Chapter 8 Sequences And Series
- Chapter 9 Straight Lines
- Chapter 10 Conic Sections
- Chapter 11 Introduction To Three Dimensional Geometry
- Chapter 12 Limits And Derivaties
- Chapter 13 Statistics
- Chapter 14 Probability
Chapter 2 Relations And Functions
RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS
Mathematics is the indispensable instrument of
all physical research. - BERTHELOT
2.1 Introduction
Much of mathematics is about finding a pattern - a recognisable link between quantities that change. In our daily life, we come across many patterns that characterise relations such as brother and sister, father and son, teacher and student. In mathematics also, we come across many relations such as number $m$ is less than number $n$, line $l$ is parallel to line $m$, set $A$ is a subset of set $B$. In all these, we notice that a relation involves pairs of objects in certain order. In this Chapter, we will learn how to link pairs of objects from two sets and then introduce relations between the two objects in the pair. Finally, we will learn about special relations which will qualify to be functions. The

concept of function is very important in mathematics since it captures the idea of a mathematically precise correspondence between one quantity with the other.
2.2 Cartesian Products of Sets
Suppose A is a set of 2 colours and B is a set of 3 objects, i.e.,
$$ A=\{\text { red, blue }\} \text { and } B=\{b, c, s\} \text {, } $$
where $b, c$ and $s$ represent a particular bag, coat and shirt, respectively.
How many pairs of coloured objects can be made from these two sets?
Proceeding in a very orderly manner, we can see that there will be 6 distinct pairs as given below:
(red, $b$ ), (red, $c$ ), (red, $s$ ), (blue, $b$ ), (blue, $c$ ), (blue, $s$ ).
Thus, we get 6 distinct objects (Fig 2.1).

Let us recall from our earlier classes that an ordered pair of elements taken from any two sets $P$ and $Q$ is a pair of elements written in small brackets and grouped together in a particular order, i.e., $(p, q), p \in P$ and $q \in Q$. This leads to the following definition:
Definition 1 Given two non-empty sets $P$ and $Q$. The cartesian product $P \times Q$ is the set of all ordered pairs of elements from $P$ and $Q$, i.e.,
$$ P \times Q=\{(p, q): p \in P, q \in Q\} $$
If either $P$ or $Q$ is the null set, then $P \times Q$ will also be empty set, i.e., $P \times Q=\phi$
From the illustration given above we note that
$A \times B=\{(red, b),($ red,$c),($ red,$s),($ blue,$b),($ blue,$c),($ blue,$s)\}$.
Again, consider the two sets:
$A=\{DL, MP, KA\}$, where DL, MP, KA represent Delhi, Madhya Pradesh and Karnataka, respectively and B $=\{01,02, 03 \}$ representing codes for the licence plates of vehicles issued by DL, MP and KA.
If the three states, Delhi, Madhya Pradesh and Karnataka were making codes for the licence plates of vehicles, with the restriction that the code begins with an element from set $A$, which are the pairs available from these sets and how many such pairs will there be (Fig 2.2)?

The available pairs are:(DL,01), (DL,02), (DL,03), (MP,01), (MP,02), (MP,03), $(KA, 01),(KA, 02),(KA, 03)$ and the product of set $A$ and set $B$ is given by $A \times B=\{(DL, 01),(DL, 02),(DL, 03),(MP, 01),(MP, 02),(MP, 03),(KA, 01),(KA, 02)$, $(KA, 03)\}$.
It can easily be seen that there will be 9 such pairs in the Cartesian product, since there are 3 elements in each of the sets A and B. This gives us 9 possible codes. Also note that the order in which these elements are paired is crucial. For example, the code (DL, 01 ) will not be the same as the code $(01, DL)$.
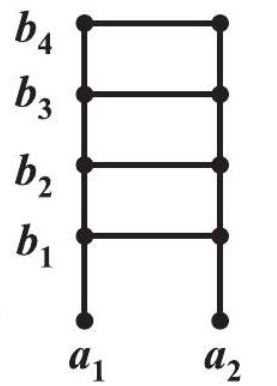
As a final illustration, consider the two sets $A=\{a_1, a_2\}$ and
$B=\{b_1, b_2, b_3, b_4\}$ (Fig 2.3).
$A \times B=\{(a_1, b_1),(a_1, b_2),(a_1, b_3),(a_1, b_4),(a_2, b_1),(a_2, b_2),(a_2, b_3),(a_2, b_4)\} .$
The 8 ordered pairs thus formed can represent the position of points in the plane if A and B are subsets of the set of real numbers and it is obvious that the point in the position $(a_1, b_2)$ will be distinct from the point in the position $(b_2, a_1)$.
Remarks
(i) Two ordered pairs are equal, if and only if the corresponding first elements are equal and the second elements are also equal.
(ii) If there are $p$ elements in $A$ and $q$ elements in $B$, then there will be $p q$ elements in $A \times B$, i.e., if $n(A)=p$ and $n(B)=q$, then $n(A \times B)=p q$.
(iii) If $A$ and $B$ are non-empty sets and either $A$ or $B$ is an infinite set, then so is $A \times B$.
(iv) $A \times A \times A=\{(a, b, c): a, b, c \in A\}$. Here $(a, b, c)$ is called an ordered triplet.
Example 1 If $(x+1, y-2)=(3,1)$, find the values of $x$ and $y$.
Solution Since the ordered pairs are equal, the corresponding elements are equal.
Therefore
$$ x+1=3 \text { and } y-2=1 \text {. } $$
Solving we get $\quad x=2$ and $y=3$.
Example 2 If $P=\{a, b, c\}$ and $Q=\{r\}$, form the sets $P \times Q$ and $Q \times P$.
Are these two products equal?
Solution By the definition of the cartesian product,
$$ P \times Q=\{(a, r),(b, r),(c, r)\} \text { and } Q \times P=\{(r, a),(r, b),(r, c)\} $$
Since, by the definition of equality of ordered pairs, the pair $(a, r)$ is not equal to the pair $(r, a)$, we conclude that $P \times Q \neq Q \times P$.
However, the number of elements in each set will be the same.
Example 3 Let $A=\{1,2,3\}, B=\{3,4\}$ and $C=\{4,5,6\}$. Find
(i) $A \times(B \cap C)$
(ii) $(A \times B) \cap(A \times C)$
(iii) $A \times(B \cup C)$
(iv) $(A \times B) \cup(A \times C)$
Solution (i) By the definition of the intersection of two sets, $(B \cap C)=\{4\}$.
Therefore, $A \times(B \cap C)=\{(1,4),(2,4),(3,4)\}$.
(ii) Now $(A \times B)=\{(1,3),(1,4),(2,3),(2,4),(3,3),(3,4)\}$ and $(A \times C)=\{(1,4),(1,5),(1,6),(2,4),(2,5),(2,6),(3,4),(3,5),(3,6)\}$
Therefore, $(A \times B) \cap(A \times C)=\{(1,4),(2,4),(3,4)\}$.
(iii) Since, $\quad(B \cup C)=\{3,4,5,6\}$, we have
$A \times(B \cup C)=\{(1,3),(1,4),(1,5),(1,6),(2,3),(2,4),(2,5),(2,6),(3,3)$, $(3,4),(3,5),(3,6)\}$.
(iv) Using the sets $A \times B$ and $A \times C$ from part (ii) above, we obtain $(A \times B) \cup(A \times C)=\{(1,3),(1,4),(1,5),(1,6),(2,3),(2,4),(2,5),(2,6)$, $(3,3),(3,4),(3,5),(3,6)\}$.
Example 4 If $P=\{1,2\}$, form the set $P \times P \times P$.
Solution We have, $ P \times P \times P=\{(1,1,1),(1,1,2),(1,2,1),(1,2,2),(2,1,1),(2,1,2),(2,2,1)$, $(2,2,2)\} $.
Example 5 If $\mathbf{R}$ is the set of all real numbers, what do the cartesian products $\mathbf{R} \times \mathbf{R}$ and $\mathbf{R} \times \mathbf{R} \times \mathbf{R}$ represent?
Solution The Cartesian product $\mathbf{R} \times \mathbf{R}$ represents the set $\mathbf{R} \times \mathbf{R}=\{(x, y): x, y \in \mathbf{R}\}$ which represents the coordinates of all the points in two dimensional space and the cartesian product $\mathbf{R} \times \mathbf{R} \times \mathbf{R}$ represents the set $\mathbf{R} \times \mathbf{R} \times \mathbf{R}=\{(x, y, z): x, y, z \in \mathbf{R}\}$ which represents the coordinates of all the points in three-dimensional space.
Example 6 If $A \times B=\{(p, q),(p, r),(m, q),(m, r)\}$, find $A$ and $B$.
Solution
$$ \begin{aligned} & A=\text { set of first elements }=\{p, m\} \\ & B=\text { set of second elements }=\{q, r\} . \end{aligned} $$
EXERCISE 2.1
1. If $(\frac{x}{3}+1, y-\frac{2}{3})=(\frac{5}{3}, \frac{1}{3})$, find the values of $x$ and $y$.
Answer : It is given that $(\frac{x}{3}+1, y-\frac{2}{3})=(\frac{5}{3}, \frac{1}{3})$ Since the ordered pairs are equal, the corresponding elements will also be equal. Therefore, $\frac{x}{3}+1=\frac{5}{3}$ and $y-\frac{2}{3}=\frac{1}{3}$. $\frac{x}{3}+1=\frac{5}{3}$ $\Rightarrow \frac{x}{3}=\frac{5}{3}-1 \quad y-\frac{2}{3}=\frac{1}{3}$ $\Rightarrow \frac{x}{3}=\frac{2}{3} \Rightarrow y=\frac{1}{3}+\frac{2}{3}$ $\Rightarrow x=2 \quad \Rightarrow y=1$ $\therefore x=2$ and $y=1$Show Answer
Answer : It is given that set A has 3 elements and the elements of set B are 3, 4, and 5 . $\Rightarrow$ Number of elements in set $B=3$ Number of elements in $(A \times B)$ $=($ Number of elements in $A) \times($ Number of elements in $B)$ $=3 \times 3=9$ Thus, the number of elements in $(A \times B)$ is 9 .Show Answer
Answer : $G={7,8}$ and $H={5,4,2}$ We know that the Cartesian product $P \times Q$ of two non-empty sets $P$ and $Q$ is defined as $P \times Q={(p, q): p \in P, q \in Q}$ $\therefore G \times H={(7,5),(7,4),(7,2),(8,5),(8,4),(8,2)}$ $H \times G={(5,7),(5,8),(4,7),(4,8),(2,7),(2,8)}$Show Answer
(i) If $P=\{m, n\}$ and $Q=\{n, m\}$, then $P \times Q=\{(m, n),(n, m)\}$.
(ii) If $A$ and $B$ are non-empty sets, then $A \times B$ is a non-empty set of ordered pairs $(x, y)$ such that $x \in A$ and $y \in B$.
(iii) If $A=\{1,2\}, B=\{3,4\}$, then $A \times(B \cap \phi)=\phi$.
Answer : (i) False If $P={m, n}$ and $Q={n, m}$, then $P \times Q={(m, m),(m, n),(n, m),(n, n)}$ (ii) True (iii) TrueShow Answer
Answer : It is known that for any non-empty set $A, A \times A \times A$ is defined as $A \times A \times A={(a, b, c): a, b, c \in A}$ It is given that $A=\{-1,1\}$ $\therefore A \times A \times A=\{(-1,-1,-1),(-1,-1,1),(-1,1,-1),(-1,1,1)$, $(1,-1,-1),(1,-1,1),(1,1,-1),(1,1,1)\}$Show Answer
Answer : It is given that $A \times B={(a, x),(a, y),(b, x),(b, y)}$ We know that the Cartesian product of two non-empty sets $P$ and $Q$ is defined as $P \times Q={(p, q): p \in P, q \in Q}$ $\therefore A$ is the set of all first elements and $B$ is the set of all second elements. Thus, $A={a, b}$ and $B={x, y}$Show Answer
Answer : (i) To verify: $A \times(B \cap C)=(A \times B) \cap(A \times C)$ We have $B \cap C={1,2,3,4} \cap{5,6}=\Phi$ $\therefore$ L.H.S. $=A \times(B \cap C)=A \times \Phi=\Phi$ $A \times B={(1,1),(1,2),(1,3),(1,4),(2,1),(2,2),(2,3),(2,4)}$ $A \times C={(1,5),(1,6),(2,5),(2,6)}$ $\therefore$ R.H.S. $=(A \times B) \cap(A \times C)=\Phi$ $\therefore$ L.H.S. $=$ R.H.S Hence, $A \times(B \cap C)=(A \times B) \cap(A \times C)$ (ii) To verify: $A \times C$ is a subset of $B \times D$ $A \times C={(1,5),(1,6),(2,5),(2,6)}$ $B \times D={(1,5),(1,6),(1,7),(1,8),(2,5),(2,6),(2,7),(2,8),(3,5),(3,6),(3,7),(3,8),(4,5),(4,6),(4,7),(4,8)}$ We can observe that all the elements of set $A \times C$ are the elements of set $B \times D$. Therefore, $A \times C$ is a subset of $B \times D$.Show Answer
Answer : $A={1,2}$ and $B={3,4}$ $\therefore A \times B={(1,3),(1,4),(2,3),(2,4)}$ $\Rightarrow n(A \times B)=4$ We know that if $C$ is a set with $n(C)=m$, then $n[P(C)]=2^{m}$. Therefore, the set $A \times B$ has $2^{4}=16$ subsets. These are $\Phi,{(1,3)},{(1,4)},{(2,3)},{(2,4)},{(1,3),(1,4)},{(1,3),(2,3)}$, ${(1,3),(2,4)},{(1,4),(2,3)},{(1,4),(2,4)},{(2,3),(2,4)}$, ${(1,3),(1,4),(2,3)},{(1,3),(1,4),(2,4)},{(1,3),(2,3),(2,4)}$, ${(1,4),(2,3),(2,4)},{(1,3),(1,4),(2,3),(2,4)}$Show Answer
Answer : It is given that $n(A)=3$ and $n(B)=2$; and $(x, 1),(y, 2),(z, 1)$ are in $A \times B$. We know that $A=$ Set of first elements of the ordered pair elements of $A \times B$ $B=$ Set of second elements of the ordered pair elements of $A \times B$. $\therefore x, y$, and zare the elements of $A$; and 1 and 2 are the elements of $B$. Since $n(A)=3$ and $n(B)=2$, it is clear that $A={x, y, z}$ and $B={1,2}$.Show Answer
Show Answer
Answer :
We know that if $n(A)=p$ and $n(B)=q$, then $n(A \times B)=p q$.
$\therefore n(A \times A)=n(A) \times n(A)$
It is given that $n(A \times A)=9$
$\therefore n(A) \times n(A)=9$
$\Rightarrow n(A)=3$
The ordered pairs $(-1,0)$ and $(0,1)$ are two of the nine elements of $A \times A$.
We know that $A \times A={(a, a): a \in A}$. Therefore, $-1,0$, and 1 are elements of $A$.
Since $n(A)=3$, it is clear that $A={-1,0,1}$.
The remaining elements of set $A \times A$ are $(-1,-1),(-1,1),(0,-1),(0,0)$,
$(1,-1),(1,0)$, and $(1,1)$
2.1 Relations
Consider the two sets $P=\{a, b, c\}$ and $Q=\{$ Ali, Bhanu, Binoy, Chandra, Divya $\}$.
The cartesian product of $P$ and $Q$ has 15 ordered pairs which can be listed as $P \times Q=\{(a, \text{Ali})$, (a, Bhanu), (a, Binoy), …, (c, Divya) $\}$.

We can now obtain a subset of $P \times Q$ by introducing a relation $R$ between the first element $x$ and the second element $y$ of each ordered pair $(x, y)$ as
$R=\{(x, y): x$ is the first letter of the name $y, x \in P, y \in Q\}$.
Then $R=\{(a, Ali),(b, Bhanu),(b, Binoy),(c$, Chandra $)\}$
A visual representation of this relation $R$ (called an arrow diagram) is shown in Fig 2.4.
Definition 2 A relation $R$ from a non-empty set $A$ to a non-empty set $B$ is a subset of the cartesian product $A \times B$. The subset is derived by describing a relationship between the first element and the second element of the ordered pairs in $A \times B$. The second element is called the image of the first element.
Definition 3 The set of all first elements of the ordered pairs in a relation $R$ from a set A to a set $B$ is called the domain of the relation $R$.
Definition 4 The set of all second elements in a relation $R$ from a set $A$ to a set $B$ is called the range of the relation $R$. The whole set $B$ is called the codomain of the relation $R$. Note that range $\subset$ codomain.
Remarks (i) A relation may be represented algebraically either by the Roster method or by the Set-builder method.
(ii) An arrow diagram is a visual representation of a relation.
Example 7 Let $A=\{1,2,3,4,5,6\}$. Define a relation $R$ from $A$ to $A$ by
$R=\{(x, y): y=x+1\}$
(i) Depict this relation using an arrow diagram.
(ii) Write down the domain, codomain and range of $R$.
Solution (i) By the definition of the relation,
$R=\{(1,2),(2,3),(3,4),(4,5),(5,6)\}$.
The corresponding arrow diagram is shown in Fig 2.5.

(ii) We can see that the domain $=\{1,2,3,4,5\}$
Similarly, the range $=\{2,3,4,5,6\}$ and the codomain $=\{1,2,3,4,5,6\}$.
Example 8 The Fig 2.6 shows a relation between the sets $P$ and $Q$. Write this relation (i) in set-builder form, (ii) in roster form. What is its domain and range?

Solution It is obvious that the relation $R$ is “$x$ is the square of $y$”.
(i) In set-builder form, $R=\{(x, y): x$ is the square of $y, x \in P, y \in \mathbf{Q}\}$
(ii) In roster form, $R=\{(9,3)$, $(9,-3),(4,2),(4,-2),(25,5),(25,-5)\}$
The domain of this relation is $\{4,9,25\}$.
The range of this relation is $\{-2,2,-3,3,-5,5\}$.
Note that the element 1 is not related to any element in set $P$.
The set $Q$ is the codomain of this relation.
Note - The total number of relations that can be defined from a set $A$ to a set $B$ is the number of possible subsets of $A \times B$. If $n(A)=p$ and $n(B)=q$, then $n(A \times B)=p q$ and the total number of relations is $2^{p q}$.
Example 9 Let $A=\{1,2\}$ and $B=\{3,4\}$. Find the number of relations from A to B.
Solution We have,
$$ A \times B=\{(1,3),(1,4),(2,3),(2,4)\} $$
Since $n(A \times B)=4$, the number of subsets of $A \times B$ is $2^{4}$. Therefore, the number of relations from $A$ into $B$ will be $2^{4}$.
Remark A relation $R$ from $A$ to $A$ is also stated as a relation on $A$.
EXERCISE 2.2
1. Let $A=\{1,2,3, \ldots, 14\}$. Define a relation $R$ from $A$ to $A$ by $R=\{(x, y): 3 x-y=0$, where $x, y \in A\}$. Write down its domain, codomain and range.
Answer : The relation $R$ from $A$ to $A$ is given as $ R=\{(x, y): 3 x-y=0$, where $x, y \in A \}$ i.e., $R=\{(x, y): 3 x=y$, where $ x, y \in A \}$ $\therefore R={(1,3),(2,6),(3,9),(4,12)}$ The domain of $R$ is the set of all first elements of the ordered pairs in the relation. $\therefore$ Domain of $R={1,2,3,4}$ The whole set $A$ is the codomainof the relation $R$. $\therefore$ Codomain of $R=A={1,2,3, \ldots, 14}$ The range of $R$ is the set of all second elements of the ordered pairs in the relation. $\therefore$ Range of $R={3,6,9,12}$Show Answer
Answer : $ R= \{(x, y): y=x+5, x$ is a natural number less than $ 4, x, y \in \mathbf{N} \}$ The natural numbers less than 4 are 1,2 , and 3 . $\therefore R={(1,6),(2,7),(3,8)}$ The domain of $R$ is the set of all first elements of the ordered pairs in the relation. $\therefore$ Domain of $R={1,2,3}$ The range of $R$ is the set of all second elements of the ordered pairs in the relation. $\therefore$ Range of $R={6,7,8}$Show Answer
Answer : $A={1,2,3,5}$ and $B={4,6,9}$ $R=\{(x, y)$ : the difference between $x$ and yis odd; $x \in A, y \in B\}$ $\therefore R=\{(1,4),(1,6),(2,9),(3,4),(3,6),(5,4),(5,6)\}$Show Answer
(i) in set-builder form (ii) roster form. What is its domain and range?
Answer : According to the given figure, $P={5,6,7}, Q={3,4,5}$ (i) $R={(x, y): y=x-2 ; x \in P}$ or $R=\{(x, y): y=x-2$ for $x=5,6,7\}$ (ii) $R=\{(5,3),(6,4),(7,5)\}$ Domain of $R=\{5,6,7\}$ Range of $R=\{3,4,5\}$Show Answer

Fig 2.7 $\{(a, b): a, b \in A, b$ is exactly divisible by $a\}$.
(i) Write $R$ in roster form
(ii) Find the domain of $R$
(iii) Find the range of $R$.
Answer : $A=\{1,2,3,4,6\}, R=\{(a, b): a, b \in A, b$ is exactly divisible by $a\}$ (i)
$R=\{(1,1),(1,2),(1,3),(1,4),\\
(1,6),(2,2),(2,4),(2,6),(3,3),(3,6),(4,4),(6,6)\}$ (ii) Domain of $R=\{1,2,3,4,6\}$ (iii) Range of $R=\{1,2,3,4,6\}$Show Answer
Answer : $R=\{(x, x+5): x \in{0,1,2,3,4,5}\}$ $\therefore R=\{(0,5),(1,6),(2,7),(3,8),(4,9),(5,10)\}$ $\therefore$ Domain of $R=\{0,1,2,3,4,5\}$ Range of $R=\{5,6,7,8,9,10\}$Show Answer
Answer : $R=\{(x, x^{3}): x.$ is a prime number less than 10 $\}$ The prime numbers less than 10 are 2, 3, 5, and 7 . $\therefore R=\{(2,8),(3,27),(5,125),(7,343) \}$Show Answer
Answer : It is given that $A=\{x, y, z\}$ and $B=\{1,2\}$. $\therefore A \times B=\{(x, 1),(x, 2),(y, 1),(y, 2),(z, 1),(z, 2)\}$ Since $n(A \times B)=6$, the number of subsets of $A \times B$ is $2^{6}$. Therefore, the number of relations from $A$ to $B$ is $2^{6}$.Show Answer
Show Answer
Answer :
$R=\{(a, b): a, b \in \mathbf{Z}, a-b$ is an integer $\}$
It is known that the difference between any two integers is always an integer.
$\therefore$ Domain of $R=Z$
Range of $R=Z$
Functions
In this Section, we study a special type of relation called function. It is one of the most important concepts in mathematics. We can, visualise a function as a rule, which produces new elements out of some given elements. There are many terms such as ‘map’ or ‘mapping’ used to denote a function.
Definition 5 A relation $f$ from a set $A$ to a set $B$ is said to be a function if every element of set $A$ has one and only one image in set $B$.
In other words, a function $f$ is a relation from a non-empty set $A$ to a non-empty set $B$ such that the domain of $f$ is $A$ and no two distinct ordered pairs in $f$ have the same first element.
If $f$ is a function from A to B and $(a, b) \in f$, then $f(a)=b$, where $b$ is called the image of $a$ under $f$ and $a$ is called the preimage of $b$ under $f$.
The function $f$ from $A$ to $B$ is denoted by $f: A \rightarrow B$.
Looking at the previous examples, we can easily see that the relation in
Example 7 is not a function because the element 6 has no image.
Again, the relation in
Example 8 is not a function because the elements in the domain are connected to more than one images. Similarly, the relation in
Example 9 is also not a function. (Why?) In the examples given below, we will see many more relations some of which are functions and others are not.
Example 10 Let $\mathbf{N}$ be the set of natural numbers and the relation $R$ be defined on $N$ such that $R=\{(x, y): y=2 x, x, y \in \mathbf{N}\}$.
What is the domain, codomain and range of $R$ ? Is this relation a function?
Solution The domain of $R$ is the set of natural numbers $\mathbf{N}$. The codomain is also $\mathbf{N}$. The range is the set of even natural numbers.
Since every natural number $n$ has one and only one image, this relation is a function.
Example 11 Examine each of the following relations given below and state in each case, giving reasons whether it is a function or not?
(i) $R=\{(2,1),(3,1),(4,2)\}$, (ii) $R=\{(2,2),(2,4),(3,3),(4,4)\}$
(iii) $R=\{(1,2),(2,3),(3,4),(4,5),(5,6),(6,7)\}$
Solution (i) Since 2, 3, 4 are the elements of domain of R having their unique images, this relation $R$ is a function.
(ii) Since the same first element 2 corresponds to two different images 2 and 4 , this relation is not a function.
(iii) Since every element has one and only one image, this relation is a function.
Definition 6 A function which has either $R$ or one of its subsets as its range is called a real valued function. Further, if its domain is also either $R$ or a subset of $R$, it is called a real function.
Example 12 Let $\mathbf{N}$ be the set of natural numbers. Define a real valued function
$f: \mathbf{N} \rightarrow \mathbf{N}$ by $f(x)=2 x+1$. Using this definition, complete the table given below.
| $x$ | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $y$ | $f(1)=\ldots$ | $f(2)=\ldots$ | $f(3)=\ldots$ | $f(4)=\ldots$ | $f(5)=\ldots$ | $f(6)=\ldots$ | $f(7)=\ldots$ |
Solution The completed table is given by
| $x$ | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $y$ | $f(1)=3$ | $f(2)=5$ | $f(3)=7$ | $f(4)=9$ | $f(5)=11$ | $f(6)=13$ | $f(7)=15$ |
Some functions and their graphs
(i) Identity function Let $\mathbf{R}$ be the set of real numbers. Define the real valued function $f: \mathbf{R} \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$ by $y=f(x)=x$ for each $x \in \mathbf{R}$. Such a function is called the identity function. Here the domain and range of $f$ are $\mathbf{R}$. The graph is a straight line as shown in Fig 2.8. It passes through the origin.

(ii) Constant function Define the function $f: \mathbf{R} \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$ by $y=f(x)=c, x \in \mathbf{R}$ where $c$ is a constant and each $x \in \mathbf{R}$. Here domain of $f$ is $\mathbf{R}$ and its range is $\{c\}$.

The graph is a line parallel to $x$-axis. For example, if $f(x)=3$ for each $x \in \mathbf{R}$, then its graph will be a line as shown in the Fig 2.9.
(iii) Polynomial function A function $f: \mathbf{R} \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$ is said to be polynomial function if for each $x$ in $\mathbf{R}, y=f(x)=a_0+a_1 x+a_2 x^{2}+\ldots+a_{n} x^{n}$, where $n$ is a non-negative integer and $a_0, a_1, a_2, \ldots, a_{n} \in \mathbf{R}$.
The functions defined by $f(x)=x^{3}-x^{2}+2$, and $g(x)=x^{4}+\sqrt{2} x$ are some examples
of polynomial functions, whereas the function $h$ defined by $h(x)=x^{\frac{2}{3}}+2 x$ is not a polynomial function.(Why?)
Example 13 Define the function $f: \mathbf{R} \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$ by $y=f(x)=x^{2}, x \in \mathbf{R}$. Complete the Table given below by using this definition. What is the domain and range of this function? Draw the graph of $f$.
| $x$ | -4 | -3 | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $y=f(x)=x^{2}$ |
Solution The completed Table is given below:
| $x$ | -4 | -3 | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $y=f(x)=x^{2}$ | 16 | 9 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 9 | 16 |
Domain of $f=\{x: x \in \mathbf{R}\}$. Range of $f=\{x^{2}: x \in \mathbf{R}\}$. The graph of $f$ is given by Fig 2.10

$f(x)=x^{2}$
Fig 2.10
Example 14 Draw the graph of the function $\boldsymbol{f}: \mathbf{R} \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$ defined by $f(x)=x^{3}, x \in \mathbf{R}$.
Solution We have
$f(0)=0, f(1)=1, f(-1)=-1, f(2)=8, f(-2)=-8, f(3)=27 ; f(-3)=-27$, etc.
Therefore, $f=\{(x, x^{3}): x \in \mathbf{R}\}$.
The graph of $f$ is given in Fig 2.11.

(iv) Rational functions are functions of the type $\frac{f(x)}{g(x)}$, where $f(x)$ and $g(x)$ are polynomial functions of $x$ defined in a domain, where $g(x) \neq 0$.
Example 15 Define the real valued function $f: \mathbf{R}-\{0\} \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$ defined by $f(x)=\frac{1}{x}$, $x \in \mathbf{R}-\{0\}$. Complete the Table given below using this definition. What is the domain and range of this function?
| $x$ | -2 | -1.5 | -1 | -0.5 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $y=\frac{1}{x}$ | $\ldots$ | $\ldots$ | $\ldots$ | $\ldots$ | $\ldots$ | $\ldots$ | $\ldots$ | $\ldots$ | $\ldots$ |
Solution The completed Table is given by
| $x$ | -2 | -1.5 | -1 | -0.5 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $y=\frac{1}{x}$ | -0.5 | -0.67 | -1 | -2 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0.67 | 0.5 |
The domain is all real numbers except 0 and its range is also all real numbers except 0 . The graph of $f$ is given in Fig 2.12.

(v) The Modulus function The function $f: \mathbf{R} \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$ defined by $f(x)=|x|$ for each $x \in \mathbf{R}$ is called modulus function. For each non-negative value of $x, f(x)$ is equal to $x$. But for negative values of $x$, the value of $f(x)$ is the negative of the value of $x$, i.e.,
$f(x)=\begin{cases}x,x \geq 0 \\ -x, x <0 \end{cases}$

(vi) Signum function The function $f: \mathbf{R} \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$ defined by
$$ f(x)=\begin{cases} 1, \text { if } x>0 \\ 0, \text { if } x=0 \\ -1, \text { if } x<0 \end{cases} $$
$$ f(x)=|x| $$
Fig 2.13 is called the signum function. The domain of the signum function is $\mathbf{R}$ and the range is the set $\{-1,0,1\}$. The graph of the signum function is given by the Fig 2.14 .

$$ f(x)=\frac{|x|}{x}, x^{\prime} \quad 0 \text { and } 0 \text { for } x=0 $$
(vii) Greatest integer function The function $f: \mathbf{R} \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$ defined by $f(x)=[x], x \in \mathbf{R}$ assumes the value of the greatest integer, less than or equal to $x$. Such a function is called the greatest integer function.
From the definition of $[x]$, we can see that
$$ \begin{aligned} & {[x]=-1 \text { for }-1 \leq x<0} \\ & {[x]=0 \text { for } 0 \leq x<1} \\ & {[x]=1 \text { for } 1 \leq x<2} \\ & {[x]=2 \text { for } 2 \leq x<3 \text { and }} \end{aligned} $$
so on.

The graph of the function is Fig 2.15 shown in Fig 2.15.
2.4.2 Algebra of real functions In this Section, we shall learn how to add two real functions, subtract a real function from another, multiply a real function by a scalar (here by a scalar we mean a real number), multiply two real functions and divide one real function by another.
(i) Addition of two real functions Let $f: X \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$ and $g: X \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$ be any two real functions, where $X \subset \mathbf{R}$. Then, we define $(f+g): X \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$ by
$(f+g)(x)=f(x)+g(x)$, for all $x \in \mathbf{X}$.
(ii) Subtraction of a real function from another $Let f: X \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$ and $g: X \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$ be any two real functions, where $\mathbf{X} \subset \mathbf{R}$. Then, we define $(f-g): X \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$ by $(f-g)(x)=f(x)-g(x)$, for all $x \in X$.
(iii) Multiplication by a scalar Let $f: X \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$ be a real valued function and $\alpha$ be a scalar. Here by scalar, we mean a real number. Then the product $\alpha f$ is a function from $X$ to $\mathbf{R}$ defined by $(\alpha f)(x)=\alpha f(x), x \in X$.
(iv) Multiplication of two real functions The product (or multiplication) of two real functions $f: \mathbf{X} \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$ and $g: X \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$ is a function $f g: X \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$ defined by $(f g)(x)=f(x) g(x)$, for all $x \in X$.
This is also called pointwise multiplication.
(v) Quotient of two real functions Let $f$ and $g$ be two real functions defined from $X \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$, where $X \subset \mathbf{R}$. The quotient of $f$ by $g$ denoted by $\frac{f}{g}$ is a function defined by , $(\frac{f}{g})(x)=\frac{f(x)}{g(x)}$, provided $g(x) \neq 0, x \in X$
Example 16 Let $f(x)=x^{2}$ and $g(x)=2 x+1$ be two real functions.Find
$$ (f+g)(x),(f-g)(x),(f g)(x),(\frac{f}{g})(x) $$
Solution We have,
$$ \begin{aligned} & (f+g)(x)=x^{2}+2 x+1,(f-g)(x)=x^{2}-2 x-1, \\ & (f g)(x)=x^{2}(2 x+1)=2 x^{3}+x^{2},(\frac{f}{g})(x)=\frac{x^{2}}{2 x+1}, x \neq-\frac{1}{2} \end{aligned} $$
Example 17 Let $f(x)=\sqrt{x}$ and $g(x)=x$ be two functions defined over the set of nonnegative real numbers. Find $(f+g)(x),(f-g)(x),(f g)(x)$ and $(\frac{f}{g})(x)$.
Solution We have
$$ \begin{aligned} & (f+g)(x)=\sqrt{x}+x,(f-g)(x)=\sqrt{x}-x, \\ & (f g) x=\sqrt{x}(x)=x^{\frac{3}{2}} \text { and }(\frac{f}{g})(x)=\frac{\sqrt{x}}{x}=x^{-\frac{1}{2}}, x \neq 0 \end{aligned} $$
EXERCISE 2.3
1. Which of the following relations are functions? Give reasons. If it is a function, determine its domain and range.
(i) $\{(2,1),(5,1),(8,1),(11,1),(14,1),(17,1)\}$
(ii) $\{(2,1),(4,2),(6,3),(8,4),(10,5),(12,6),(14,7)\}$
(iii) $\{(1,3),(1,5),(2,5)\}$.
Answer : (i) ${(2,1),(5,1),(8,1),(11,1),(14,1),(17,1)}$ Since $2,5,8,11,14$, and 17 are the elements of the domain of the given relation having their unique images, this relation is a function. Here, domain $={2,5,8,11,14,17}$ and range $={1}$ (ii) ${(2,1),(4,2),(6,3),(8,4),(10,5),(12,6),(14,7)}$ Since $2,4,6,8,10,12$, and 14 are the elements of the domain of the given relation having their unique images, this relation is a function. Here, domain $={2,4,6,8,10,12,14}$ and range $={1,2,3,4,5,6,7}$ (iii) ${(1,3),(1,5),(2,5)}$ Since the same first element i.e., 1 corresponds to two different images i.e., 3 and 5, this relation is not a function.Show Answer
(i) $f(x)=-|x|$
(ii) $f(x)=\sqrt{9-x^{2}}$.
Answer : (i) $f(x)=-|x|, x \in R$ We know that $|x|=\begin{cases} x, x \geq 0 \\ -x, x<0 \end{cases} .$ $\therefore f(x)=-|x|=\begin{cases} -x, x \geq 0 \\ x, x<0 \end{cases} .$ Since $f(x)$ is defined for $x \in \mathbf{R}$, the domain of fis $\mathbf{R}$. It can be observed that the range of $f(x)=-|x|$ is all real numbers except positive real numbers. $\therefore$ The range of fis $(- \infty, 0]$. (ii) $f(x)=\sqrt{9-x^{2}}$ Since $\sqrt{9-x^{2}}$ is defined for all real numbers that are greater than or equal to 3 and less than or equal to 3 , the domain of $f(x)$ is $\{x$ : -3 $ x \leq 3\}$ or [- 3,3$]$. For any value of $x$ such that $-3 \leq x \leq 3$, the value of $f(x)$ will lie between 0 and 3 . $\therefore$ The range of $f(x)$ is ${x: 0 \leq x \leq 3}$ or $[0,3]$.Show Answer
(i) $f(0)$,
(ii) $f(7)$,
(iii) $f(-3)$.
Answer : The given function is $f(x)=2 x-5$. Therefore, (i) $f(0)=2 \times 0-5=0-5=-5$ (ii) $f(7)=2 \times 7-5=14-5=9$ (iii) $f(-3)=2 \times(-3)-5=-6-5=-11$Show Answer
Find (i) $t(0)$
(ii) $t(28)$
(iii) $t(-10)$
(iv) The value of $C$, when $t(C)=212$.
Answer : The given function is $
t(C)=\frac{9 C}{5}+32
$ Therefore, (i) $
\begin{aligned}
& t(0)=\frac{9 \times 0}{5}+32=0+32=32 \\
& t(28)=\frac{9 \times 28}{5}+32=\frac{252+160}{5}=\frac{412}{5}
\end{aligned}
$ (ii) (iii) $
t(-10)=\frac{9 \times(-10)}{5}+32=9 \times(-2)+32=-18+32=14
$ (iv) It is given that $t(C)=212$ $\therefore 212=\frac{9 C}{5}+32$ $\Rightarrow \frac{9 C}{5}=212-32$ $\Rightarrow \frac{9 C}{5}=180$ $\Rightarrow 9 C=180 \times 5$ $\Rightarrow C=\frac{180 \times 5}{9}=100$ Thus, the value of $t$, when $t(C)=212$, is 100 .Show Answer
(i) $f(x)=2-3 x, x \in \mathbf{R}, x>0$.
(ii) $f(x)=x^{2}+2, x$ is a real number.
(iii) $f(x)=x, x$ is a real number.
Show Answer
Answer :
(i) $f(x)=2 - 3 x, x \in \mathbf{R}, x>0$
The values of $f(x)$ for various values of real numbers $x>0$ can be written in the tabular form as
| $x$ | 0.01 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 1 | 2 | 2.5 | 4 | 5 | … |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $f(x)$ | 1.97 | 1.7 | -0.7 | -1 | $\hat{a} €$ ““4 | -5.5 | -‘10 | -13 | . |
Thus, it can be clearly observed that the range of fis the set of all real numbers less than 2.
i.e., range of $f=(- \infty, 2)$
Alter:
Let $x>0$
$\Rightarrow 3 x>0$
$\Rightarrow 2 - 3 x<2$
$\Rightarrow f(x)<2$
$\therefore$ Range of $f=(- \infty, 2)$
(ii) $f(x)=x^{2}+2, x$, is a real number
The values of $f(x)$ for various values of real numbers $x$ can be written in the tabular form as
| $x$ | 0 | $\pm 0.3$ | $\pm 0.8$ | $\pm 1$ | $\pm 2$ | $\pm 3$ | $\ldots$ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $f(x)$ | 2 | 2.09 | 2.64 | 3 | 6 | 11 | $\ldots \ldots$ |
Thus, it can be clearly observed that the range of fis the set of all real numbers greater than 2 .
i.e., range of $f=[2, \infty)$
Alter:
Let $x$ be any real number.
Accordingly,
$x^{2} \geq 0$
$\Rightarrow x^{2}+2 \geq 0+2$
$\Rightarrow x^{2}+2 \geq 2$
$\Rightarrow f(x) \geq 2$
$\therefore$ Range of $f=[2, \infty)$
(iii) $f(x)=x, x$ is a real number
It is clear that the range of fis the set of all real numbers.
$\therefore$ Range of $f=\mathbf{R}$
Miscellaneous Examples
Example 18 Let $\mathbf{R}$ be the set of real numbers.
Define the real function
$$ f: \mathbf{R} \rightarrow \mathbf{R} \text { by } f(x)=x+10 $$
and sketch the graph of this function.
Solution Here $f(0)=10, f(1)=11, f(2)=12, \ldots$, $f(10)=20$, etc., and
$f(-1)=9, f(-2)=8, \ldots, f(-10)=0$ and so on.
Therefore, shape of the graph of the given function assumes the form as shown in Fig 2.16.

Remark The function $f$ defined by $f(x)=m x+c$, $x \in \mathbf{R}$, is called linear function, where $m$ and $c$ are constants. Above function is an example of a linear function.
Example 19 Let $R$ be a relation from $\mathbf{Q}$ to $\mathbf{Q}$ defined by $R=\{(a, b): a, b \in \mathbf{Q}$ and $a-b \in \mathbf{Z}\}$. Show that
(i) $(a, a) \in R$ for all $a \in \mathbf{Q}$
(ii) $(a, b) \in R$ implies that $(b, a) \in R$
(iii) $(a, b) \in R$ and $(b, c) \in R$ implies that $(a, c) \in R$
Solution (i) Since, $a-a=0 \in \mathbf{Z}$, if follows that $(a, a) \in R$.
(ii) $(a, b) \in R$ implies that $a-b \in \mathbf{Z}$. So, $b-a \in \mathbf{Z}$. Therefore, $(b, a) \in R$
(iii) $(a, b)$ and $(b, c) \in R$ implies that $a-b \in \mathbf{Z} . b-c \in \mathbf{Z}$. So, $a-c=(a-b)+(b-c) \in \mathbf{Z}$. Therefore, $(a, c) \in R$
Example 20 Let $f=\{(1,1),(2,3),(0,-1),(-1,-3)\}$ be a linear function from $\mathbf{Z}$ into $\mathbf{Z}$. Find $f(x)$.
Solution Since $f$ is a linear function, $f(x)=m x+c$. Also, since $(1,1),(0,-1) \in R$, $f(1)=m+c=1$ and $f(0)=c=-1$. This gives $m=2$ and $f(x)=2 x-1$.
Example 21 Find the domain of the function $f(x)=\frac{x^{2}+3 x+5}{x^{2}-5 x+4}$
Solution Since $x^{2}-5 x+4=(x-4)(x-1)$, the function $f$ is defined for all real numbers except at $x=4$ and $x=1$. Hence the domain of $f$ is $\mathbf{R}-\{1,4\}$.
Example 22 The function $f$ is defined by
$$ f(x)= \begin{cases}1-x & , x<0 \\ 1 & , x=0 \\ x+1, & x>0\end{cases} $$
Draw the graph of $f(x)$.
Solution Here, $f(x)=1-x, x<0$, this gives
$ \begin{aligned} & f(-4)=1-(-4)=5 \\ & f(-3)=1-(-3)=4 \\ & f(-2)=1-(-2)=3 \\ & f(-1)=1-(-1)=2 ; \text { etc } \end{aligned} $
and $f(1)=2, f(2)=3, f(3)=4$
$f(4)=5$ and so on for $f(x)=x+1, x>0$.
Thus, the graph of $f$ is as shown in Fig 2.17

Miscellaneous Exercise on Chapter 2
1. The relation $f$ is defined by $f(x)=\ \begin{cases} x^{2}, 0 \leq x \leq 3 \\ 3 x, 3 \leq x \leq 10\end{cases}$
The relation $g$ is defined by $g(x)=\ \begin{cases} x^{2}, 0 \leq x \leq 2 \\ 3 x, 2 \leq x \leq 10\end{cases}$
Show that $f$ is a function and $g$ is not a function.
2. If $f(x)=x^{2}$, find $\frac{f(1.1)-f(1)}{(1.1-1)}$.
Answer : The relation fis defined as $
f(x)= \begin{cases}x^{2}, & 0 \leq x \leq 3 \\ 3 x, & 3 \leq x \leq 10\end{cases}
$ It is observed that for $0 \leq x<3, f(x)=x^{2}$ $3<x \leq 10, f(x)=3 x$ Also, at $x=3, f(x)=3^{2}=9$ or $f(x)=3 \times 3=9$ i.e., at $x=3, f(x)=9$ Therefore, for $0 \leq x \leq 10$, the images of $f(x)$ are unique. Thus, the given relation is a function. The relation gis defined as $g(x)= \begin{cases}x^{2}, 0 \leq x \leq 2 \\ 3 x, 2 \leq x \leq 10\end{cases}$ It can be observed that for $x=2, g(x)=2^{2}=4$ and $g(x)=3 \times 2=6$ Hence, element 2 of the domain of the relation gcorresponds to two different images i.e., 4 and 6 . Hence, this relation is not a function.Show Answer
Answer : The given function is $
f(x)=\frac{x^{2}+2 x+1}{x^{2}-8 x+12}
$ $f(x)=\frac{x^{2}+2 x+1}{x^{2}-8 x+12}=\frac{x^{2}+2 x+1}{(x-6)(x-2)}$ It can be seen that function fis defined for all real numbers except at $x=6$ and $x=2$. Hence, the domain of fis $\mathbf{R}$ - ${2,6}$.Show Answer
Answer : The given real function is $f(x)=\sqrt{x-1}$. It can be seen that $\sqrt{x-1}$ is defined for (xâ “ $.^{\prime} 1) \geq 0$. i.e., $f(x)=\sqrt{(x-1)}$ is defined for $x \geq 1$. Therefore, the domain of $f$ is the set of all real numbers greater than or equal to 1 i.e., the domain of $f=[1, \infty)$. As $x \geq 1 \Rightarrow(x - 1) \geq 0 \Rightarrow \sqrt{x-1} \geq 0$ Therefore, the range of fis the set of all real numbers greater than or equal to 0 i.e., the range of $f=[0, \infty)$.Show Answer
Answer : The given real function $is f(x)=|x-1|$. It is clear that $|x-1|$ is defined for all real numbers. $\therefore$ Domain of $f=\mathbf{R}$ Also, for $x \in \mathbf{R},|x-1|$ assumes all real numbers. Hence, the range of fis the set of all non-negative real numbers.Show Answer
Answer : $
\begin{aligned}
& f={(x, \frac{x^{2}}{1+x^{2}}): x \in \mathbf{R}} \\
& ={(0,0),( \pm 0.5, \frac{1}{5}),( \pm 1, \frac{1}{2}),( \pm 1.5, \frac{9}{13}),( \pm 2, \frac{4}{5}),(3, \frac{9}{10}),(4, \frac{16}{17}), \ldots}
\end{aligned}
$ The range of fis the set of all second elements. It can be observed that all these elements are greater than or equal to 0 but less than 1. [Denominator is greater numerator] Thus, range of $f=[0,1)$Show Answer
Answer : $f, g: \mathbf{R} \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$ is defined as $f(x)=x+1, g(x)=2 x$ - 3 $(f+g)(x)=f(x)+g(x)=(x+1)+(2 x - 3)=3 x$ - 2 $\therefore(f+g)(x)=3 x$ - 2 $(f - g)(x)=f(x) - g(x)=(x+1)$ -$(2 x - 3)=x+1 -2 x+3= -x+4$ $\therefore(f-g)(x)=\hat{a}-x+4$ $
\begin{aligned}
& (\frac{f}{g})(x)=\frac{f(x)}{g(x)}, g(x) \neq 0, x \in \mathbf{R} \\
& \therefore(\frac{f}{g})(x)=\frac{x+1}{2 x-3}, 2 x-3 \neq 0 \text{ or } 2 x \neq 3 \\
& \therefore(\frac{f}{g})(x)=\frac{x+1}{2 x-3}, x \neq \frac{3}{2}
\end{aligned}
$Show Answer
Answer : $f={(1,1),(2,3),(0,-1),(-1,-3)}$ $f(x)=a x+b$ $(1,1) \in f$ $\Rightarrow f(1)=1$ $\Rightarrow a \times 1+b=1$ $\Rightarrow a+b=1$ $(0,-1) \in f$ $\Rightarrow f(0)=-1$ $\Rightarrow a \times 0+b=-1$ $\Rightarrow b=-1$ On substituting $b=-1$ in $a+b=1$, we obtain $a+(-1)=1 \Rightarrow a=1+1=2$. Thus, the respective values of aand bare 2 and -1 .Show Answer
(i) $(a, a) \in R$, for all $a \in \mathbf{N}$
(ii) $(a, b) \in R$, implies $(b, a) \in R$
(iii) $(a, b) \in R,(b, c) \in R$ implies $(a, c) \in R$.
Justify your answer in each case.
Answer: $ R=\{(a, b): a, b \in \mathbf{N}.$ and $.a=b^{2} \}$ (i) It can be seen that $2 \in \mathbf{N}$;however, $2 \neq 2^{2}=4$. Therefore, the statement " $(a, a) \in R$, for all $a \in \mathbf{N}$ " is not true. (ii) It can be seen that $(9,3) \in \mathbf{N}$ because $9,3 \in \mathbf{N}$ and $9=3^{2}$. Now, $3 \neq 9^{2}=81$; therefore, $(3,9) \in N$ Therefore, the statement " $(a, b) \in R$, implies $(b, a) \in R$ " is not true. (iii) It can be seen that $(16,4) \in R,(4,2) \in R$ because $16,4,2 \in \mathbf{N}$ and $16=4^{2}$ and $4=2^{2}$. Now, $16 \neq 2^{2}=4$; therefore, $(16,2) \in N$ Therefore, the statement " $(a, b) \in R,(b, c) \in R$ implies $(a, c) \in R$ " is not true.Show Answer
(i) $f$ is a relation from $A$ to $B$
(ii) $f$ is a function from $A$ to $B$.
Justify your answer in each case.
Answer : $A=\{1,2,3,4\}$ and $B=\{1,5,9,11,15,16\}$ $\therefore A \times B=\{(1,1),(1,5),(1,9),(1,11),(1,15),(1,16),(2,1),(2,5),(2,9),(2,11),(2,15),(2,16),(3,1),(3,5),(3,9)$, $(3,11),(3,15),(3,16),(4,1),(4,5),(4,9),(4,11),(4,15),(4,16)\}$ It is given that $f=\{(1,5),(2,9),(3,1),(4,5),(2,11)\}$ (i) A relation from a non-empty set $A$ to a non-empty set $B$ is a subset of the Cartesian product $A \times B$. It is observed that fis a subset of $A \times B$. Thus, fis a relation from $A$ to $B$. (ii) Since the same first element i.e., 2 corresponds to two different images i.e., 9 and 11 , relation $f$ is not a function.Show Answer
Answer : The relation fis defined as $f={(a b, a+b): a, b \in \mathbf{Z}}$ We know that a relation ffrom a set $A$ to a set $B$ is said to be a function if every element of set $A$ has unique images in set B. Since 2, 6, -2, -6 $\in \mathbf{Z},(2 \times 6,2+6),(-2 \times-6,-2+(-6)) \in f$ i.e., $(12,8),(12,-8) \in f$ It can be seen that the same first element i.e., 12 corresponds to two different images i.e., 8 and -8. Thus, relation fis not a function.Show Answer
Show Answer
Answer :
$A=\{9,10,11,12,13\}$
$f: A \to$ Nis defined as
$f(n)=$ The highest prime factor of $n$
Prime factor of $9=3$
Prime factors of $10=2,5$
Prime factor of $11=11$
Prime factors of $12=2,3$
Prime factor of $13=13$
$\therefore f(9)=$ The highest prime factor of $9=3$
$f(10)=$ The highest prime factor of $10=5$
$f(11)=$ The highest prime factor of $11=11$
$f(12)=$ The highest prime factor of $12=3$
$f(13)=$ The highest prime factor of $13=13$
The range of fis the set of all $f(n)$, where $n \in A$.
$\therefore$ Range of $f={3,5,11,13}$
Summary
In this Chapter, we studied about relations and functions. The main features of this Chapter are as follows:
Ordered pair A pair of elements grouped together in a particular order.
Cartesian product $A \times B$ of two sets $A$ and $B$ is given by
$A \times B=\{(a, b): a \in A, b \in B\}$
In particular $\mathbf{R} \times \mathbf{R}=\{(x, y): x, y \in \mathbf{R}\}$
and $\mathbf{R} \times \mathbf{R} \times \mathbf{R}=\{(x, y, z): x, y, z \in \mathbf{R}\}$
If $(a, b)=(x, y)$, then $a=x$ and $b=y$. If $n(A)=p$ and $n(B)=q$, then $n(A \times B)=p q$.
$\Delta A \times \phi=\phi$
In general, $A \times B \neq B \times A$.
Relation A relation $R$ from a set $A$ to a set $B$ is a subset of the cartesian product $A \times B$ obtained by describing a relationship between the first element $x$ and the second element $y$ of the ordered pairs in $A \times B$.
The image of an element $x$ under a relation $R$ is given by $y$, where $(x, y) \in R$,
The domain of $R$ is the set of all first elements of the ordered pairs in a relation $R$.
The range of the relation $R$ is the set of all second elements of the ordered pairs in a relation $R$.
Function A function $f$ from a set $A$ to a set $B$ is a specific type of relation for which every element $x$ of set $A$ has one and only one image $y$ in set $B$.
We write $f: A \rightarrow B$, where $f(x)=y$.
A is the domain and B is the codomain of $f$.
The range of the function is the set of images.
A real function has the set of real numbers or one of its subsets both as its domain and as its range.
Algebra of functions For functions $f: X \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$ and $g: X \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$, we have
$$ \begin{aligned} & (f+g)(x)=f(x)+g(x), x \in X \\ & (f-g)(x)=f(x)-g(x), x \in X \\ & (f . g)(x) \quad=f(x) \cdot g(x), x \in X \\ & (k f)(x) \quad=k(f(x)), x \in X, \text { where } k \text { is a real number. } \\ & (\frac{f}{g})(x)=\frac{f(x)}{g(x)}, x \in X, g(x) \neq 0 \end{aligned} $$
Historical Note
The word FUNCTION first appears in a Latin manuscript “Methodus tangentium inversa, seu de fuctionibus” written by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibnitz (1646-1716) in 1673; Leibnitz used the word in the non-analytical sense. He considered a function in terms of “mathematical job” - the “employee” being just a curve.
On July 5, 1698, Johan Bernoulli, in a letter to Leibnitz, for the first time deliberately assigned a specialised use of the term function in the analytical sense. At the end of that month, Leibnitz replied showing his approval.
Function is found in English in 1779 in Chambers’ Cyclopaedia: “The term function is used in algebra, for an analytical expression any way compounded of a variable quantity, and of numbers, or constant quantities”.






