Wave Motion 2 Question 43
43. A
Show Answer
Answer:
Correct Answer: 43.
Solution:
- Speed of sound
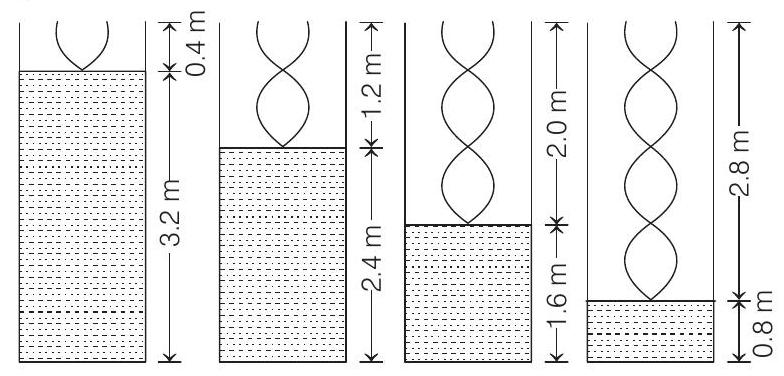
Let
In closed pipe only odd harmonics are obtained. Now let
or heights of water level are
Velocity of efflux,
Continuity equation at 1 and 2 gives
Substituting the values, we get
Between first two resonances, the water level falls from
or
or
NOTE
- Rate of fall of level at a heighth is
i.e., rate decreases as the height of water ( or any other liquid) decreases in the tank. That is why, the time required to empty the first half of the tank is less than the time required to empty the rest half of the tank.






