Properties of Matter 1 Question 6
6. A load of mass
(2019 Main, 12 Jan II)
(a) zero
(b)
(c)
(d)
Show Answer
Answer:
Correct Answer: 6. (d)
Solution:
- When load
where,
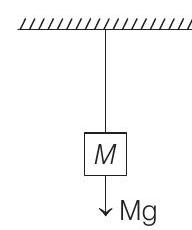
when load is immersed in liquid of relative density 2, increase in length of wire as shown in the figure is
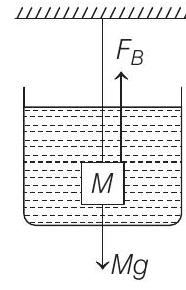
where,
Here given that,
So,
Dividing Eqs. (ii) by (i), we get






