Optics 7 Question 1
1. A convex lens (of focal length
(2019 Main, 8 April II)
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Show Answer
Solution:
- The given situation can be drawn as shown below
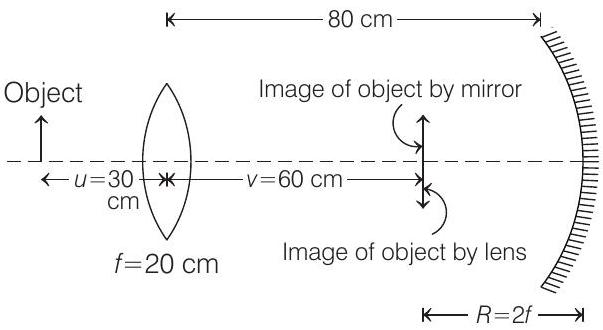
For lens formula,
Substituting given values, we get
So, this image is at a distance of
As, the image formed by the mirror coincides with image formed by the lens. This condition is only possible, if any object that has been placed in front of concave mirror is at centre of curvature, i.e. at
So, radius of curvature of mirror is
As, for virtual image, the object is to kept between pole and focus of the mirror.






