Optics 4 Question 22
23. A right angled prism
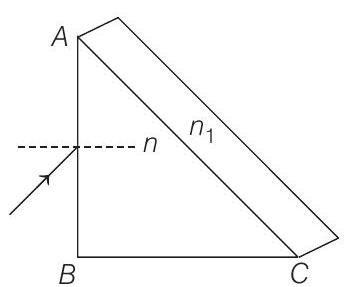
(1996, 3M)
(a) Calculate the angle of incidence at
(b) Assuming
Show Answer
Answer:
Correct Answer: 23. (a)
Solution:
- (a) Critical angle
Now, it is given that
Applying Snell’s law at face
Substituting value of
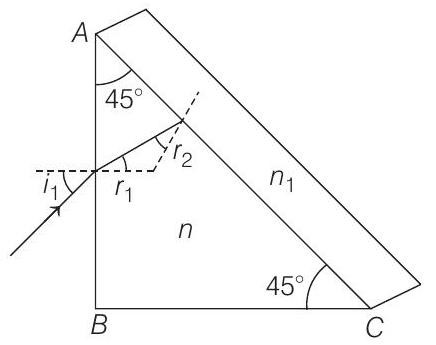
Therefore, required angle of incidence (
(b) The ray will pass undeviated through face
Here
or
Now applying Snell’s law at face
Therefore, required angle of incidence is






