Modern Physics 2 Question 34
33. Photoelectrons are emitted when
Show Answer
Answer:
Correct Answer: 33. During combination
Solution:
- Given work function,
Wavelength of incident light,
(Substituting the values of
Therefore, maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons
Now the situation is as shown below :
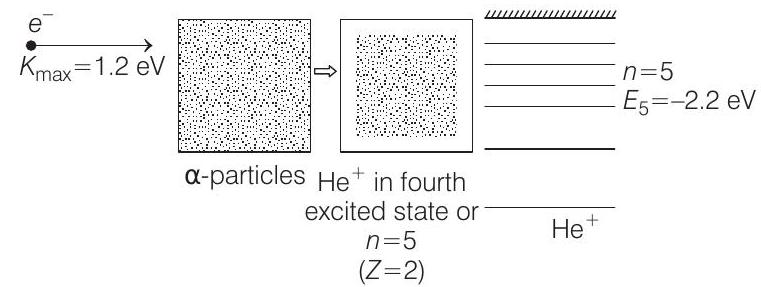
Energy of electron in
Therefore, energy released during the combination
Similarly, energies in other energy states of
The possible transitions are
Hence, the energy of emitted photons in the range of






