Heat and Thermodynamics 5 Question 48
49. Two moles of an ideal monoatomic gas initially at pressure $p _1$ and volume $V _1$ undergo an adiabatic compression until its volume is $V _2$. Then the gas is given heat $Q$ at constant volume $V _2$.
(1999, 10M)
(a) Sketch the complete process on a $p$ - $V$ diagram.
(b) Find the total work done by the gas, the total change in internal energy and the final temperature of the gas.
(Give your answer in terms of $p _1, V _1, V _2, Q$ and $R$ )
Show Answer
Solution:
- (a) The $p-V$ diagram for the complete process will be as shown below :
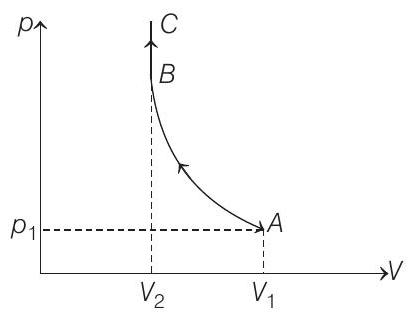
Process $A \rightarrow B$ is adiabatic compression and Process $B \rightarrow C$ is isochoric.
(b) (i) Total work done by the gas
Process $A \rightarrow B$
$$ \begin{aligned} W _{A B} & =\frac{p _A V _A-p _B V _B}{\gamma-1} \\ W _{\text {adiabatic }} & =\frac{p _i V _i-p _f V _f}{\gamma-1}=\frac{p _1 V _1-p _2 V _2}{\frac{5}{3}-1} \end{aligned} $$
$\gamma=5 / 3$ for monoatomic gas
$$ \begin{aligned} & =\frac{p _1 V _1-p _1\left(\frac{V _1}{V _2}\right)^{\gamma} V _2}{2 / 3} \quad\left[\begin{array}{c} p _1 V _1^{\gamma}=p _2 V _2^{\gamma} \\ \therefore p _2=p _1\left(\frac{V _1}{V _2}\right)^{\gamma} \end{array}\right] \\ & =\frac{3}{2} p _1 V _1\left[1-\left(\frac{V _1}{V _2}\right)^{\gamma-1}\right]=-\frac{3}{2} p _1 V _1\left[\left(\frac{V _1}{V _2}\right)^{5 / 3-1}-1\right] \\ & =-\frac{3}{2} p _1 V _1\left[\left(\frac{V _1}{V _2}\right)^{2 / 3}-1\right] \end{aligned} $$
Process $\boldsymbol{B} \rightarrow \boldsymbol{C} W _{B C}=0(V=$ constant $)$
$$ \begin{aligned} \therefore \quad W _{\text {Total }} & =W _{A B}+W _{B C} \\ & =-\frac{3}{2} p _1 V _1\left[\left(\frac{V _1}{V _2}\right)^{2 / 3}-1\right] \end{aligned} $$
(ii) Total change in internal energy
Process $\boldsymbol{A} \rightarrow \boldsymbol{B} Q _{A B}=0$ (Process is adiabatic)
$\therefore \Delta U _{A B}=-W _{A B}=\frac{3}{2} p _1 V _1\left[\left(\frac{V _1}{V _2}\right)^{2 / 3}-1\right]$
Process $\boldsymbol{B} \rightarrow \boldsymbol{C} W _{B C}=0$
$$ \therefore \quad \Delta U _{B C}=Q _{B C}=Q $$
$$ \therefore \quad \Delta U _{\text {Total }}=\Delta U _{A B}+\Delta U _{B C} $$
$$ =\frac{3}{2} p _1 V _1\left[\left(\frac{V _1}{V _2}\right)^{2 / 3}-1\right]+Q $$
(iii) Final temperature of the gas
$$ \begin{aligned} & \Delta U _{\text {Total }}=n C _V \Delta T=2\left(\frac{R}{\gamma-1}\right)\left(T _C-T _A\right) \\ & \therefore \frac{3}{2} p _1 V _1\left[\left(\frac{V _1}{V _2}\right)^{2 / 3}-1\right]+Q=\frac{2 R}{5 / 3-1}\left(T _C-\frac{p _A V _A}{2 R}\right) \\ & \text { or } \frac{3}{2} p _1 V _1\left[\left(\frac{V _1}{V _2}\right)^{2 / 3}-1\right]+Q=3 R\left(T _C-\frac{p _1 V _1}{2 R}\right) \\ & \therefore T _C=\frac{Q}{3 R}+\frac{p _1 V _1}{2 R}\left(\frac{V _1}{V _2}\right)^{2 / 3}=T _{\text {final }} \end{aligned} $$






