Electrostatics 2 Question 26
27. Four point charges $+8 \mu C,-1 \mu C,-1 \mu C$ and $+8 \mu C$ are fixed at the points $-\sqrt{27 / 2} m,-\sqrt{3 / 2} m,+\sqrt{3 / 2} m$ and $+\sqrt{27 / 2} m$ respectively on the $y$-axis. A particle of mass $6 \times 10^{-4} kg$ and charge $+0.1 \mu C$ moves along the $x$-direction. Its speed at $x=+\infty$ is $v _0$. Find the least value of $v _0$ for which the particle will cross the origin. Find also the kinetic energy of the particle at the origin. Assume that space is gravity free. $\left(1 / 4 \pi \varepsilon _0=9 \times 10^{9} Nm^{2} / C^{2}\right)$.
(2000, 10 M)
Show Answer
Solution:
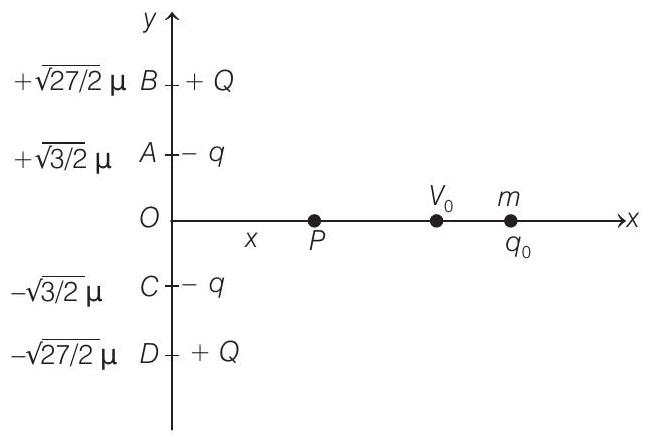
In the figure, $q=1 \mu C=10^{-6} C, q _0=+0.1 \mu C=10^{-7} C$
and $m=6 \times 10^{-4} kg$ and $Q=8 \mu C=8 \times 10^{-6} C$
Let $P$ be any point at a distance $x$ from origin $O$. Then
$$ \begin{aligned} & A P=C P=\sqrt{\frac{3}{2}+x^{2}} \\ & B P=D P=\sqrt{\frac{27}{2}+x^{2}} \end{aligned} $$
Electric potential at point $P$ will be, $V=\frac{2 K Q}{B P}-\frac{2 K q}{A P}$
where, $K=\frac{1}{4 \pi \varepsilon _0}=9 \times 10^{9} Nm^{2} / C^{2}$
$$ \begin{aligned} \therefore \quad V & =2 \times 9 \times 10^{9} \frac{8 \times 10^{-6}}{\sqrt{\frac{27}{2}+x^{2}}}-\frac{10^{-6}}{\sqrt{\frac{3}{2}+x^{2}}} \\ V & =1.8 \times 10^{4} \frac{8}{\sqrt{\frac{27}{2}+x^{2}}}-\frac{1}{\sqrt{\frac{3}{2}+x^{2}}} \end{aligned} $$
$\therefore \quad$ Electric field at point $P$ is
$$ \begin{array}{r} E=-\frac{d V}{d X}=1.8 \times 10^{4} \text { (8) } \frac{-1}{2} \quad \frac{27}{2}+x^{2} \\ -\frac{1}{2} \quad \frac{3}{2}+x^{2} \end{array} $$
$E=0$ on $x$-axis where $x=0$,
or $\quad \frac{8}{\frac{27}{2}+x^{2}}=\frac{1}{\frac{3}{2}+x^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \quad \frac{(4)^{3 / 2}}{\frac{27}{2}+x^{2}}{ }^{3 / 2}=\frac{1}{\frac{3}{2}+x^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \quad \frac{27}{2}+x^{2}=4 \frac{3}{2}+x^{2}$
This equation gives, $x= \pm \sqrt{\frac{5}{2}} m$
The least value of kinetic energy of the particle at infinity should be enough to take the particle upto $x=+\sqrt{\frac{5}{2}} m$ because at $x=+\sqrt{\frac{5}{2}} m, E=0$.
$\Rightarrow$ Electrostatic force on charge $q$ is zero or $F _e=0$.
For at $x>\sqrt{\frac{5}{2}} m, E$ is repulsive (towards positive $x$-axis)
and for $x<\sqrt{\frac{5}{2}} m, E$ is attractive (towards negative $x$-axis)
Now, from Eq. (i), potential at $x=\sqrt{\frac{5}{2}} m$
$$ V=1.8 \times 10^{4} \frac{8}{\sqrt{\frac{27}{2}+\frac{5}{2}}}-\frac{1}{\sqrt{\frac{3}{2}+\frac{5}{2}}} $$
$$ V=2.7 \times 10^{4} V $$
Applying energy conservation at $x=\infty$ and $x=\sqrt{\frac{5}{2}} m$
$$ \begin{aligned} \frac{1}{2} m v _0^{2} & =q _0 V \\ \therefore \quad v _0 & =\sqrt{\frac{2 q _0 V}{m}} \end{aligned} $$
Substituting these values,
$$ v _0=\sqrt{\frac{2 \times 10^{-7} \times 2.7 \times 10^{4}}{6 \times 10^{-4}}} . \Rightarrow v _0=3 m / s $$
$\therefore$ Minimum value of $v _0$ is $3 m / s$
From Eq. (i), potential at origin $(x=0)$ is
$$ V _0=1.8 \times 10^{4} \frac{8}{\sqrt{\frac{27}{2}}}-\frac{1}{\sqrt{\frac{3}{2}}} \approx 2.4 \times 10^{4} V $$
Let $K$ be the kinetic energy of the particle at origin. Applying energy conservation at $x=0$ and at $x=\infty$
$$ K+q _0 V _0=\frac{1}{2} m v _0^{2} $$
But $\quad \frac{1}{2} m v _0^{2}=q _0 V$ [from Eq. (ii)]
$$ \begin{aligned} & K=q _0\left(V-V _0\right) \\ & K=\left(10^{-7}\right)\left(2.7 \times 10^{4}-2.4 \times 10^{4}\right) \\ & K=3 \times 10^{-4} J \end{aligned} $$
NOTE $E=0$ or $F _e$ on $q _0$ is zero at $x=0$ and $x= \pm \sqrt{\frac{5}{2}} m$ of
these $x=0$ is stable equilibrium position and $x= \pm \sqrt{\frac{5}{2}}$ is
unstable equilibrium position.






