Current Electricity 4 Question 6
6. The galvanometer deflection, when key
(Main 2019, 12 Jan I)
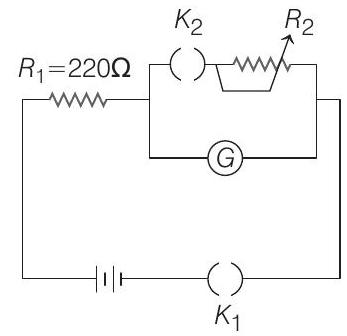
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Show Answer
Solution:
- For a galvanometer,
where,
and
Now,
where,
Hence, galvanometer current is
i.e.,
where,
As deflection is given
When both keys
Current through galvanometer will be
Now, dividing Eq. (i) by Eq. (ii), we get
Substituting
we get






