Theory of Equations 5 Question 12
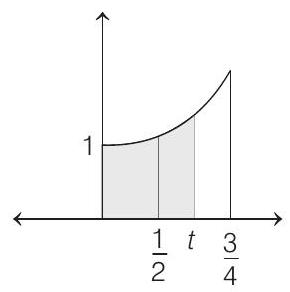
12. The smallest value of
(2009)
Then, the quadratic equation
(a) no root in
(b) atleast one root in
(c) a double root in
(d) two imaginary roots
Objective Questions II
(One or more than one correct option)
Show Answer
Solution:
Now,