Straight Line and Pair of Straight Lines 2 Question 8
8. Lines
Show Answer
Answer:
Correct Answer: 8.
Solution:
- Since, the required line
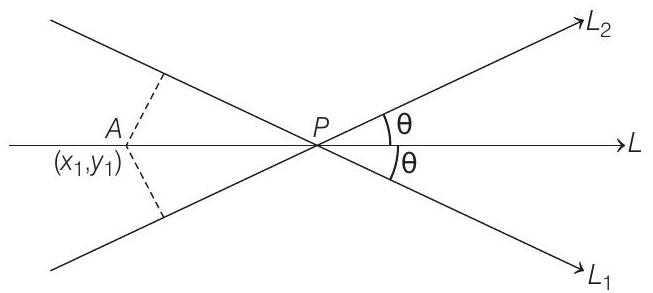
So, the equation of the required line
i.e.
where,
Since,
But,
On substituting
On substituting the value of
which is the required equation of line






