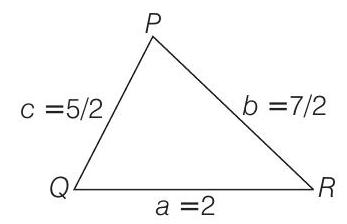Properties of Triangles 2 Question 2
2. If
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(2012)
Show Answer
Answer:
Correct Answer: 2. (c)
Solution:
- PLAN If
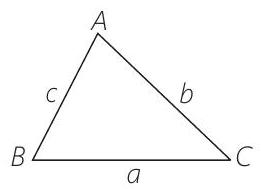
Then,