Limit Continuity and Differentiability 4 Question 5
5. For each positive integer
For
Fill in the Blank
Show Answer
Answer:
Correct Answer: 5. (c)
Solution:
- Given function
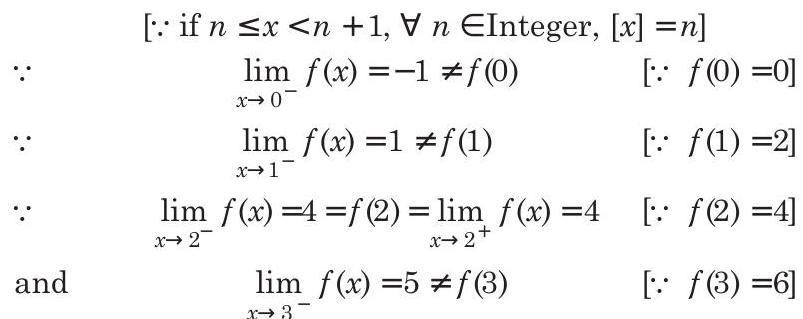
For
Correct Answer: 5. (c)
Solution:
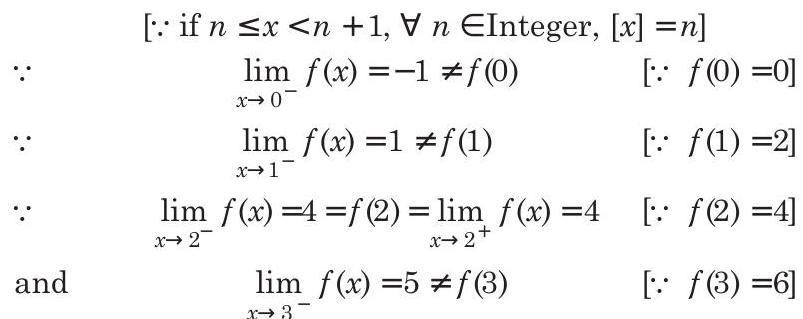
© 2024 कॉपीराइट SATHEE
द्वारा संचालित Prutor@IITK
Welcome to SATHEE !
Select from 'Menu' to explore our services, or ask SATHEE to get started. Let's embark on this journey of growth together! 🌐📚🚀🎓
I'm relatively new and can sometimes make mistakes.
If you notice any error, such as an incorrect solution, please use the thumbs down icon to aid my learning.
To begin your journey now, click on "I understand".