Complex Numbers 2 Question 20
20. The inequality
(1982, 2M)
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) None of these
Show Answer
Answer:
Correct Answer: 20. (b)
Solution:
- Given,
Since,
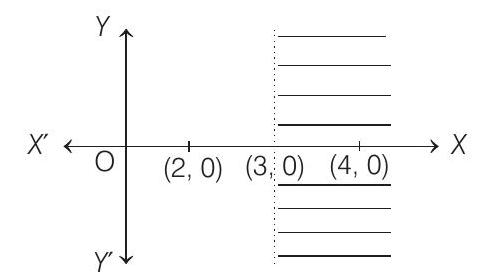
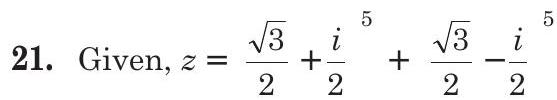
Now,
Alternate Solution
We know that,
If






