Application of Derivatives 4 Question 45
47. If
Show Answer
Answer:
Correct Answer: 47.
Solution:
- Let the square
We have,
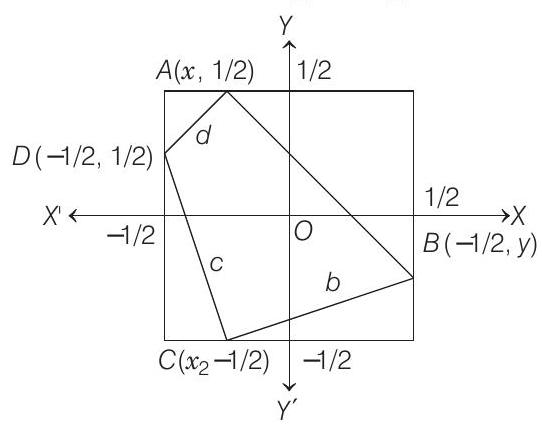
Similarly,
Therefore,
Alternate Solution
On adding Eqs. (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv), we get
where
Now, consider the function
Again
Hence,






