3D Geometry 1 Question 3
The vertices
(2019 Main, 9 April II)
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) 6
Show Answer
Answer:
Correct Answer: (a)
Solution:
Method 1:
Let’s approach this step-by-step:
-
First, we need to find the coordinates of points B and C. We know they lie on the line given by the equation:
-
This line passes through the point (-2, 1, 0) and is parallel to the vector (3, 0, 4). So we can parameterize the line as:
-
Now, we’re told that the distance between B and C is 5 units. Using the distance formula in 3D, we get:
-
Without loss of generality, let’s choose
-
Now we have the coordinates of all three vertices of the triangle:
-
To find the area of the triangle, we can use the formula:
where
-
-
Therefore, the area of the triangle is:
So the correct answer is (a)
Alternate Method
Given line is
Vector along line is,
and vector joining the points
and
Now, area of required
[where
and
On substituting these values in Eq. (i), we get
Required area
Alternate Method
Given line is
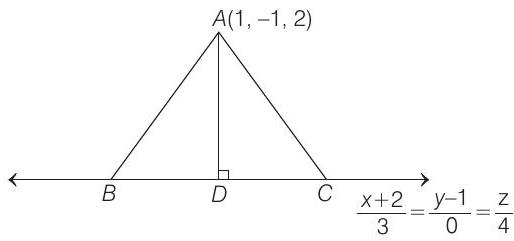
Since, point
Now,
and
Since,
Now,






