Question: Q. 10. A ray of light, incident on an equilateral glass prism
A [Delhi I, II, III 2012]
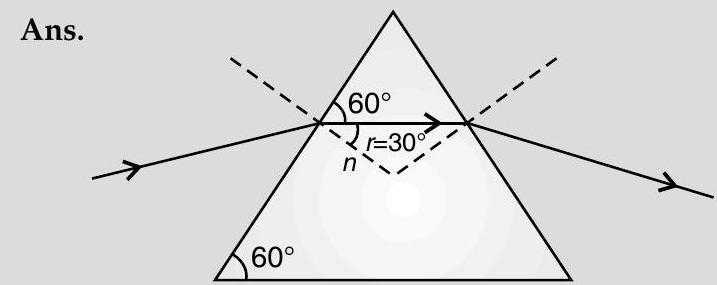
From the diagram,
Also
or,
or,
or,
[CBSE Marking Scheme 2012]
Short Answer Type Questions-II
(3 marks each)
Q. 1. (i) Show using a proper diagram how unpolarized light can be linearly polarised by reflection from a transparent glass surface.
(ii) The figure shows a ray of light falling normally on on the face
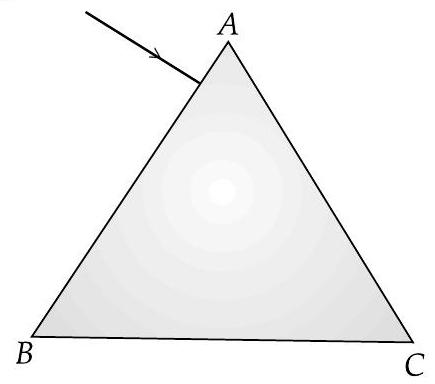
A [CBSE 2018, 2012]
Show Answer
Solution:
Ans. (i) The diagram, showing polarisation by reflection is as shown. [Here the reflected and refracted rays are at right angle to each other.
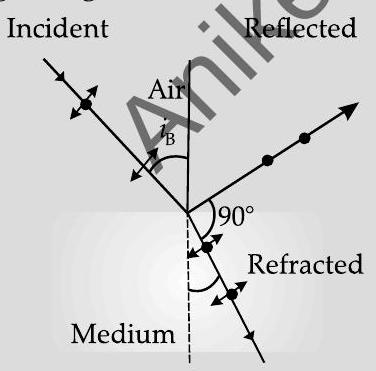
Thus light gets totally polarised by reflection when it is incident at an angle
(ii) The angle of incidence, of the ray, on striking the face
Also, relative refractive index of glass, with respect to the surrounding water, is
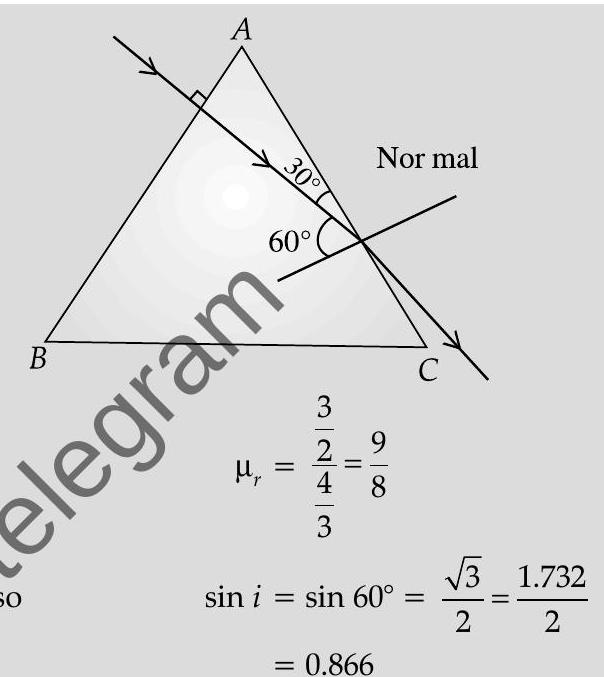
For total internal reflection, the required critical angle, in this case, is given by
Hence the ray would not suffer total internal reflection on striking the face
[The student may just write the two conditions needed for total internal reflection without analysis of the given case.
The student may be awarded
[CBSE Marking Scheme 2018]
AT Q. 2. (i) Monochromatic light of wavelength
(ii) A double convex lens is made of a glass of refractive index 1.55, with both faces of the same radius of curvature. Find the radius of curvature required, if the focal length is
U [OD I, II, III, 2016]
Ans. (i)
Frequency,
Speed
(ii)
[CBSE Marking Scheme 2016]






