Question: Q. 3. (i) Explain, using suitable diagrams, the difference in the behaviour of (a) conductor and (b) dielectric in the presence of an external electric field. Define the terms polarization of a dielectric and write its relation with susceptibility.
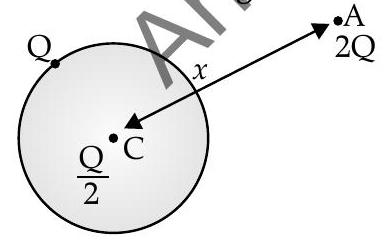
(ii) A thin metallic spherical shell of radius
U] [Delhi I, II, III 2015]
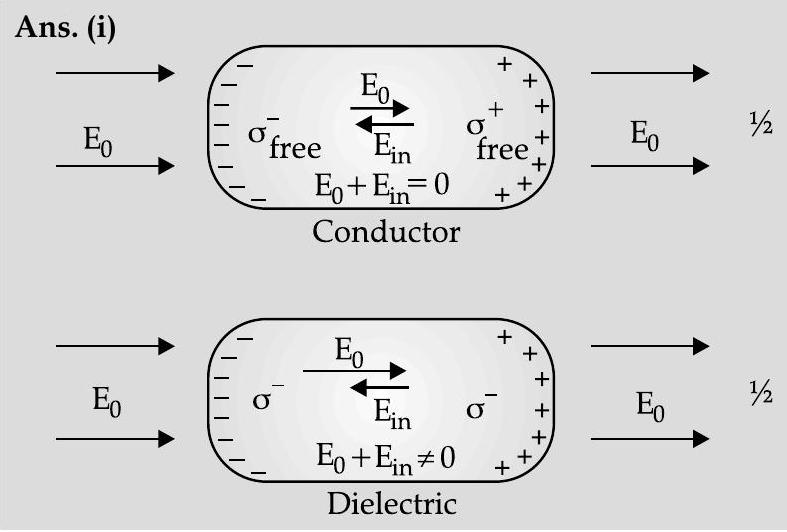
(a) In the presence of electric field, the free charge carriers, in a conductor, move the charge distribution in the conductor re-adjusting itself so that the net electric field within the conductor becomes zero.
(b) In a dielectric, the external electric field induces a net dipole moment, by stretching/reorienting the molecules. The electric field, due to this induced dipole moment, opposes, but does not exactly cancel, the external electric field.
(ii) (a) Net Force on the charge
1 Force oncharge
OR
where,
(b) Electric flux through the shell
[CBSE Marking Scheme 2015]
AT Q. 4. (i) Compare the individual dipole moment and the specimen dipole moment for $\mathrm{H}{2} \mathrm{O}
(a) Absence of external electric field.
(b) Presence of external electric field.
Justify your answer.
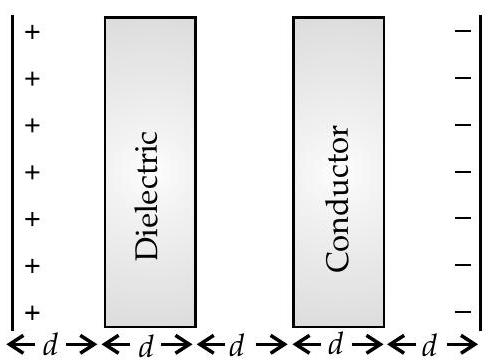
(ii) Given two parallel conducting plates of area
(a) Find the potential difference between the plates.
(b) Plot
U[CBSE SQP 2015-16]
Show Answer
Solution:
Ans. (i)
| Non-polar |
Polar |
|
|---|---|---|
| In absence of electric field |
No dipole moment exists. |
Dipole moment exists. |
| Individual | No dipole moment exists. |
Dipoles randomly oriented. Net |
| In presence of electric field |
Dipole moment exists (molecules become polarised.) |
Torque acts on the molecules to align them parallel to E. |
| Individual dipole | ||
| Specimen | Dipole moment exists. |
Net moment parallel to E. |
(ii) (a)