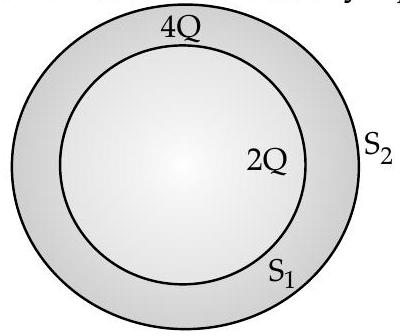
Question: Q. 10. Consider two hollow concentric spheres, and enclosing charges and respectively as shown in the figure. (i) Find out the ratio of the electric flux through them. (ii) How will the electric flux through the sphere change if a medium of dielectric constant ’ ’ is introduced in the space inside in place of air ? Deduce the necessary expression.
[O.D. I, II, III 2014]
Show Answer
Solution:
Ans. According to the Gauss’s law,
Forsphere , flux enclosed
nd for sphere , flux enclosed
When a medium of dielectric constant is introduced in the space inside sphere , the flux through would be .
[CBSE Marking Scheme, 2014]
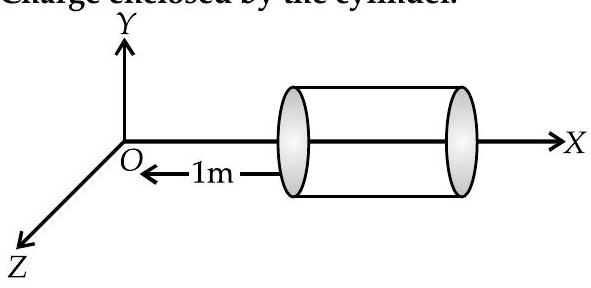
AI Q. 11. A hollow cylindrical box of length and area of cross-section is placed in a three dimensional coordinate system as shown in the figure. The electric field in the region is given by , where is in and is in metres. Find
(i) Net flux through the cylinder.
(ii) Charge enclosed by the cylinder.
A&E [Delhi I, II, III 2013]
Ans. (i) Given :
and
or
As the electric field is only along the -axis, hence, flux will pass only through the cross-section of cylinder.
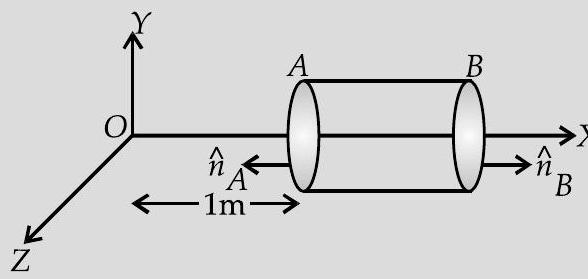
Magnitude of electric field at cross-section ,
Magnitude of electric field at cross-section ,
The corresponding electric fluxes are
So, the net flux through the cylinder,
(ii) Using the Gauss’s law,









