Question: Q. 6. Draw an arrangement for winding of primary and secondary coils in a transformer with two coils on a separate limb of the core.
State the underlying principle of a transformer. Deduce the expression for the ratio of secondary voltage to the primary voltage in terms of the ratio of the number of turns of primary and secondary winding. For an ideal transformer, obtain the ratio of primary and secondary currents in terms of the ratio of the voltages in the secondary and primary voltages.
Write any two reasons for the energy losses which occur in actual transformers.
U] [Delhi Comptt. 2016]
Show Answer
Solution:
Ans. Try yourself, Similar to Q. 1 (i), Long Answer type Questions.
Two reasons for energy losses
Flux leakage / joule heat losses in the windings / Eddy currents / hysteresis
(Any two)
[CBSE Marking Scheme 2016]
[AT Q. 7. (i) Write the function of a transformer. State its principle of working with the help of a diagram. Mention various energy losses in this device.
(ii) The primary coil of an ideal step up transformer has 100 turns and transformation ratio is also 100. The input voltage and power are respectively
(a) number of turns in secondary
(b) current in primary
(c) voltage across secondary
(d) current in secondary
(e) power in secondary
R [Delhi I, II, III 2016]
Ans. (i) Conversion of
Working Principle :
Mutual induction : When alternating voltage is applied to primary windings, emf is induced in the secondary windings.
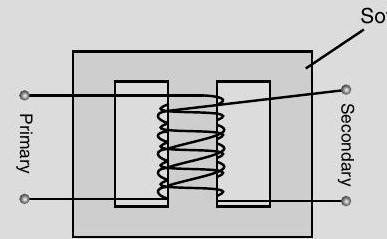
(a)
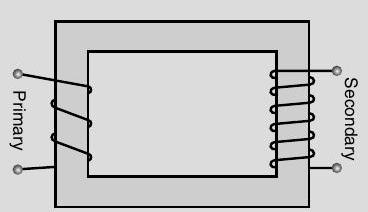
(b) (Any one of the above diagram)
Energy losses :
- Leakage of magnetic flux
- Eddy currents
- Hysteresis loss
- Copper loss
(ii)
Transformation ratio
(a) Number of turns in secondary coil
(b) Input Power
(c)
(d)
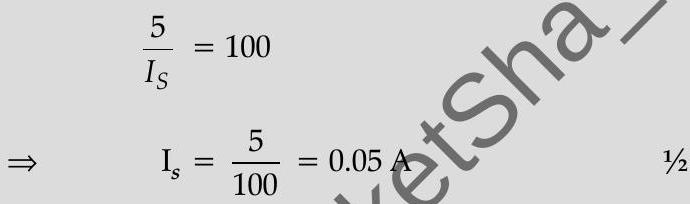
(e) Power in secondary
-
[CBSE Marking Scheme 2016]






