Chapter-08 Application of Integrals
One should study Mathematics because it is only through Mathematics that nature can be conceived in harmonious form. - BIRKHOFF
8.1 Introduction
In geometry, we have learnt formulae to calculate areas of various geometrical figures including triangles, rectangles, trapezias and circles. Such formulae are fundamental in the applications of mathematics to many real life problems. The formulae of elementary geometry allow us to calculate areas of many simple figures. However, they are inadequate for calculating the areas enclosed by curves. For that we shall need some concepts of Integral Calculus.
In the previous chapter, we have studied to find the area bounded by the curve $y=f(x)$, the ordinates $x=a$, $x=b$ and $x$-axis, while calculating definite integral as the limit of a sum. Here, in this chapter, we shall study a specific application of integrals to find the area under simple curves, area between lines and arcs of circles, parabolas and

A.L. Cauchy (1789-1857) ellipses (standard forms only). We shall also deal with finding the area bounded by the above said curves.
8.2 Area under Simple Curves
In the previous chapter, we have studied definite integral as the limit of a sum and how to evaluate definite integral using Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. Now, we consider the easy and intuitive way of finding the area bounded by the curve $y=f(x), x$-axis and the ordinates $x=a$ and $x=b$. From Fig 8.1, we can think of area under the curve as composed of large number of very thin vertical strips. Consider an arbitrary strip of height $y$ and width $d x$, then $d A$ (area of the elementary strip) $=y d x$, where, $y=f(x)$.

This area is called the elementary area which is located at an arbitrary position within the region which is specified by some value of $x$ between $a$ and $b$. We can think of the total area A of the region between $x$-axis, ordinates $x=a, x=b$ and the curve $y=f(x)$ as the result of adding up the elementary areas of thin strips across the region PQRSP. Symbolically, we express
$$ \mathrm{A}=\int _{a}^{b} d \mathrm{~A}=\int _{a}^{b} y d x=\int _{a}^{b} f(x) d x $$
The area $A$ of the region bounded by the curve $x=g(y), y$-axis and the lines $y=c$, $y=d$ is given by
$$ \mathrm{A}=\int _{c}^{d} x d y=\int _{c}^{d} g(y) d y $$
Here, we consider horizontal strips as shown in the Fig 8.2

Fig 8.2
Remark If the position of the curve under consideration is below the $x$-axis, then since $f(x)<0$ from $x=a$ to $x=b$, as shown in Fig 8.3, the area bounded by the curve, $x$-axis and the ordinates $x=a, x=b$ come out to be negative. But, it is only the numerical value of the area which is taken into consideration. Thus, if the area is negative, we take its absolute value, i.e., $|\int_a^{b} f(x) d x|$.

Fig 8.3
Generally, it may happen that some portion of the curve is above $x$-axis and some is below the $x$-axis as shown in the Fig 8.4. Here, $A_1<0$ and $A_2>0$. Therefore, the area A bounded by the curve $y=f(x), x$-axis and the ordinates $x=a$ and $x=b$ is given by $A=|A_1|+A_2$.

Fig 8.4
Example 1 Find the area enclosed by the circle $x^{2}+y^{2}=a^{2}$.
Solution From Fig 8.5, the whole area enclosed by the given circle $=4$ (area of the region AOBA bounded by the curve, $x$-axis and the ordinates $x=0$ and $x=a$ ) [as the circle is symmetrical about both $x$-axis and $y$-axis]
$$ \begin{aligned} & =4 \int_0^{a} y d x \text{ (taking vertical strips) } \\ & =4 \int_0^{a} \sqrt{a^{2}-x^{2}} d x \end{aligned} $$
Since $x^{2}+y^{2}=a^{2}$ gives $\quad y= \pm \sqrt{a^{2}-x^{2}}$

Fig 8.5
As the region AOBA lies in the first quadrant, $y$ is taken as positive. Integrating, we get the whole area enclosed by the given circle
$ \begin{aligned} & =4[\frac{x}{2} \sqrt{a^{2}-x^{2}}+\frac{a^{2}}{2} \sin ^{-1} \frac{x}{a}]_0^{a} \\ & =4[(\frac{a}{2} \times 0+\frac{a^{2}}{2} \sin ^{-1} 1)-0]=4(\frac{a^{2}}{2})(\frac{\pi}{2})=\pi a^{2} \end{aligned} $
Alternatively, considering horizontal strips as shown in Fig 8.6, the whole area of the region enclosed by circle
$ \begin{aligned} & =4 \int_0^{a} x d y=4 \int_0^{a} \sqrt{a^{2}-y^{2}} d y \text{(Why?)} \\ & =4[\frac{y}{2} \sqrt{a^{2}-y^{2}}+\frac{a^{2}}{2} \sin ^{-1} \frac{y}{a}]_0^{a} \\ & =4[(\frac{a}{2} \times 0+\frac{a^{2}}{2} \sin ^{-1} 1)-0] \\ & =4 \frac{a^{2}}{2} \frac{\pi}{2}=\pi a^{2} \end{aligned} $

Fig 8.6
Example 2 Find the area enclosed by the ellipse $\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}+\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}=1$
Solution From Fig 8.7, the area of the region $ABA^{\prime} B^{\prime} A$ bounded by the ellipse
$=4(\begin{matrix} \text{ area of the region } A O B A \text{ in the first quadrant bounded } \\ \text{ by the curve, } x-\text{ axis and theordinates } x=0, x=a\end{matrix} )$
(as the ellipse is symmetrical about both $x$-axis and $y$-axis)
$=4 \int_0^{a} y d x \quad$ (taking vertical strips)
Now $\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}+\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}=1$ gives $y= \pm \frac{b}{a} \sqrt{a^{2}-x^{2}}$, but as the region AOBA lies in the first quadrant, $y$ is taken as positive. So, the required area is
$ \begin{aligned} & =4 \int _{0}^{a} \frac{b}{a} \sqrt{a^{2}-x^{2}} d x \\ & =\frac{4 b}{a}\left[\frac{x}{2} \sqrt{a^{2}-x^{2}}+\frac{a^{2}}{2} \sin ^{-1} \frac{x}{a}\right] _{0}^{a} \text { (Why) } \\ & =\frac{4 b}{a}\left[\left(\frac{a}{2} \times 0+\frac{a^{2}}{2} \sin ^{-1} 1\right)-0\right] \\ & =\frac{4 b}{a} \frac{a^{2}}{2} \frac{\pi}{2}=\pi a b \text { } \end{aligned} $

Fig 8.7
Alternatively, considering horizontal strips as shown in the Fig 8.8, the area of the ellipse is
$$ \begin{aligned} & =4 \int_0^{b} x d y=4 \frac{a}{b} \int_0^{b} \sqrt{b^{2}-y^{2}} d y \text{ (Why?) } \\ & =\frac{4 a}{b}[\frac{y}{2} \sqrt{b^{2}-y^{2}}+\frac{b^{2}}{2} \sin ^{-1} \frac{y}{b}]_0^{b} \\ & =\frac{4 a}{b}[(\frac{b}{2} \times 0+\frac{b^{2}}{2} \sin ^{-1} 1)-0] \\ & =\frac{4 a}{b} \frac{b^{2}}{2} \frac{\pi}{2}=\pi a b \end{aligned} $$

Fig 8.8
EXERCISE 8.1
1. Find the area of the region bounded by the ellipse $\frac{x^{2}}{16}+\frac{y^{2}}{9}=1$.
Show Answer
Solution
The given equation of the ellipse, $\frac{x^{2}}{16}+\frac{y^{2}}{9}=1$, can be represented as
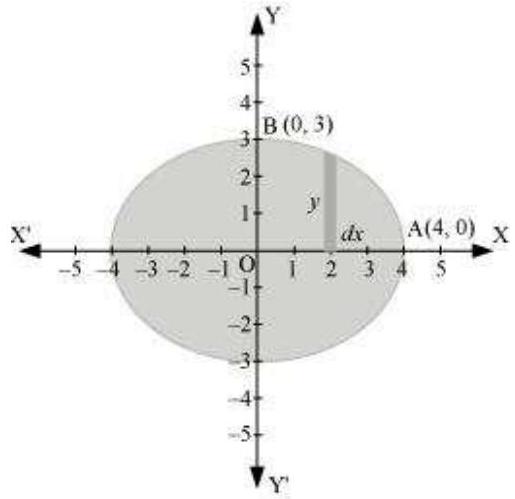
It can be observed that the ellipse is symmetrical about $x$-axis and $y$-axis.
$\therefore$ Area bounded by ellipse $=4 \times$ Area of OAB
$ \begin{aligned} \text{ Area of } OAB & =\int_0^{4} y d x \\ & =\int_0^{4} 3 \sqrt{1-\frac{x^{2}}{16}} d x \\ & =\frac{3}{4} \int_0^{4} \sqrt{16-x^{2}} d x \\ & =\frac{3}{4}[\frac{x}{2} \sqrt{16-x^{2}}+\frac{16}{2} \sin ^{-1} \frac{x}{4}]_0^{4} \\ & =\frac{3}{4}[2 \sqrt{16-16}+8 \sin ^{-1}(1)-0-8 \sin ^{-1}(0)] \\ & =\frac{3}{4}[\frac{8 \pi}{2}] \\ & =\frac{3}{4}[4 \pi] \\ & =3 \pi \end{aligned} $
Therefore, area bounded by the ellipse $=4 \times 3\pi =12 \pi$ units
2. Find the area of the region bounded by the ellipse $\frac{x^{2}}{4}+\frac{y^{2}}{9}=1$.
Show Answer
Solution
The given equation of the ellipse can be represented as
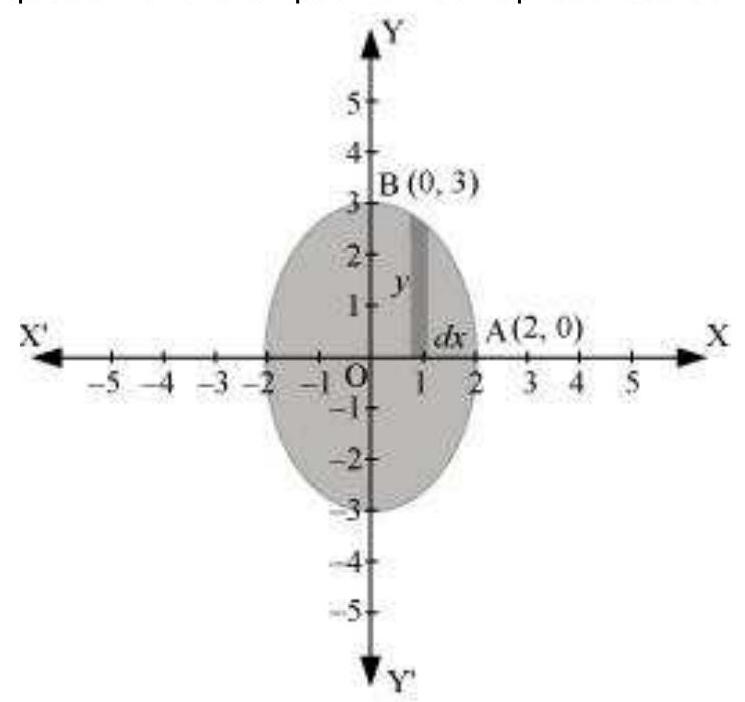
$\frac{x^{2}}{4}+\frac{y^{2}}{9}=1$
$\Rightarrow y=3 \sqrt{1-\frac{x^{2}}{4}}$
It can be observed that the ellipse is symmetrical about $x$-axis and $y$-axis.
$\therefore$ Area bounded by ellipse $=4 \times$ Area OAB $\therefore$ Area of $OAB=\int_0^{2} y d x$
$ \begin{aligned} & =\int_0^{2} 3 \sqrt{1-\frac{x^{2}}{4}} d x \quad \text{ [Using (1)] } \\ & =\frac{3}{2} \int_0^{2} \sqrt{4-x^{2}} d x \\ & =\frac{3}{2}[\frac{x}{2} \sqrt{4-x^{2}}+\frac{4}{2} \sin ^{-} \frac{x}{2}]_0^{2} \\ & =\frac{3}{2}[\frac{2 \pi}{2}] \\ & =\frac{3 \pi}{2} \end{aligned} $
Therefore, area bounded by the ellipse $=4 \times \frac{3 \pi}{2}=6 \pi$ units
Choose the correct answer in the following Exercises 3 and 4.
3. Area lying in the first quadrant and bounded by the circle $x^{2}+y^{2}=4$ and the lines $x=0$ and $x=2$ is
$\quad\quad$(A) $\pi$
$\quad\quad$(B) $\frac{\pi}{2}$
$\quad\quad$(C) $\frac{\pi}{3}$
$\quad\quad$(D) $\frac{\pi}{4}$
Show Answer
Solution
The area bounded by the circle and the lines, $x=0$ and $x=2$, in the first quadrant is represented as
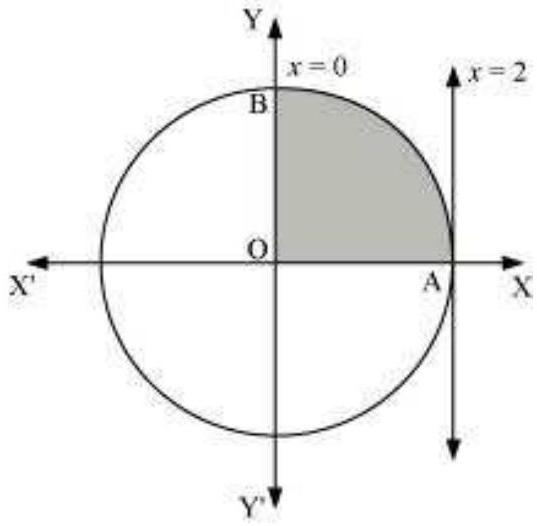
$ \begin{aligned} \therefore \text{ Area OAB } & =\int_0^{2} y d x \\ & =\int_0^{2} \sqrt{4-x^{2}} d x \\ & =[\frac{x}{2} \sqrt{4-x^{2}}+\frac{4}{2} \sin ^{-1} \frac{x}{2}]_0^{2} \\ & =2(\frac{\pi}{2}) \\ & =\pi \text{ units } \end{aligned} $
Thus, the correct answer is $A$.
4. Area of the region bounded by the curve $y^{2}=4 x, y$-axis and the line $y=3$ is
$\quad\quad$(A) 2
$\quad\quad$(B) $\frac{9}{4}$
$\quad\quad$(C) $\frac{9}{3}$
$\quad\quad$(D) $\frac{9}{2}$
Show Answer
Solution
The area bounded by the curve, $y^{2}=4 x, y$-axis, and $y=3$ is represented as
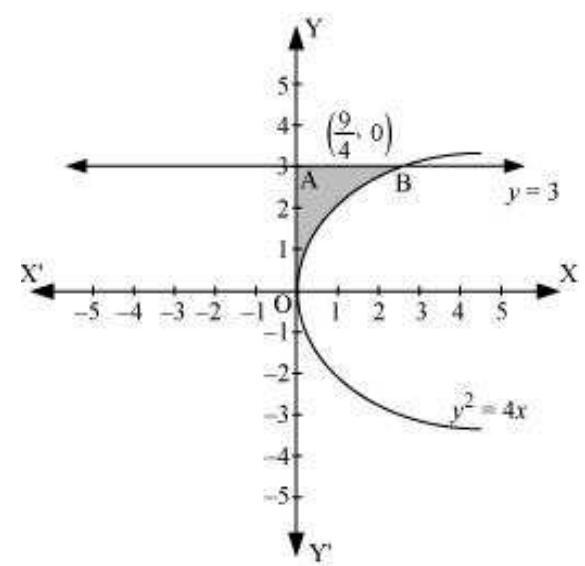
$\therefore$ Area $OAB=\int_0^{3} x d y$
$ =\int_0^{3} \frac{y^{2}}{4} d y $
$ \begin{aligned} & =\frac{1}{4}[\frac{y^{3}}{3}]_0^{3} \\ & =\frac{1}{12}(27) \\ & =\frac{9}{4} \text{ units } \end{aligned} $
Thus, the correct answer is $B$.
Miscellaneous Examples
Example 3 Find the area of the region bounded by the line $y=3 x+2$, the $x$-axis and the ordinates $x=-1$ and $x=1$.
Solution As shown in the Fig 8.9, the line $y=3 x+2$ meets $x$-axis at $x=\frac{-2}{3}$ and its graph lies below $x$-axis for $x \in(-1, \frac{-2}{3})$ and above $x$-axis for $x \in(\frac{-2}{3}, 1)$.
The required area $=$ Area of the region $ACBA+$ Area of the region ADEA
$ \begin{aligned} & =|\int _{-1}^{\frac{-2}{3}}(3 x+2) d x|+\int _{\frac{-2}{3}}^{1}(3 x+2) d x \\ & =|[\frac{3 x^{2}}{2}+2 x] _{-1}^{\frac{-2}{3}}|+[\frac{3 x^{2}}{2}+2 x] _{\frac{-2}{3}}^{1}=\frac{1}{6}+\frac{25}{6}=\frac{13}{3} \end{aligned} $

Fig 8.9
Example 4 Find the area bounded by the curve $y=\cos x$ between $x=0$ and $x=2 \pi$.
Solution From the Fig 8.10, the required area $=$ area of the region $OABO+$ area of the region $BCDB+$ area of the region DEFD.

Fig 8.10
Thus, we have the required area
$ \begin{aligned} & =\int_ 0^{\frac{\pi}{2}} \cos x d x+|\int_ {\frac{\pi}{2}}^{\frac{3 \pi}{2}} \cos x d x|+\int_ {\frac{3 \pi}{2}}^{2 \pi} \cos x d x \\ & =[\sin x]_ 0^{\frac{\pi}{2}}+|[\sin x]_ {\frac{\pi}{2}}^{\frac{3 \pi}{2}}|+[\sin x]_ {\frac{3 \pi}{2}}^{2 \pi} \\ & =1+2+1=4 \end{aligned} $
Miscellaneous Exercise on Chapter 8
1. Find the area under the given curves and given lines:
$\quad\quad$(i) $y=x^{2}, x=1, x=2$ and $x$-axis
$\quad\quad$(ii) $y=x^{4}, x=1, x=5$ and $x$-axis
Show Answer
Solution
i. The required area is represented by the shaded area ADCBA as
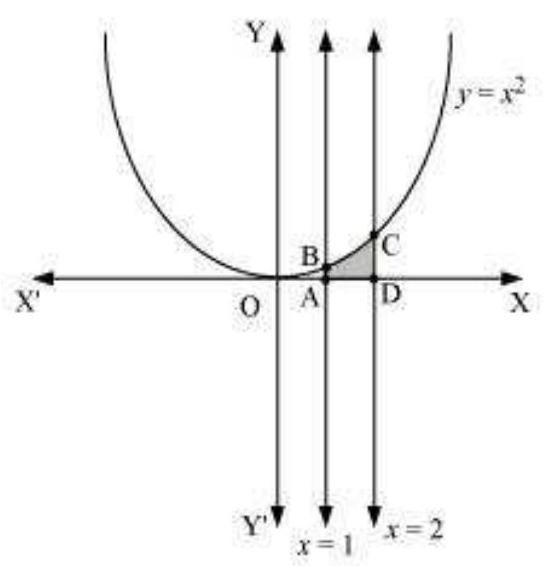
$ \begin{aligned} \text{ Area ADCBA } & =\int_1^{2} y d x \\ & =\int_1^{2} x^{2} d x \\ & =[\frac{x^{3}}{3}]_1^{2} \\ & =\frac{8}{3}-\frac{1}{3} \\ & =\frac{7}{3} \text{ units } \end{aligned} $
ii. The required area is represented by the shaded area ADCBA as
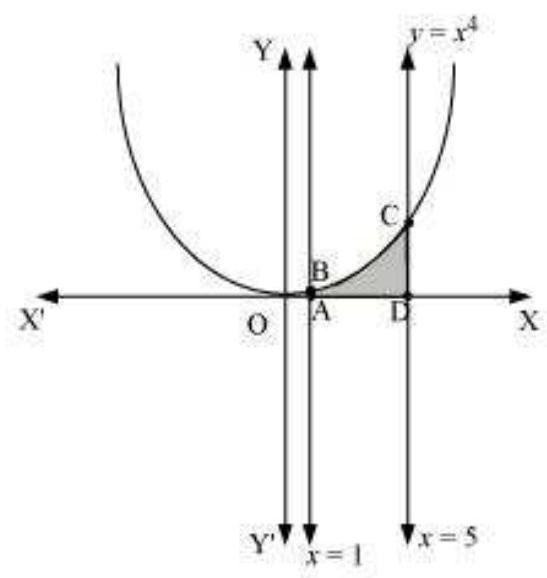
$ \begin{aligned} \text{ Area ADCBA } & =\int_1^{5} x^{4} d x \\ & =[\frac{x^{5}}{5}]_1^{5} \\ & =\frac{(5)^{5}}{5}-\frac{1}{5} \\ & =(5)^{4}-\frac{1}{5} \\ & =625-\frac{1}{5} \\ & =624.8 \text{ units } \end{aligned} $
2. Sketch the graph of $y=|x+3|$ and evaluate $\int _{-6}^{0}|x+3| d x$.
Show Answer
Solution
The given equation is $y=|x+3|$
The corresponding values of $x$ and $y$ are given in the following table.
| $x$ | -6 | -5 | -4 | -3 | -2 | -1 | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $y$ | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
On plotting these points, we obtain the graph of $y=|x+3|$ as follows.
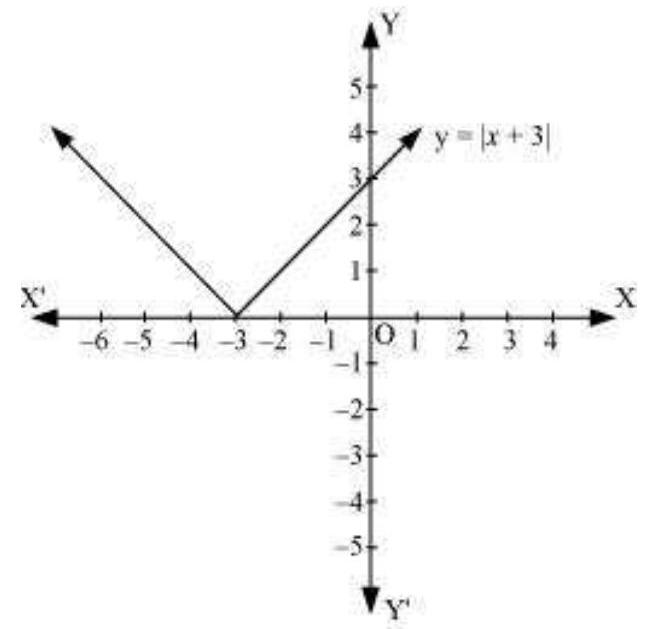
It is known that, $(x+3) \leq 0$ for $-6 \leq x \leq-3$ and $(x+3) \geq 0$ for $-3 \leq x \leq 0$
$ \begin{aligned} \therefore \int _{-6}^{0}|(x+3)| d x & =-\int _{-6}^{-3}(x+3) d x+\int _{-3}^{0}(x+3) d x \\ & =-[\frac{x^{2}}{2}+3 x] _{-6}^{-3}+[\frac{x^{2}}{2}+3 x] _{-3}^{0} \\ & =-[(\frac{(-3)^{2}}{2}+3(-3))-(\frac{(-6)^{2}}{2}+3(-6))]+[0-(\frac{(-3)^{2}}{2}+3(-3)]] \\ & =-[-\frac{9}{2}]-[-\frac{9}{2}] \\ & =9 \end{aligned} $
3. Find the area bounded by the curve $y=\sin x$ between $x=0$ and $x=2 \pi$.
Show Answer
Solution
The graph of $y=\sin x$ can be drawn as
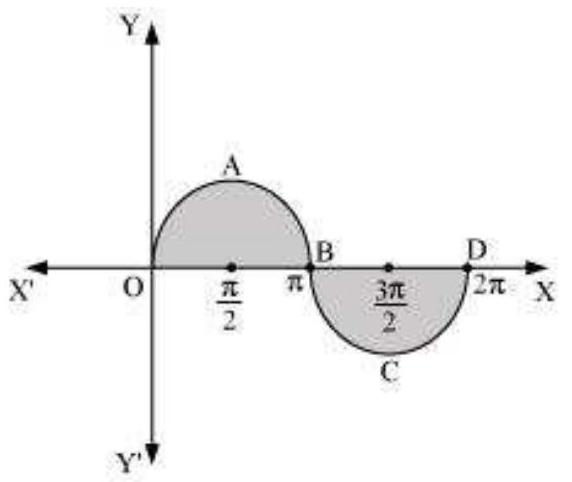
$\therefore$ Required area $=$ Area $OABO+$ Area $BCDB$
$ \begin{aligned} & =\int_0^{\pi} \sin x d x+|\int _{\pi}^{2 \pi} \sin x d x| \\ & =[-\cos x]_0^{\pi}+|[-\cos x] _{\pi}^{2 \pi}| \\ & =[-\cos \pi+\cos 0]+|-\cos 2 \pi+\cos \pi| \\ & =1+1+|(-1-1)| \\ & =2+|-2| \\ & =2+2=4 \text{ units } \end{aligned} $
Choose the correct answer in the following Exercises from 4 to 5.
4. Area bounded by the curve $y=x^{3}$, the $x$-axis and the ordinates $x=-2$ and $x=1$ is
$\quad\quad$(A) -9
$\quad\quad$(B) $\frac{-15}{4}$
$\quad\quad$(C) $\frac{15}{4}$
$\quad\quad$(D) $\frac{17}{4}$
Show Answer
Solution
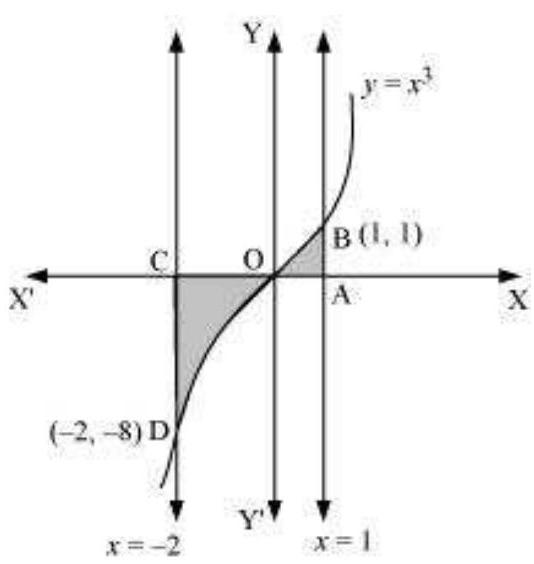
Required area $=\int _{-2}^{1} y d x$
1- Identify positive and negative areas:
- We know the curve dips below the x-axis between x = -2 and x = 0 (roughly at the point where x = -1).
- So, we’ll calculate the area under the curve in two sections:
- Area above the x-axis: from x = 0 to x = 1 (positive)
- Area below the x-axis: from x = -2 to x = 0 (negative)
2- Set up definite integrals:
- Area above the x-axis: ∫₀¹ (x^3) dx
- Area below the x-axis: ∫-20 (x^3) dx (notice the negative sign here to account for the area below the x-axis)
3- Evaluate the integrals: Following the same steps as before using the power rule of integration:
- Area above the x-axis: [(x^4)/4]₀¹ = (1/4)
- Area below the x-axis: |[(-x^4)/4]₋²⁰| = (16/4) (absolute value to consider the positive area enclosed below the x-axis)
4- Calculate the net enclosed area:
- Net Enclosed Area = Area above the x-axis+ Area below the x-axis = (1/4) + (16/4) = 17/4
The correct option is D.
5. The area bounded by the curve $y=x|x|, x$-axis and the ordinates $x=-1$ and $x=1$ is given by
$\quad\quad$(A) 0
$\quad\quad$(B) $\frac{1}{3}$
$\quad\quad$(C) $\frac{2}{3}$
$\quad\quad$(D) $\frac{4}{3}$
[Hint : $y=x^{2}$ if $x>0$ and $y=-x^{2}$ if $.x<0$].
Show Answer
Solution

Required area $=\int _{-1}^{1} y d x$
$=-\int _{-1}^{1} x|x| d x$
$=-\int _{-1}^{0} x^{2} d x+\int_0^{1} x^{2} d x$
$=-[\frac{x^{3}}{3}] _{-1}^{0}+[\frac{x^{3}}{3}]_0^{1}$
$=-(-\frac{1}{3})+\frac{1}{3}$
$=\frac{2}{3}$ units
Thus, the correct answer is C.
Summary
The area of the region bounded by the curve $y=f(x), x$-axis and the lines $x=a$ and $x=b(b>a)$ is given by the formula: Area $=\int_a^{b} y d x=\int_a^{b} f(x) d x$. The area of the region bounded by the curve $x=\phi(y), y$-axis and the lines $y=c, y=d$ is given by the formula: Area $=\int_c^{d} x d y=\int_c^{d} \phi(y) d y$.
Historical Note
The origin of the Integral Calculus goes back to the early period of development of Mathematics and it is related to the method of exhaustion developed by the mathematicians of ancient Greece. This method arose in the solution of problems on calculating areas of plane figures, surface areas and volumes of solid bodies etc. In this sense, the method of exhaustion can be regarded as an early method of integration. The greatest development of method of exhaustion in the early period was obtained in the works of Eudoxus (440 B.C.) and Archimedes (300 B.C.)
Systematic approach to the theory of Calculus began in the 17th century. In 1665, Newton began his work on the Calculus described by him as the theory of fluxions and used his theory in finding the tangent and radius of curvature at any point on a curve. Newton introduced the basic notion of inverse function called the anti derivative (indefinite integral) or the inverse method of tangents.
During 1684-86, Leibnitz published an article in the Acta Eruditorum which he called Calculas summatorius, since it was connected with the summation of a number of infinitely small areas, whose sum, he indicated by the symbol ’ ’ ‘. In 1696 , he followed a suggestion made by J. Bernoulli and changed this article to Calculus integrali. This corresponded to Newton’s inverse method of tangents.
Both Newton and Leibnitz adopted quite independent lines of approach which was radically different. However, respective theories accomplished results that were practically identical. Leibnitz used the notion of definite integral and what is quite certain is that he first clearly appreciated tie up between the antiderivative and the definite integral.
Conclusively, the fundamental concepts and theory of Integral Calculus and primarily its relationships with Differential Calculus were developed in the work of P.de Fermat, I. Newton and G. Leibnitz at the end of 17th century. However, this justification by the concept of limit was only developed in the works of A.L. Cauchy in the early 19th century. Lastly, it is worth mentioning the following quotation by Lie Sophie’s:
“It may be said that the conceptions of differential quotient and integral which in their origin certainly go back to Archimedes were introduced in Science by the investigations of Kepler, Descartes, Cavalieri, Fermat and Wallis …. The discovery that differentiation and integration are inverse operations belongs to Newton and Leibnitz”.
One should study Mathematics because it is only through Mathematics that nature can be conceived in harmonious form. - BIRKHOFF
8.1 भूमिका (Introduction)
ज्यामिति में, हमने त्रिभुजों आयतों, समलंब चतुर्भुजों एवं वृत्तों सहित विभिन्न ज्यामितीय आकृतियों के क्षेत्रफल के परिकलन के लिए सूत्रों का अध्ययन किया है। वास्तविक जीवन की अनेक समस्याओं के लिए गणित के अनुप्रयोग में इस प्रकार के सूत्र मूल होते हैं। प्रारंभिक ज्यामिति के सूत्रों की सहायता से हम अनेक साधारण आकृतियों के क्षेत्रफल का परिकलन कर सकते हैं। यद्यपि ये सूत्र वक्रों द्वारा घिरे क्षेत्रफल के परिकलन के लिए अपर्याप्त हैं इसके लिए हमें समाकलन गणित की कुछ संकल्पनाओं की आवश्यकता होगी।
पिछले अध्याय में हमने योगफल की सीमा के रूप में निश्चित समाकलनों का परिकलन करते समय वक्र $y=f(x)$, कोटियों $x=a, x=b$ एवं $x$-अक्ष से घिरे क्षेत्रफल को ज्ञात करने का अध्ययन किया है। इस अध्याय में हम साधारण वक्रों के अंतर्गत, सरल रेखाओं एवं वृत्तों, परवलयों, तथा दीघवृत्तों (केवल मानक रूप) की चापों के बीच घिरे क्षेत्रफल को ज्ञात करने के लिए समाकलनों के एक विशिष्ट अनुप्रयोग का अध्ययन करेंगे।

A.L. Cauchy (1789-1857) उपरोक्त वक्रों से घिरे क्षेत्रफल को भी ज्ञात करेंगे।
8.2 साधारण वक्रों के अंतर्गत क्षेत्रफल (Area Under Simple Curves)
पिछले अध्याय में हमने, योगफल की सीमा के रूप में निश्चित समाकलन एवं कलन की आधारभूत प्रमेय का उपयोग करते हुए निश्चित समाकलन का परिकलन कैसे किया जाए, का अध्ययन किया है। अब हम वक्र $y=f(x), x$-अक्ष एवं कोटियाँ $x=a$ तथा $x=b$ से घिरे क्षेत्रफल को ज्ञात करने की आसान एवं अंतर्जान से प्राप्त विधि की चर्चा करते हैं। आकृति 8.1 से हम वक्र के अंतर्गत क्षेत्रफल को बहुत सी पतली एवं उर्ध्वाधर बहुत सी पट्टियों से निर्मित मान सकते हैं। $y$ उँचाई एवं $d x$ चौड़ाई वाली एक स्वेच्छ पट्टी पर विचार कीजिए, इसमें $d \mathrm{~A}$ (प्रारंभिक पट्टी का क्षेत्रफल) $=y d x$, जहाँ $y=f(x)$ है।

यह क्षेत्रफल प्रारंभिक क्षेत्रफल कहलाता है जो कि क्षेत्र के भीतर किसी स्वेच्छ स्थिति पर स्थापित है एवं $a$ तथा $b$ के मध्य $x$ के किसी मान से विनिर्दिष्ट है। वक्र $y=f(x)$, कोटियों $x=a, x=b$ एवं $x$-अक्ष से घिरे क्षेत्र के कुल क्षेत्रफल $\mathrm{A}$ को, क्षेत्र $\mathrm{PQRSP}$ में सभी पतली पट्टियों के क्षेत्रफलों के योगफल के परिणाम के रूप में देख सकते हैं। सांकेतिक भाषा में हम इसे इस प्रकार अभिव्यक्त करते हैं:
$$ \mathrm{A}=\int _{a}^{b} d \mathrm{~A}=\int _{a}^{b} y d x=\int _{a}^{b} f(x) d x $$
वक्र $x=g(y), y$-अक्ष एवं रेखाएँ $y=c, y=d$ से घिरे क्षेत्र का क्षेत्रफल निम्नलिखित सूत्र द्वारा प्राप्त किया जाता है।
$$ \mathrm{A}=\int _{c}^{d} x d y=\int _{c}^{d} g(y) d y $$
यहाँ हम क्षैतिज पट्टियों पर विचार करते हैं जैसा कि आकृति 8.2 में दर्शाया गया है।

आकृति 8.2
टिप्पणी यदि चर्चित वक्र की स्थिति $x$-अक्ष के नीचे है, तो जैसा कि आकृति 8.3 में दर्शाया गया है, जहाँ $x=a$ से $x=b$ तक $f(x)<0$ इसलिए दिए हुए वक्र, $x$-अक्ष एवं कोटियों $x=a, x=b$ से घिरे क्षेत्र का क्षेत्रफल ॠणात्मक हो जाता है, परंतु हम क्षेत्रफल के केवल संख्यात्मक मान की ही चर्चा करते हैं। इसलिए यदि क्षेत्रफल ॠणात्मक है तो हम इसके निरपेक्ष मान, अर्थात् $\left|\int _{a}^{b} f(x) d x\right|$ को लेते हैं।

आकृति 8.3
सामान्यतः ऐसा हो सकता है कि वक्र का कुछ भाग $x$-अक्ष के ऊपर है तथा कुछ भाग $x$-अक्ष के नीचे है, जैसा कि आकृति 8.4 में दर्शाया गया है। यहाँ $\mathrm{A} _{1}<0$ तथा $\mathrm{A} _{2}>0$ है, इसलिए वक्र $y=f(x), x$-अक्ष एवं कोटियों $x=a$ तथा $x=b$ से घिरे क्षेत्र का क्षेत्रफल $\mathrm{A}$ सूत्र $\mathrm{A}=\left|\mathrm{A} _{1}\right|+\mathrm{A} _{2}$ द्वारा प्राप्त किया जाता है।

आकृति 8.4
उदाहरण 1 वृत्त $x^{2}+y^{2}=a^{2}$ का क्षेत्रफल ज्ञात कीजिए।
हल आकृति 8.5 में दिए हुए वृत्त से घिरे हुए क्षेत्र का कुल क्षेत्रफल $=4$ (दिए हुए वक्र, $x$-अक्ष एवं कोटियों $x=0$ तथा $x=a$ से घिरे क्षेत्र AOBA का क्षेत्रफल) [क्योंकि वृत्त $x$-अक्ष एवं $y$-अक्ष दोनों के परितः सममित है]
$$ \begin{aligned} & =4 \int _{0}^{a} y d x \text { (उर्ध्वाधर पट्टियाँ लेते हुए) } \\ & =4 \int _{0}^{a} \sqrt{a^{2}-x^{2}} d x \end{aligned} $$
क्योंकि $x^{2}+y^{2}=a^{2}$ से $y= \pm \sqrt{a^{2}-x^{2}}$ प्राप्त होता है।

आकृति 8.5
जैसा कि क्षेत्र AOBA प्रथम चतुर्थांश में सम्मिलित है इसलिए $y$ को धनात्मक लिया जाता है। समाकलन करने पर दिए हुए वृत्त से घिरा क्षेत्रफल निम्नलिखित रूप में प्राप्त होता है:
$ \begin{aligned} & =4[\frac{x}{2} \sqrt{a^{2}-x^{2}}+\frac{a^{2}}{2} \sin ^{-1} \frac{x}{a}]_0^{a} \\ & =4[(\frac{a}{2} \times 0+\frac{a^{2}}{2} \sin ^{-1} 1)-0]=4(\frac{a^{2}}{2})(\frac{\pi}{2})=\pi a^{2} \end{aligned} $
विकल्पतः जैसा कि आकृति 8.6 में दर्शाया गया है क्षैतिज पट्टियों की चर्चा करते हुए वृत्त द्वारा घिरे क्षेत्र का कुल क्षेत्रफल
$ \begin{aligned} & =4 \int_0^{a} x d y=4 \int_0^{a} \sqrt{a^{2}-y^{2}} d y \text{(क्यों?)} \\ & =4[\frac{y}{2} \sqrt{a^{2}-y^{2}}+\frac{a^{2}}{2} \sin ^{-1} \frac{y}{a}]_0^{a} \\ & =4[(\frac{a}{2} \times 0+\frac{a^{2}}{2} \sin ^{-1} 1)-0] \\ & =4 \frac{a^{2}}{2} \frac{\pi}{2}=\pi a^{2} \end{aligned} $

आकृति 8.6
उदाहरण 2 दीर्घवृत्त $\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}+\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}=1$ से घिरे क्षेत्र का क्षेत्रफल का ज्ञात कीजिए।
हल आकृति 8.7 में दीर्घवृत्त से घिरे क्षेत्र $\mathrm{ABA}^{\prime} \mathrm{B}^{\prime} \mathrm{A}$ का क्षेत्रफल
$=4\left(\begin{array}{l}\text { दिए हुए वक्र, } x \text {-अक्ष, कोटियों } x=0, x=a \text { द्वारा प्रथम चतुर्थांश में } \ \text { घिरे क्षेत्र } A O B A \text { का क्षेत्रफल }\end{array}\right)$
(क्योंकि दीर्घवृत्त $x$-अक्ष एवं $y$-अक्ष दोनों के परितः सममित है)
$=4 \int _{0}^{a} y d x$ (उर्ध्वाधर पट्टियाँ लेते हुए)
अब $\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}+\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}=1$ से $y= \pm \frac{b}{a} \sqrt{a^{2}-x^{2}}$ प्राप्त होता है, परंतु क्षेत्र AOBA प्रथम चतुर्थांश में है इसलिए $y$ धनात्मक लिया जाता है, इसलिए अभीष्ट क्षेत्रफल
$ \begin{aligned} & =4 \int _{0}^{a} \frac{b}{a} \sqrt{a^{2}-x^{2}} d x \\ & =\frac{4 b}{a}\left[\frac{x}{2} \sqrt{a^{2}-x^{2}}+\frac{a^{2}}{2} \sin ^{-1} \frac{x}{a}\right] _{0}^{a} \text { (क्यों?) } \\ & =\frac{4 b}{a}\left[\left(\frac{a}{2} \times 0+\frac{a^{2}}{2} \sin ^{-1} 1\right)-0\right] \\ & =\frac{4 b}{a} \frac{a^{2}}{2} \frac{\pi}{2}=\pi a b \text { है। } \end{aligned} $

आकृति 8.7
विकल्पतः जैसा कि आकृति 8.8 में दर्शाया गया है क्षैतिज पट्टियों की चर्चा करते हुए दीर्घवृत्त का क्षेत्रफल
$$ \begin{aligned} & =4 \int _{0}^{b} x d y=4 \frac{a}{b} \int _{0}^{b} \sqrt{b^{2}-y^{2}} d y \quad \text { (क्यों?) } \\ & =\frac{4 a}{b}\left[\frac{y}{2} \sqrt{b^{2}-y^{2}}+\frac{b^{2}}{2} \sin ^{-1} \frac{y}{b}\right] _{0}^{b} \\ & =\frac{4 a}{b}\left[\left(\frac{b}{2} \times 0+\frac{b^{2}}{2} \sin ^{-1} 1\right)-0\right] \\ & =\frac{4 a}{b} \cdot \frac{b^{2}}{2} \cdot \frac{\pi}{2}=\pi a b \text { है। } \end{aligned} $$

आकृति 8.8
प्रश्नावली 8.1
1. दीर्घवृत्त $\frac{x^{2}}{16}+\frac{y^{2}}{9}=1$ से घिरे क्षेत्र का क्षेत्रफल ज्ञात कीजिए।
Show Answer
#missing2. दीर्घवृत्त $\frac{x^{2}}{4}+\frac{y^{2}}{9}=1$ से घिरे क्षेत्र का क्षेत्रफल ज्ञात कीजिए।
Show Answer
#missingप्रश्न 3 एवं 4 में सही उत्तर का चयन कीजिए:
3. प्रथम चतुर्थांश में वृत्त $x^{2}+y^{2}=4$ एवं रेखाओं $x=0, x=2$ से घिरे क्षेत्र का क्षेत्रफल है:
(A) $\pi$
(B) $\frac{\pi}{2}$
(C) $\frac{\pi}{3}$
(D) $\frac{\pi}{4}$
Show Answer
#missing4. वक्र $y^{2}=4 x, y$-अक्ष एवं रेखा $y=3$ से घिरे क्षेत्र का क्षेत्रफल है:
(A) 2
(B) $\frac{9}{4}$
(C) $\frac{9}{3}$
(D) $\frac{9}{2}$
Show Answer
#missingविविध उदाहरण
उदाहरण 3 रेखा $y=3 x+2, x$-अक्ष एवं कोटियों $x=-1$ एवं $x=1$ से घिरे क्षेत्र का क्षेत्रफल ज्ञात कीजिए।
हल जैसा कि आकृति 8.9 में दर्शाया गया है, रेखा $y=3 x+2, x$-अक्ष को $x=\frac{-2}{3}$ पर मिलती है और $x \in\left(-1, \frac{-2}{3}\right)$ के लिए इसका आलेख $x$-अक्ष के नीचे है तथा $x \in\left(\frac{-2}{3}, 1\right)$ के लिए इसका आलेख $x$-अक्ष से ऊपर है।
अभीष्ट क्षेत्रफल $=$ क्षेत्र $\mathrm{ACBA}$ का क्षेत्रफल + क्षेत्र ADEA का क्षेत्रफल
$ \begin{aligned} & =|\int _{-1}^{\frac{-2}{3}}(3 x+2) d x|+\int _{\frac{-2}{3}}^{1}(3 x+2) d x \\ & =|[\frac{3 x^{2}}{2}+2 x] _{-1}^{\frac{-2}{3}}|+[\frac{3 x^{2}}{2}+2 x] _{\frac{-2}{3}}^{1}=\frac{1}{6}+\frac{25}{6}=\frac{13}{3} \end{aligned} $

आकृति 8.9
उदाहरण 4 $x=0$ एवं $x=2 \pi$ के मध्य वक्र $y=\cos x$ से घिरे क्षेत्र का क्षेत्रफल ज्ञात कीजिए।
हल आकृति 8.10 से, अभीष्ट क्षेत्रफल $=$ क्षेत्र $\mathrm{OABO}$ का क्षेत्रफल + क्षेत्र $\mathrm{BCDB}$ का क्षेत्रफल + क्षेत्र DEFD का क्षेत्रफल

आकृति 8.10
इसलिए अभीष्ट क्षेत्रफल
$$ \begin{aligned} & =\int _{0}^{\frac{\pi}{2}} \cos x d x+\left|\int _{\frac{\pi}{2}}^{\frac{3 \pi}{2}} \cos x d x\right|+\int _{\frac{3 \pi}{2}}^{2 \pi} \cos x d x \\ & =[\sin x] _{0}^{\frac{\pi}{2}}+\left|[\sin x] _{\frac{\pi}{2}}^{\frac{3 \pi}{2}}\right|+[\sin x] _{\frac{3 \pi}{2}}^{2 \pi}=1+2+1=4 \end{aligned} $$
अध्याय 8 पर विविध प्रश्नावली
1. दिए हुए वक्रों एवं रेखाओं से घिरे क्षेत्र का क्षेत्रफल ज्ञात कीजिए:
(i) $y=x^{2} ; x=1, x=2$ एवं $x$-अक्ष
(ii) $y=x^{4} ; x=1, x=5$ एव $x$-अक्ष
Show Answer
#missing2. $y=|x+3|$ का ग्राफ़ खींचिए एवं $\int _{-6}^{0}|x+3| d x$ का मान ज्ञात कीजिए।
Show Answer
#missing3. $x=0$ एवं $x=2 \pi$ तथा वक्र $y=\sin x$ से घिरे क्षेत्र का क्षेत्रफल ज्ञात कीजिए।
Show Answer
#missing4 से 5 तक के प्रश्नों में सही उत्तर का चयन कीजिए:
4. वक्र $y=x^{3}, x$-अक्ष एवं कोटियों $x=-2, x=1$ से घिरे क्षेत्र का क्षेत्रफल है:
(A) -9
(B) $\frac{-15}{4}$
(C) $\frac{15}{4}$
(D) $\frac{17}{4}$
Show Answer
#missing5. वक्र $y=x|x|, x$-अक्ष एवं कोटियों $x=-1$ तथा $x=1$ से घिरे क्षेत्र का क्षेत्रफल है:
(A) 0
(B) $\frac{1}{3}$
(C) $\frac{2}{3}$
(D) $\frac{4}{3}$
Show Answer
#missing[संकेत : $y=x^{2}$ यदि $x>0$ एवं $y=-x^{2}$ यदि $x<0$ ]
सारांश
-
वक्र $y=f(x), x$-अक्ष एवं रेखाओं $x=a$ तथा $x=b(b>a)$ से घिरे क्षेत्र के क्षेत्रफल का सूत्र : क्षेत्रफल $=\int _{a}^{b} y d x=\int _{a}^{b} f(x) d x$ है।
-
वक्र $x=\phi(y), y$-अक्ष एवं रेखाओं $y=c, y=d$ से घिरे क्षेत्र के क्षेत्रफल का सूत्र : क्षेत्रफल $=\int _{c}^{d} x d y=\int _{c}^{d} \phi(y) d y$ है ।
ऐतिहासिक पृष्ठभूमि
समाकलन गणित का प्रारंभ गणित के प्रारंभिक विकास काल से ही हुआ है। यह प्राचीन यूनानी गणितज्ञों द्वारा विकसित निःशेषता विधि पर आधारित है। इस विधि का प्रारंभ समतलीय आकृतियों के क्षेत्रफल और ठोस वस्तुओं के आयतन की गणना से हुआ। इस तरह से नि:शेषता विधि, समाकलन विधि की प्रारंभिक स्थिति के रूप में समझी जा सकती है। नि:शेषता विधि का सर्वोत्कृष्ट विकास प्रारंभिक काल में यूडोक्स (Eudoxus (440 ई. पू.) और आर्किमिडीज (Archimedes (300 ई. पू.) के कार्यों से प्राप्त हुआ है।
कलन के सिद्धांत का क्रमबद्ध विकास ईसा के पश्चात् 17 वीं शताब्दी में हुआ। सन् 1665 में न्यूटन ने कलन पर अपना कार्य प्रवाहन सिद्धांत (Theory of fluxion) के रूप में प्रारंभ किया। उन्होंने इस सिद्धांत का प्रयोग वक्र के किसी बिंदु पर स्पर्शी और वक्रता-त्रिज्या ज्ञात करने में किया। न्यूटन ने व्युत्क्रम फलन की धारणा से परिचय कराया और इसको प्रतिअवकलज (अनिश्चित समाकलन) या स्पर्शियों की व्युत्क्रम विधि (Inverse Method of tangents) का नामकरण किया।
1684-86, के बीच में लैवनिज़ (Leibnitz) ने एक प्रपत्र एकटा इरोडिटोरियम (Acta Eruditorum) में प्रकाशित किया और इसे कैलक्यूलस सम्मैटोरियस (Calculous Summatorius) नाम दिया, क्योंकि यह अनंत छोटे क्षेत्रफलों के योगफल से संबंधित था, वहीं पर उन्होंने इसे योगफल के प्रतीक ‘f’ द्वारा व्यक्त किया। सन् 1696 ई. में उन्होंने जे. बरनौली (J.Bernoulli) के सुझाव को मानकर अपने प्रपत्र को कैलक्यूलस इंटेग्राली (Calculus Integrali) नाम में परिवर्तित कर दिया। यह न्यूटन द्वारा स्पर्शियों की व्युत्क्रम विधि के संगत था।
न्यूटन और लैवनिज़ दोनों ने पूर्णतः स्वतंत्र मार्ग अपनाया जो मूलतः भिन्न थे। तथापि उन दोनों के सिद्धांतों के संगत प्रतिफल तत्सम पाए गए। लैवनिज़ ने निश्चित समाकलन की धारणा का प्रयोग किया। यह निश्चित है कि उन्होंने ही सर्वप्रथम प्रतिअवकलज और निश्चित समाकलन के बीच के संबंध को स्पष्टतया सराहा।
निष्कर्ष यह है कि समाकलन गणित के आधारभूत धारणाओं, सिद्धांतों तथा अवकलन गणित से इसके प्रारंभिक संबंधों का विकास पी.डी. फर्मा, न्यूटन, और लैवनिज़ के कार्यों द्वारा 17 वीं शताब्दी के अंत में हुआ। तथापि इसका औचित्य, सीमा की संकल्पना के आधार पर 19 वीं शताब्दी के प्रारंभ में ए. एल.कोशी (A.L.Cauchy) के द्वारा किया गया। अंत में ली सोफी (Lie Sophie) का निम्नलिखित उद्धरण वर्णनीय है।
“It may be said that the conceptions of differential quotient and integral which in their origin certainly go back to Archimedes were introduced in Science by the investigations of Kepler, Descartes, Cavalieri, Fermat and Wallis… The discovery that differentiation and integration are inverse operations belongs to Newton and Leibnitz”.










