wave-optics Question 46
Question: Q. 5. (i) How does one demonstrate, using a suitable diagram, that unpolarized light when passed through a polaroid gets polarised?
(ii) A beam of unpolarized light is incident on a glass-air interface. Show, using a suitable ray diagram, that light reflected from the interface is totally polarised, when
Show Answer
Solution:
Ans.(i)
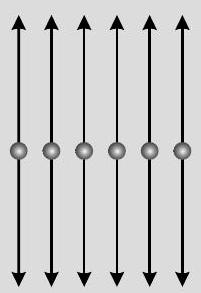
Unpolarised light
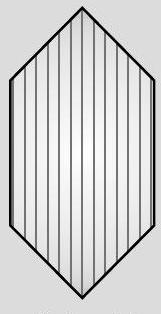
Polaroid
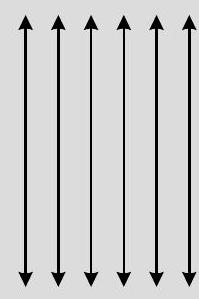
Plane polarised light The components of electric vector associated with light wave, along the direction of aligned molecules of a polaroid, get absorbed. As a result after passing through it, the components perpendicular to the direction of aligned molecules will be obtained in the form of plane polarised light. (ii) Try yourself similar to Q. 2 SATQ-II
[CBSE Marking Scheme 2014]
[II Q. 4. (i) How does an unpolarised light incident on a polaroid get polarised?
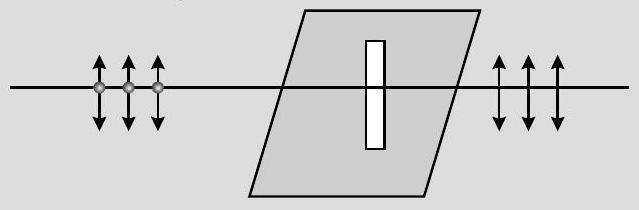
Describe briefly, with the help of a necessary diagram, the polarisation of light by reflection from a transparent medium.
(ii) Two polaroids ’
[OD I, II, III 2012]
Ans. (i) When an unpolarised light falls on a polaroid, it lets only those of its electric vectors that are oscillating along a direction perpendicular to its aligned molecules to pass through it. The incident light thus gets linearly polarised.
Alternatively,
1
1
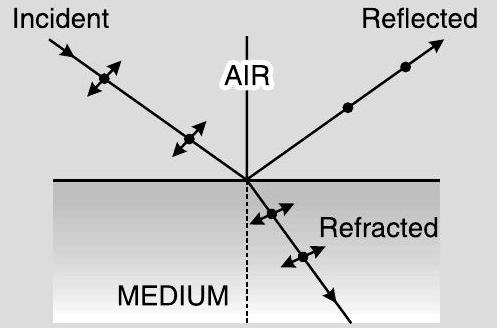
Whenever an unpolarised light is incident on a transparent surface, the reflected light gets completely polarised when the reflected and refracted light are perpendicular to each other.
(ii) Let
Intensity of light passing through
Intensity of light passing through

The third polaroid is placed at
[CBSE Marking Scheme, 2012]
OSWAAL LEARNING TOOIS
UNIT - VII






