ray-optics-and-optical-instruments Question 12
Question: Q. 1. (a) With the help of a ray diagram, show how a concave mirror is used to obtain an erect and magnified image of an object. (b) Using the above ray diagram, obtain the mirror formula and the expression for linear magnification.
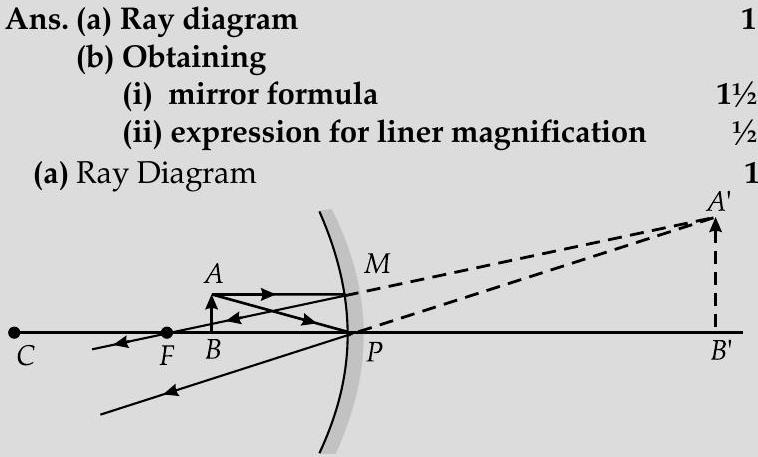
From similar triangles
From similar triangles
Hence,
Now,
or
This is the mirror formula.
Linear magnification
From similar triangte
[CBSE Marking Scheme 2018]
Q. 2. (i) Calculate the distance of an object of height
(ii) Using mirror formula, explain why does a convex mirror always produce a virtual image.
R [CBSE Delhi 2017]
Show Answer
Solution:
Ans. (i) Given,
Focal length of the mirror

Using sign convention, for convex mirror, we have From the formula
[CBSE Marking Scheme 2017]






