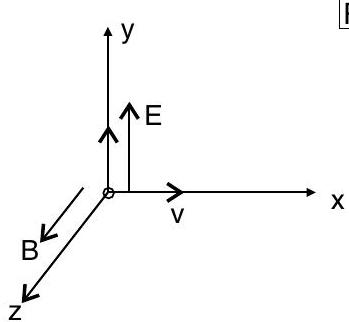
Question: Q. 2. A particle of charge is moving with velocity in the presence of crossed electric field and magnetic field as shown. Write the condition under which, the particle will continue moving along -axis. How would the trajectory of the particle be affected if the electric field is switched off ?
R] [SQP 2017-18]
Show Answer
Solution:
Ans. Condition under which, the particle will continue moving along -axis,
Trajectory becomes helical about the direction of magnetic field.
[CBSE Marking Scheme 2017]
AI Q. 3. A charge of mass is moving with a velocity of , at right angles to a uniform magnetic field . Deduce the expression for the radius of the circular path it describes. [Delhi Compt. I, III 2017]
Ans. Derivation of the expression for radius 2 Force experienced by charged particle in magnetic field ,
As and are perpendicular, This force is perpendicular to the direction of velocity and hence acts as centripetal force.
[CBSE Marking Scheme 2017]
Detailed Answer :
When a charged particle is given with initial velocity in a direction perpendicular to uniform magnetic field, it will be described in a circular path as shown. If a positively charged particle located at point is given an initial velocity perpendicular to field, the field will exert an upward force of at point .
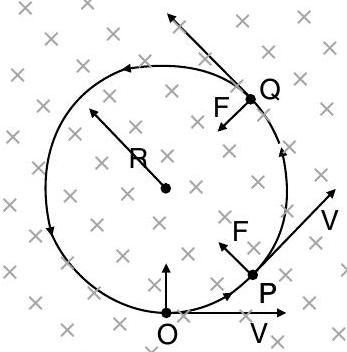
As the force is always at right angles to the velocity, it will not affect the magnitude of velocity, but will tends to change its direction. When the particle reaches points and , then in such case, directions of force and velocity will get changed. Also, a constant centripetal force will act on the particle making the particle to move in a circle.
Now the centripetal acceleration
From Newton’s second law,
Hence the radius of circular orbit will be :
where,
charge of particle








