moving-charges-and-magnetism Question 23
Question: Q. 3. (i) (a) Use Biot-Savart’s law to derive the expression for the magnetic field due to a circular coil of radius
(b) Draw the magnetic field lines due to this coil.
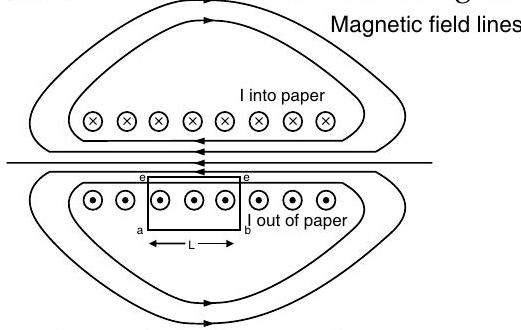
(ii) A current ’
Obtain the net magnetic field at the centre of the loop.
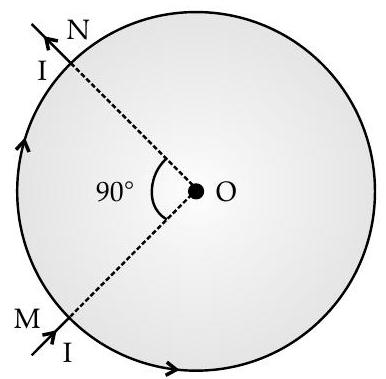
U] [Delhi I, II, III 2015]
Show Answer
Solution:
Ans. (i) (a) Try yourself, Similar to Q. 3 (b), Short Answer Type Questions-II.
(b) Try yourself, Similar to Q. 1 (ii), Short Answer Type Questions-I
(ii) Let current
Magnetic field of current
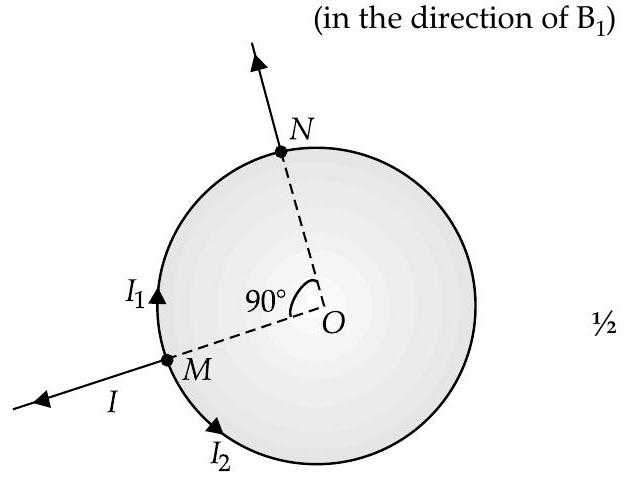
Magnetic field due to current
(in the direction of
Netmagnetic field,
But
Substituting
10
TOPIC-2
Ampere’s Circuital Law and its Applications
Revision Notes
- Ampere’s circuital law states that the line integral of magnetic field around a closed path is
where,
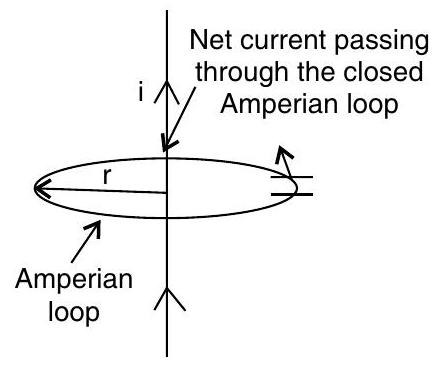
- Magnetic field at a point will not depend on the shape of Amperian loop and will remain same at every point on the loop.
Forces between two parallel currents
- Two parallel wires separated by distance
- In this, the field is orientated at right-angles to second wire where force per unit length on the second wire will be :
- Magnetic field-strength at first wire due to the current flowing in second wire will be :
One ampere is the magnitude of current which, when flowing in each parallel wire one metre apart, results in a force between the wires as
Applications of Ampere’s law to infinitely long straight wire, straight and toroidal solenoids :
(i) Magnetic Field due to long straight wire
Amperes law describes the magnitude of magnetic field of a straight wire as :
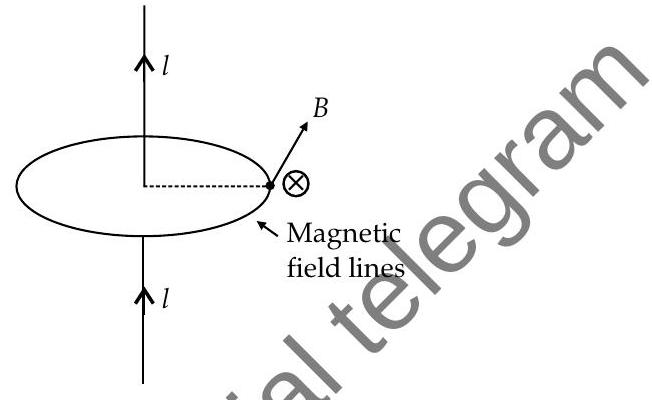
where,
- Field
- Magnetic field
(ii) Magnetic Field due to Solenoid
Solenoid : An electromagnet that generates a controlled magnetic field.
Solenoid is a tightly wound helical coil ofyire whose diameter is small compared to its length.
- Magnetic field generated in the centre, or core of a current carrying solenoid is uniform and is directed along the axis of solenoid.
- Magnetic field due to a straight solenoid:
- at any point in the solenoid,
- at the ends of solenoid,
where,
(iii) Magnetic Field due to Toroid
Toroid : It is an electronic component made of hollow circular ring wound with number of turns of copper wire.
The toroid is a hollow circular ring on which a large number of turns of a wire are closely wound.
- A toroid with
where,
Here,
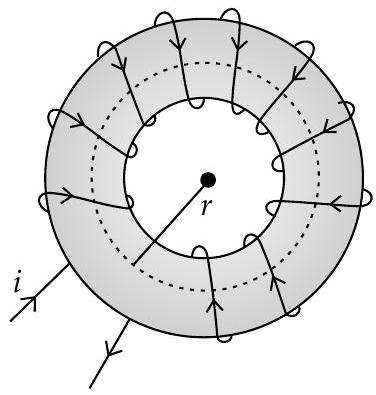
At any point, empty space surrounded by toroid and outside the toroid, magnetic field B will be zero as net current is zero.
Key Formulae
Ampere’s circuital law
- Magnetic field at the surface of a solid cylinder :
(Magnetic field inside the solenoid :
D Magnetic field in a toroid with mean radius
Force between two parallel current carrying wires :






