electrostatic-potential-and-capacitance Question 22
Question: Q. 1. Derive an expression for potential due to a dipole for distances large compared to the size of the dipole. How is the potential due to dipole different from that due to single charge?
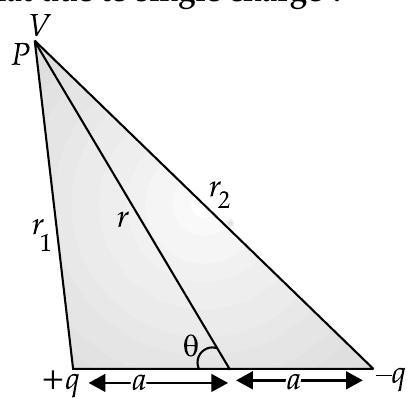
A [SQP 2017]
Show Answer
Solution:
Ans. (i) Derivation
(ii) Difference
(i) Consider origin at the centre of dipole. As per superposition principle, potential due to dipole will be the sum of potentials due to charges
Where,
From the arrangements,
If 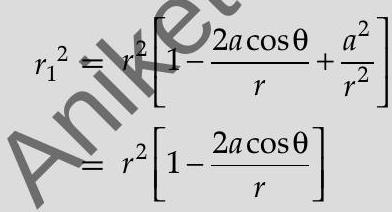
Also,
With the help of Binomial theorem, keeping terms upto first order in
As
Now,
where,
(ii) For potential at any point on axis,
It is obsered that :
potentialis positive when
poential is negative when
Hence, electric potential falls at large distance, as
[CBSE Marking Scheme 2017]
[AI Q. 2. (i) Obtain the expression for the potential to show due to a point charge.
(ii) Potential, due to an electric dipole (length
Ans. (i)
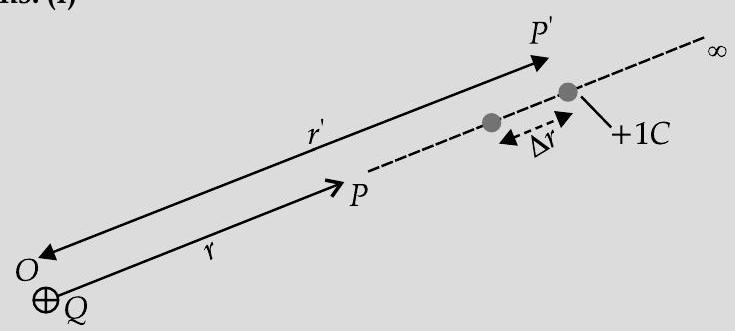
Consider a point charge ’
At some intermediate point
Work done against this force from
Total work done ’
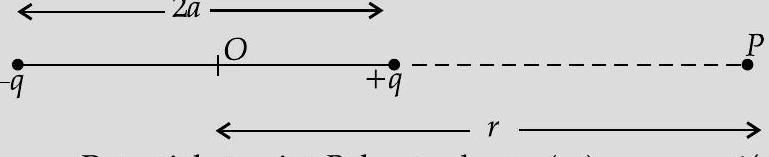
(AI Q. 3. (i) Two isolated metal spheres
(a) capacitance and
(b) energy density just outside the surface of the spheres.
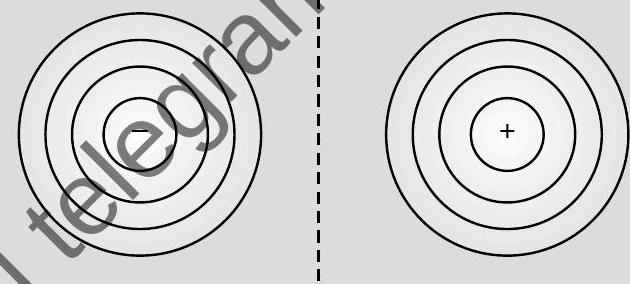
(ii) (a) Show that the equipotential surfaces are closed together in the regions of strong field and far apart in the regions of weak field. Draw equipotential surfaces for an electric dipole.
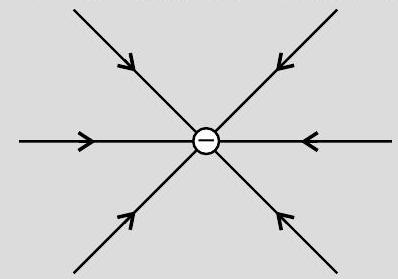
(b) Concentric equipotential surfaces due to a charged body placed at the centre are shown. Identify the polarity of the charge and draw the electric field lines due to it.
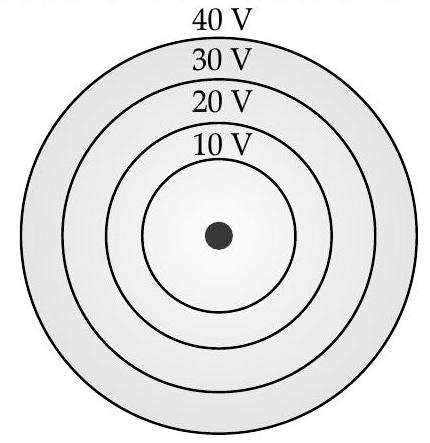
U] [CBSE SQP 2015-16] Ans. (i) (a)
(b)
(ii) (a)
For same change in
where, ’
Diagram of equipotential surface due to a dipole 1
(b) Polarity of charge : - negative
The direction of electric field is radially inward.
[CBSE Marking Scheme 2015]






