alternating-currents Question 32
Question: Q. 9. Derive an expression for the impedance of a series
Plot agraph showing variation of current with the frequency of the applied voltage. Explain briefly how the phenomenon of resonance in the circuit can be used in the tuning mechanism of a radio or TV set.
U] [O.D. Comptt. I, II, III 2013,
O.D. I, II, III 2012, Delhi I, II, III 2011]
Show Answer
Solution:
Ans. (i) Try yourself similar Q. 5 Long Answer Type Question.
(ii)
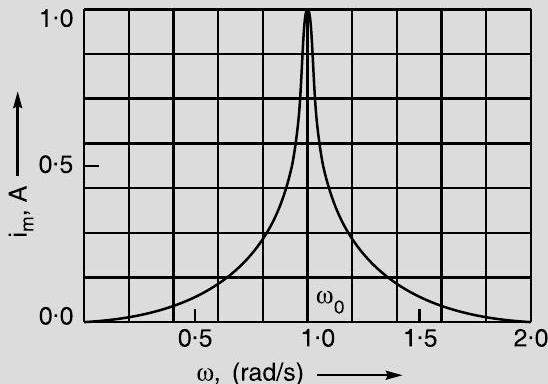
1
The capacitance of a capacitor in the tuning circuit is varied such that the resonant frequency of the circuit becomes nearly equal to the frequency of the radio signal to be received. When this happens, the amplitude of the current becomes maximum in the receiving circuit.
1
[CBSE Marking Scheme 2013]
TOPIC-3
AC Generator and Transformer
Revision Notes
- An alternator is an electrical machine which converts mechanical energy into alternating electrical energy.
Alternator or a synchronous generator has a stator and rotor.
- It is similar to the basic working principle of a
It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction where a coil gets rotated in uniform magnetic field, sets an induced emf given as :
Transformer
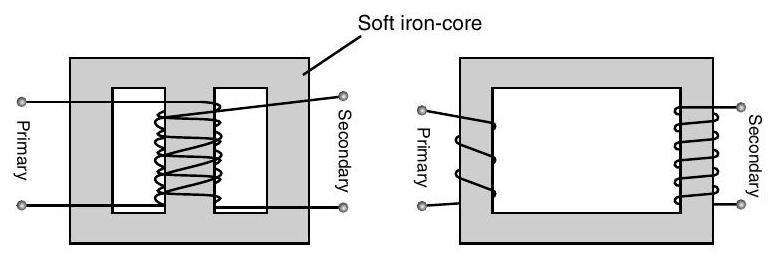
T Transformer is an electrical device used for changing the alternating voltages.
The main use of transformer is in transmission of
It comprises of two sets of coils which are insulated from each other and are wound on soft-iron core.
In this, one of the coil is called as primary (input coil) having
Transformer Ratio :
The value of turns ratio of a transformer
Step-up transformer : If secondary coil has more number of turns than primary
In this, there is less current in secondary as compared topimary
The value of transformer ratio
Step-down transformer: In this, the secondary coil has less number of turns than primary
In this, value of transformer ratio
The main use of transformers is instepping up voltage for power transmission.
- Electric power can be transmitted much more efficiently at high voltages than at low voltages due to less
Efficiency of transformer:
Inspite of heavy power losses, the efficiency in a transformer is usually above
An ideal transformer is
Real transformer is not
- A transformer operating with constant voltage and frequency with very high capacity, efficiency results as
Energy losses in transformers :
- Flux Leakage
- Resistance of windings
- Eddy currents
- Hysteresis
Know the Formulae
- The value of transformer ratio is greater than 1 for step up transformer and less than 1 for step-down transformer.






