Transistor as an Amplifier and as a Switch
Transistor as an Amplifier and as a Switch
Bipolar Junction Transistor
-
Bipolar Junction Transistor is made of back to back two p-n iunctions grown on the same semiconductor base.
-
The middle region is lightly doped and is very thin. This is called Base. One side is heavily doped and is called emitter. The other side is moderately doped and is called collector.
Transistor as an Amplifier and as a Switch
Bipolar Junction Transistor
- Arrow is put on the emitter from p to n direction. It shows the direction ofthe current when the junction is forward biased.
Transistor as an Amplifier and as a Switch
Bipolar Junction Transistor
-
Two batteries are used for biasing two iunctions. If the batteries have a common terminal and that is connected to Emitter, it is called common emitter mode.
-
Similarly you can have common base or common collector modes.
Transistor as an Amplifier and as a Switch
Transistor
-
Emitter side is the Input side and Collector side is the Output Side
-
Working of a transistor:- Emitter emits large number of charge carriers in the base region. Most of these cross over the thin base region and make collector current. Some of the carriers injected make Base current.
Transistor as an Amplifier and as a Switch
Input Characteristics
VBE = Voltage between the base and emitter
IB = Current
Input characterstics keep VCB Constant
VCB = Voltage between the collector and emitter
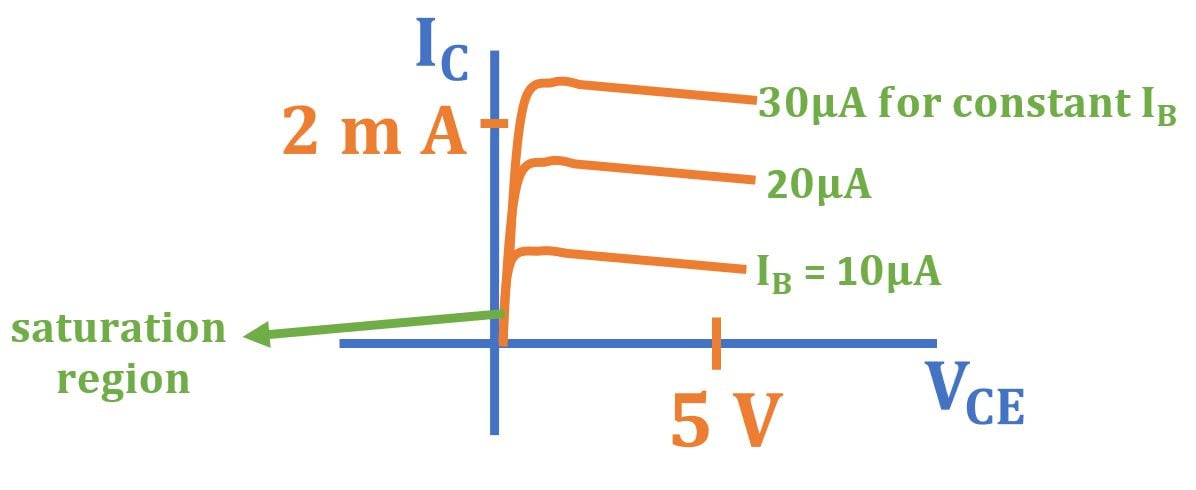
Transistor as an Amplifier and as a Switch
Output Characterstics
VCE and IC
VCB=VCE−0.7volt = VCE−VBE
If VCE = 0, VCB = 0.7 volt forward biased
Transistor as an Amplifier and as a Switch
Transistor as an Amplifier
Transistor as an Amplifier and as a Switch
Transistor as an Amplifier
At some instant, VBE
At a later instant, VBE
VCE=VCC−ICRL
V0=VCC−ICRL
ΔV0=−(ΔIC)RL
VBE=VBB−IBRB+VS
ΔVBE=−ΔIBRB+ΔVS
Transistor as an Amplifier and as a Switch
Transistor as an Amplifier
If you neglact ΔVBE
ΔVS=(ΔIB)RB
Voltage gain = ΔVSΔV0 = - (ΔIB)RB(ΔIC)RC = −BacRBRL
B≃ 50 to few hundred
Voltage gain = ΔVSΔV0 = - (ΔIB)RB(ΔIC)RC = −BacRBRL
B≃ 50 to few hundred
Transistor as an Amplifier and as a Switch
Transistor as a Switch
Vi=small,IB=0⇒IC≃0
V0=VCC−ICRL
V0=VCC
if Vi is quite large
V0≃0




