Motion in a Straight Line - Result Question 27
28. A car accelerates from rest at a constant rate $\alpha$ for some time, after which it decelerates at a constant rate $\beta$ and comes to rest. If the total time elapsed is $t$, then the maximum velocity acquired by the car is
[1994]
(a) $(\frac{\alpha^{2}+\beta^{2}}{\alpha \beta}) t$
(b) $(\frac{\alpha^{2}-\beta^{2}}{\alpha \beta}) t$
(c) $\frac{(\alpha+\beta) t}{\alpha \beta}$
(d) $\frac{\alpha \beta t}{\alpha+\beta}$
Show Answer
Answer:
Correct Answer: 28. (d)
Solution:
velocity, $v=\frac{d s}{d t}=2 a t-3 b t^{2}$
acceleration $a=\frac{d v}{d t}=2 a-6 b t$
Acceleration is zero at
$ 2 a-6 b t=0 \Rightarrow t=\frac{a}{3 b} $
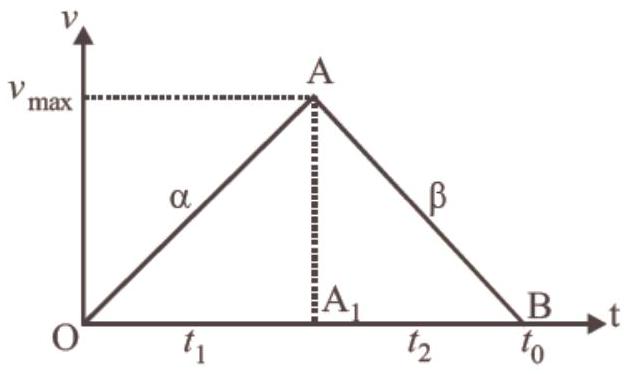
In Fig.
$AA_1=v _{\text{max. }}=\alpha t_1=\beta t_2$
But $t=t_1+t_2=\frac{v _{\max }}{\alpha}+\frac{v _{\text{max }}}{\beta}$
or, $v _{\max }=t(\frac{\alpha \beta}{\alpha+\beta})$
If a body starting from rest accelerates at a constant rate $\alpha$ for certain time and then retards at constant $\beta$ and comes to rest after t. second from the starting point, then
Distance travelled by the body $=\frac{\alpha \beta t^{2}}{(2 \alpha+2 \beta)}$










